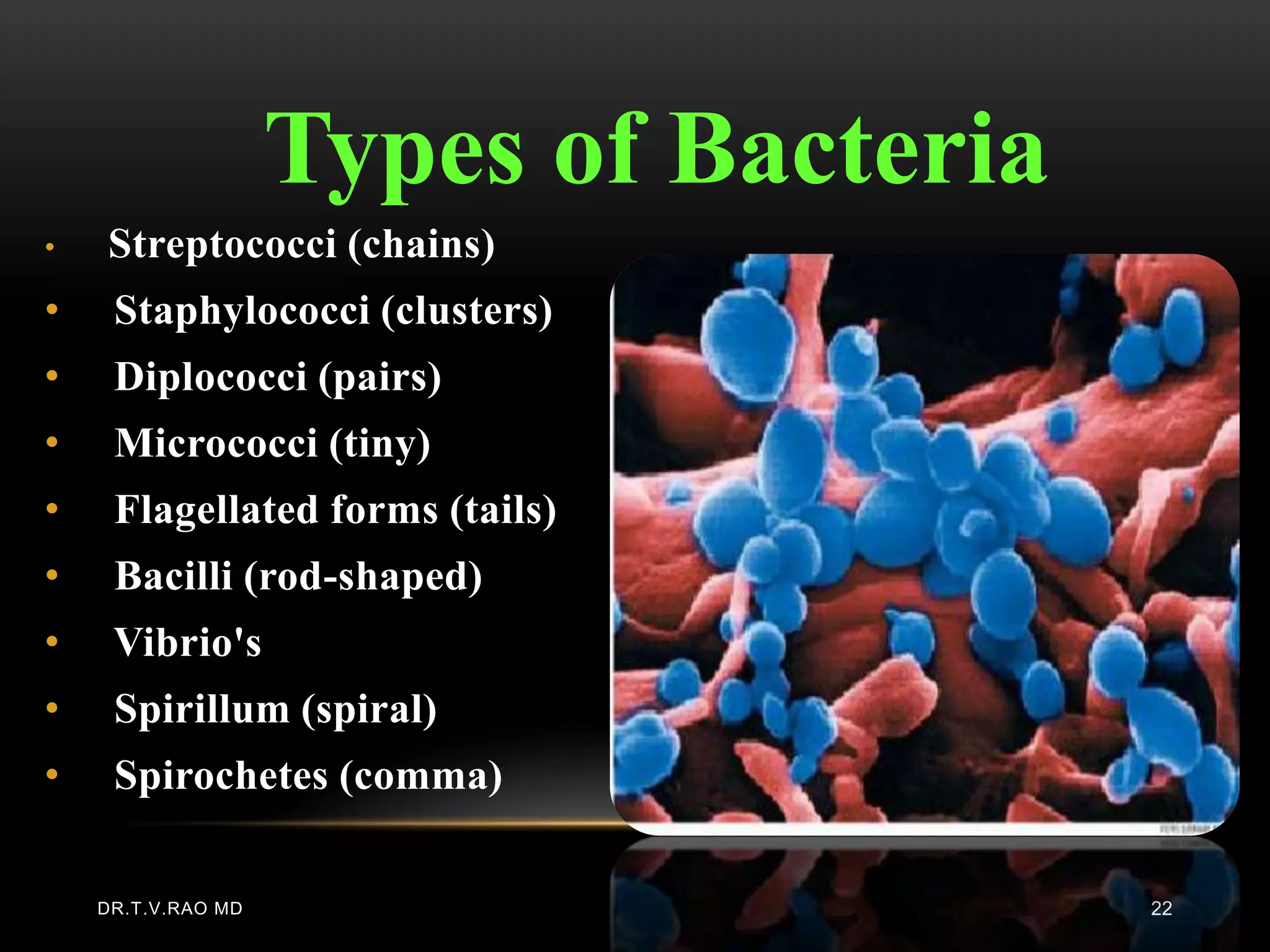
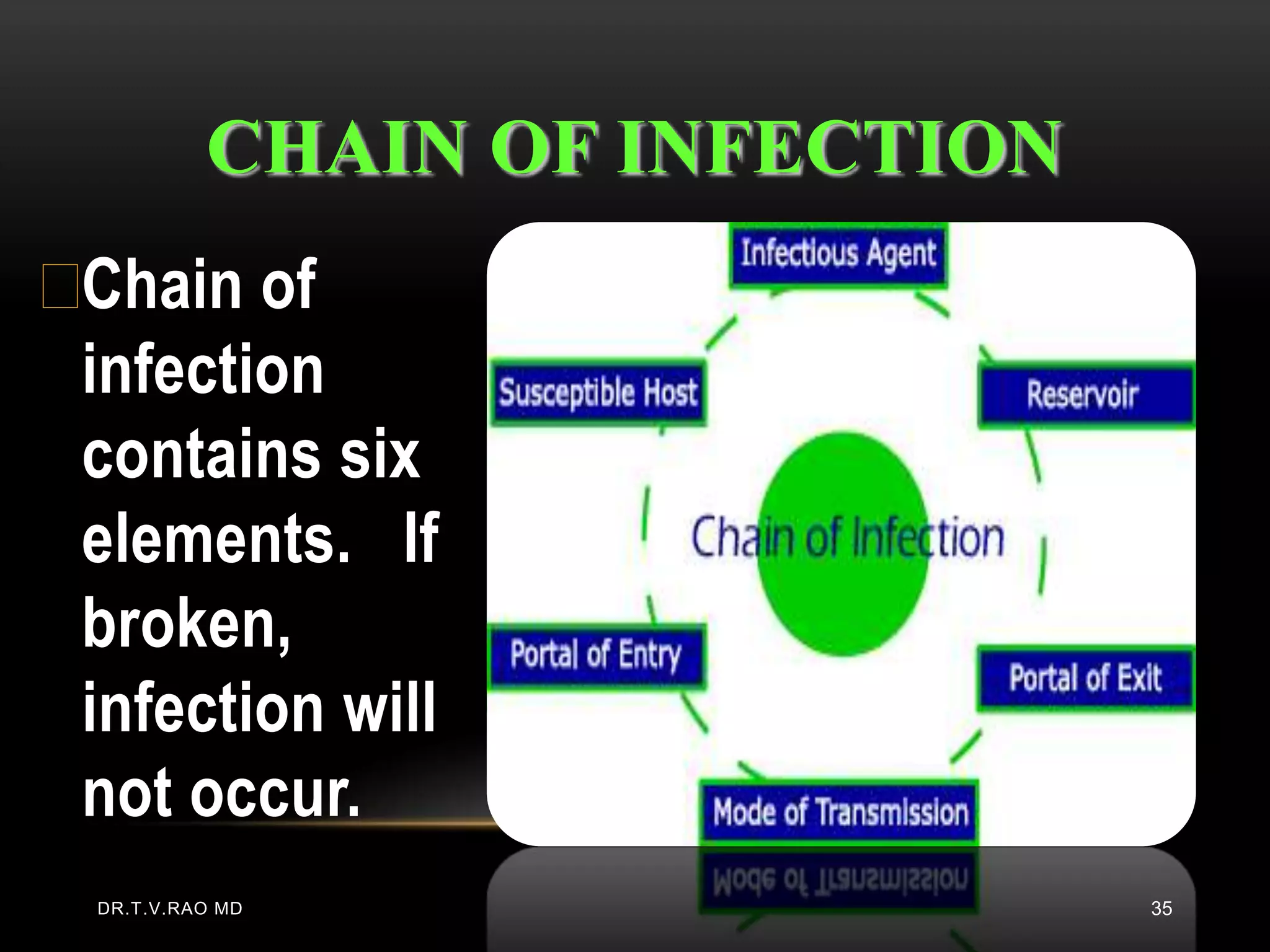
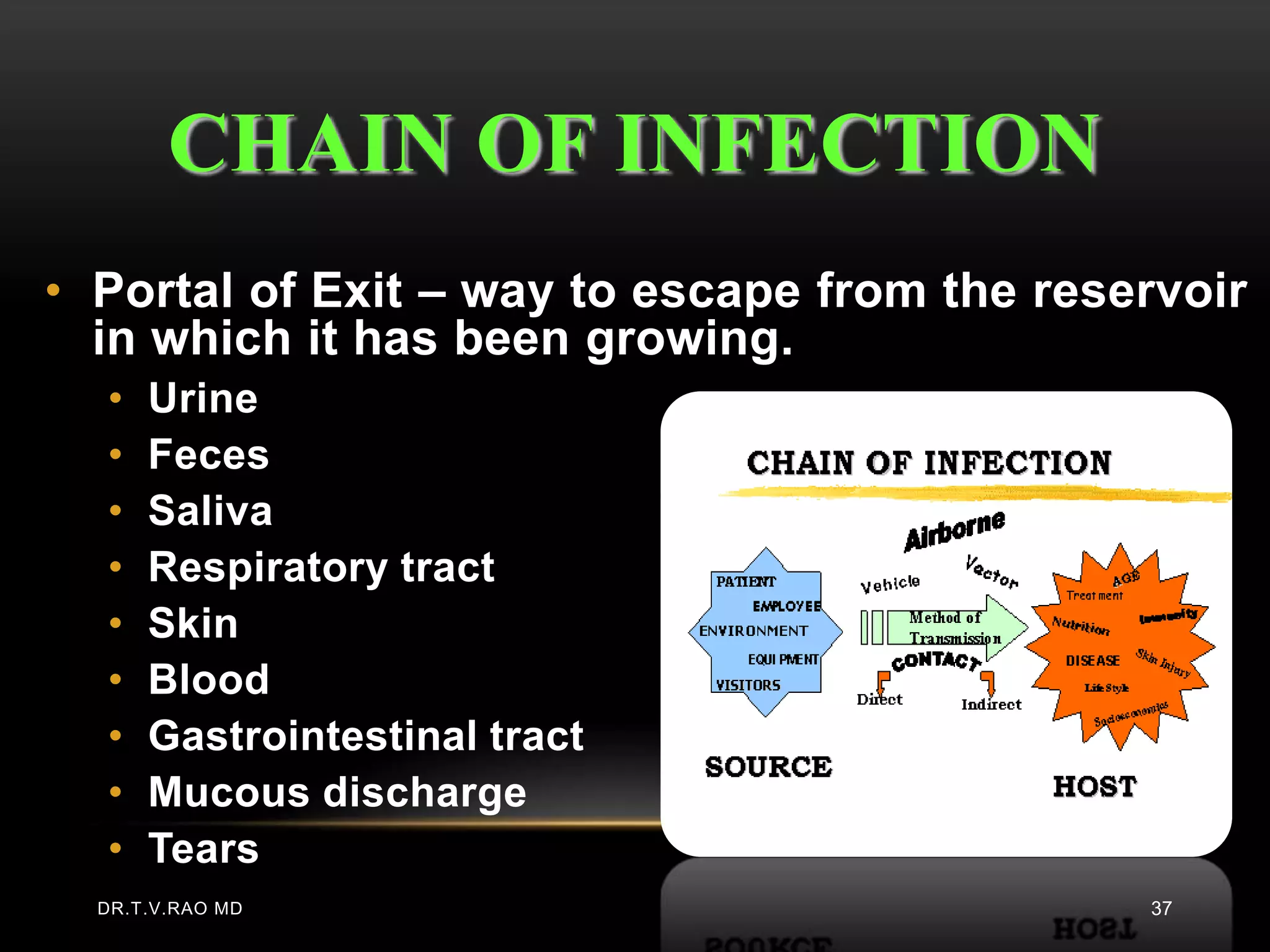
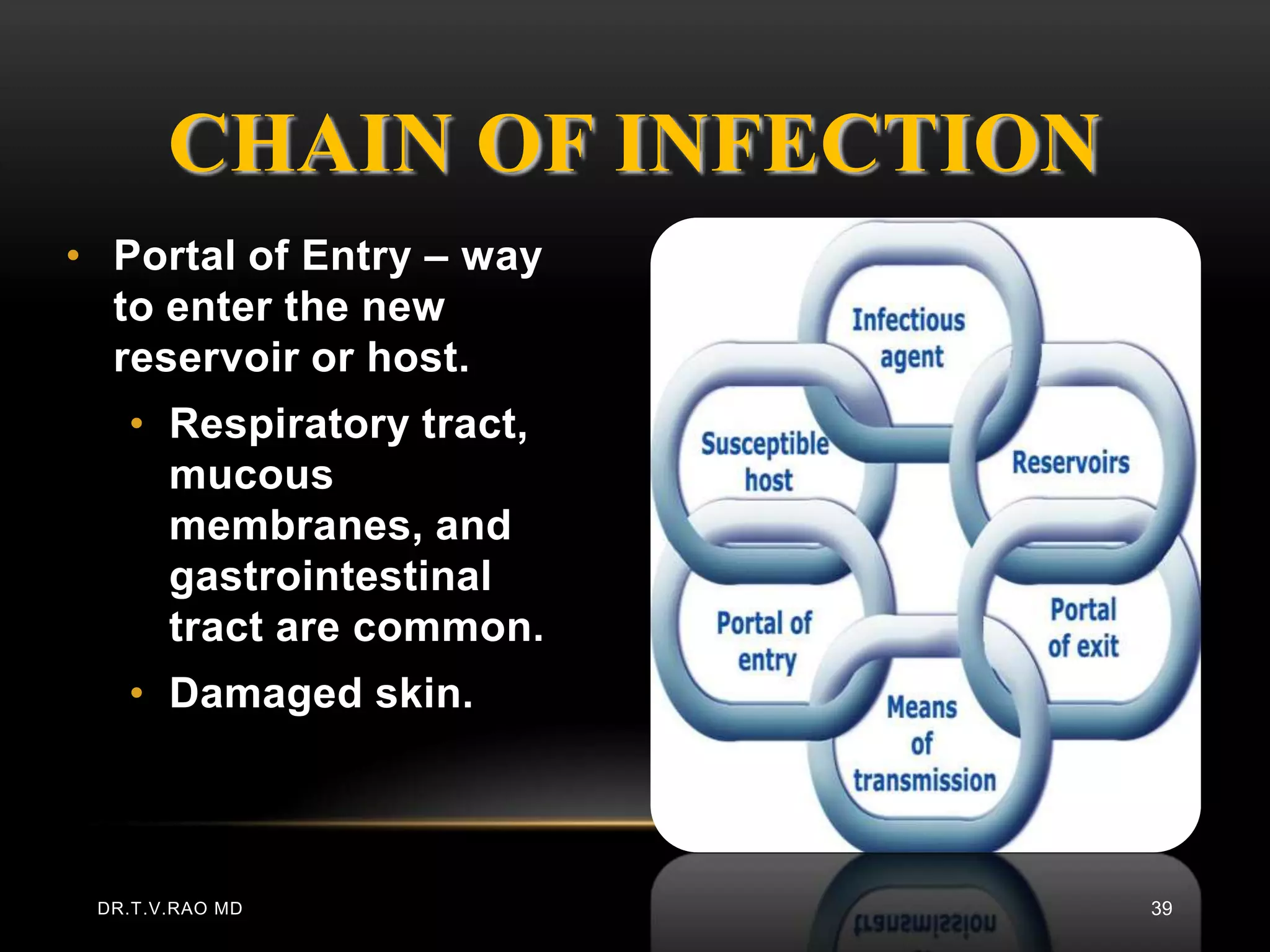
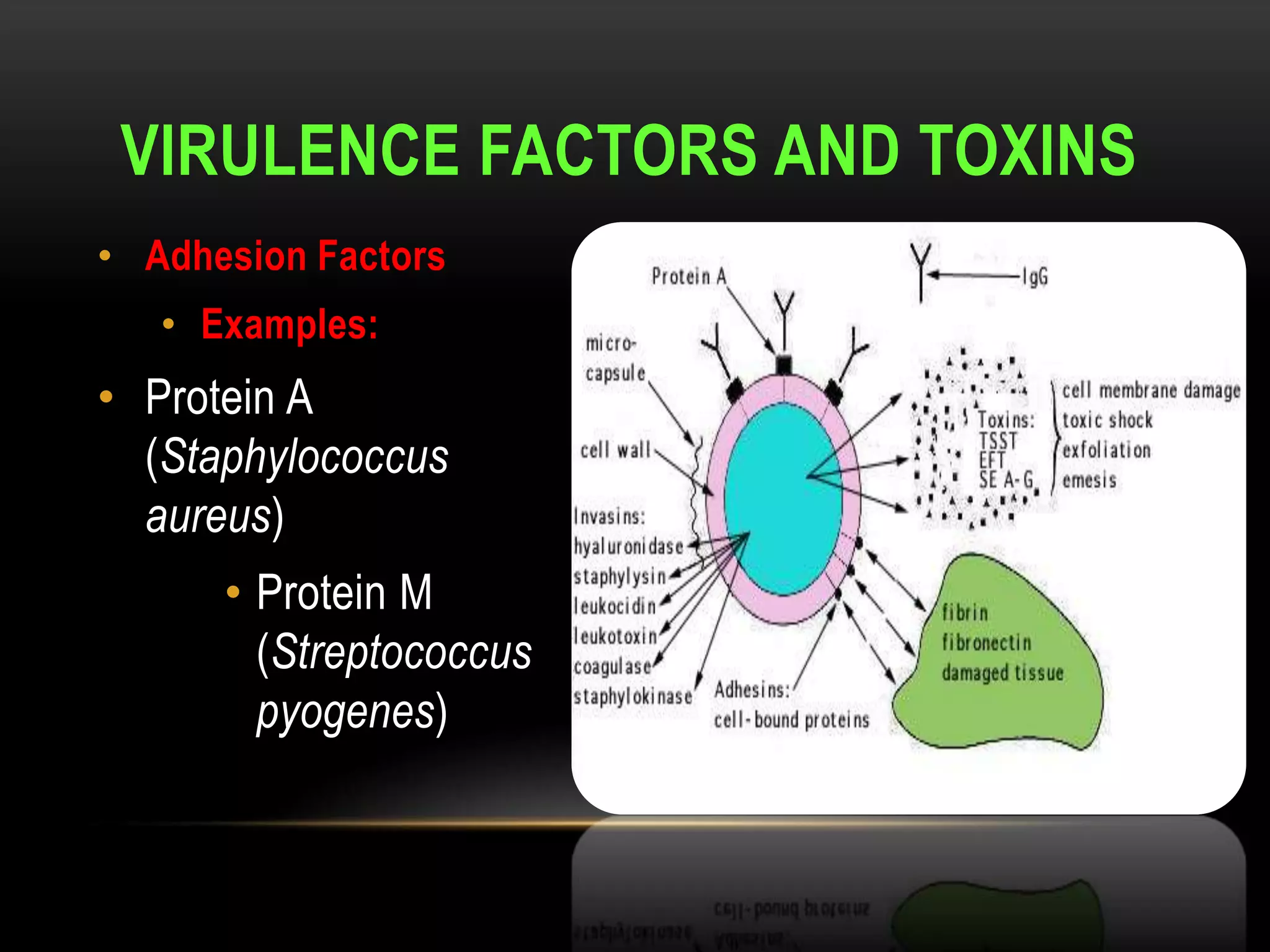
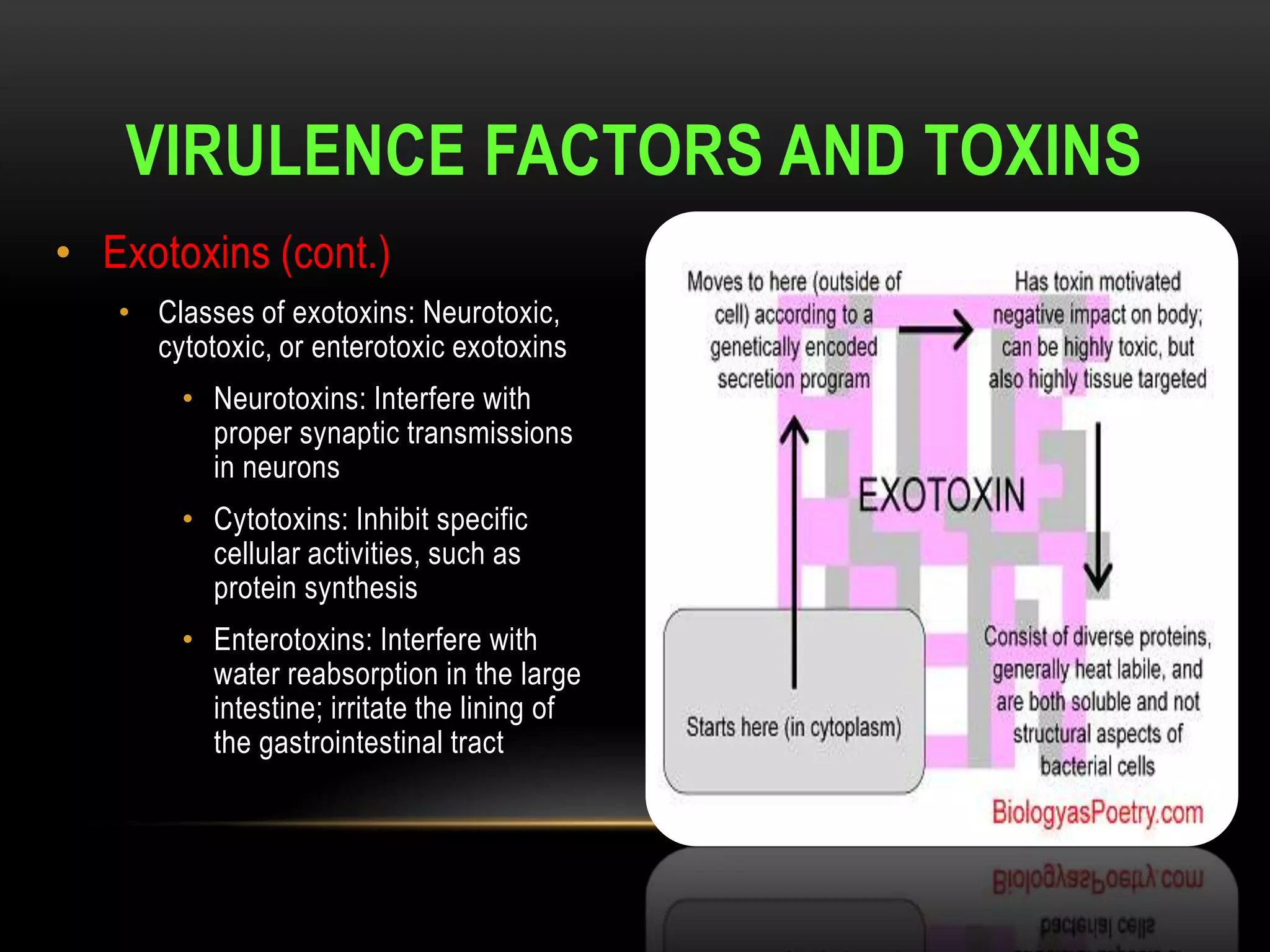
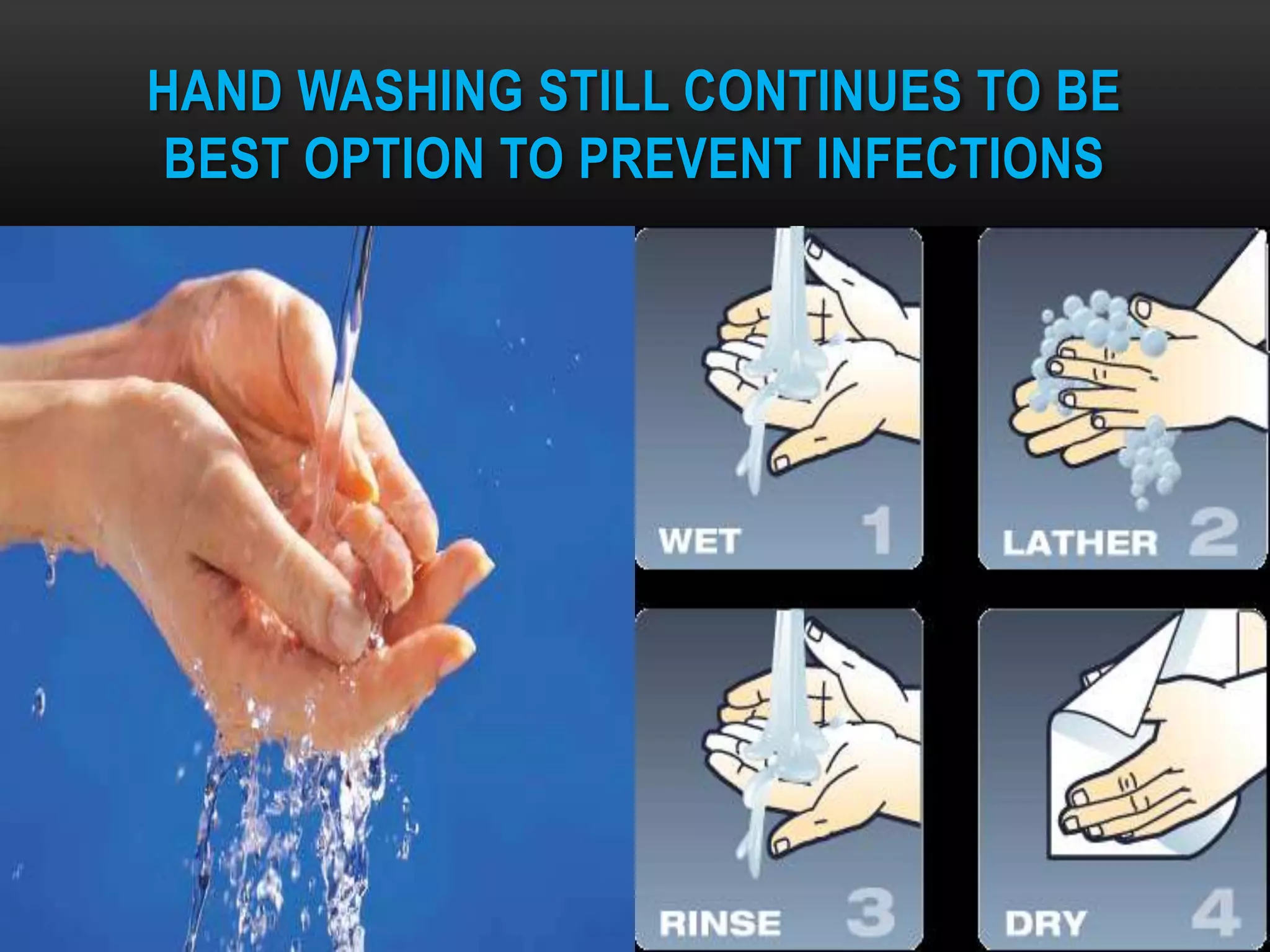
This document defines and describes various aspects of infection and infectious diseases. It begins by defining infection as the invasion of a host's tissues by disease-causing organisms and their multiplication. It then provides definitions for related terms like disease, pathogenicity, virulence, acute vs chronic infections, and more. It also describes common causative agents of human infections like bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. It discusses factors that influence microbial growth and how infections are spread.