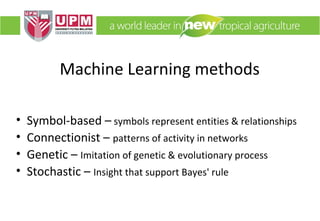
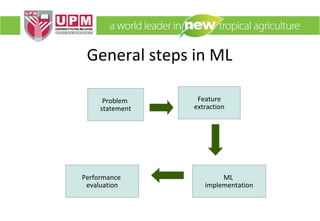
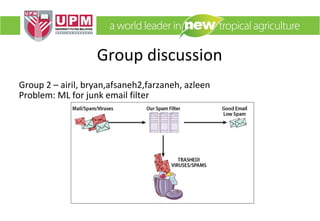
This document provides an overview of machine learning including its definition, components that can be learned, and common machine learning methods. It discusses how machine learning can be applied to problems like autonomous driving, speech recognition, and personalized news recommendations. The document outlines general steps in a machine learning process and provides an example of using the K-means clustering algorithm to classify movie critics. It also describes how machine learning could be used for problems like recycling sorting, spam filtering, and product recommendations.