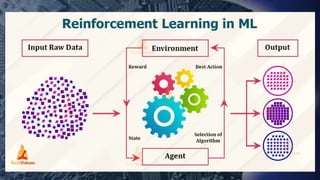
The document discusses machine learning, providing definitions and examples. It outlines the history and development of machine learning, describes common applications like image and speech recognition. It also covers different types of machine learning including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. Challenges in machine learning like data quality issues and overfitting/underfitting are addressed. Popular programming languages for machine learning like Python, Java, C/C++ are also listed.