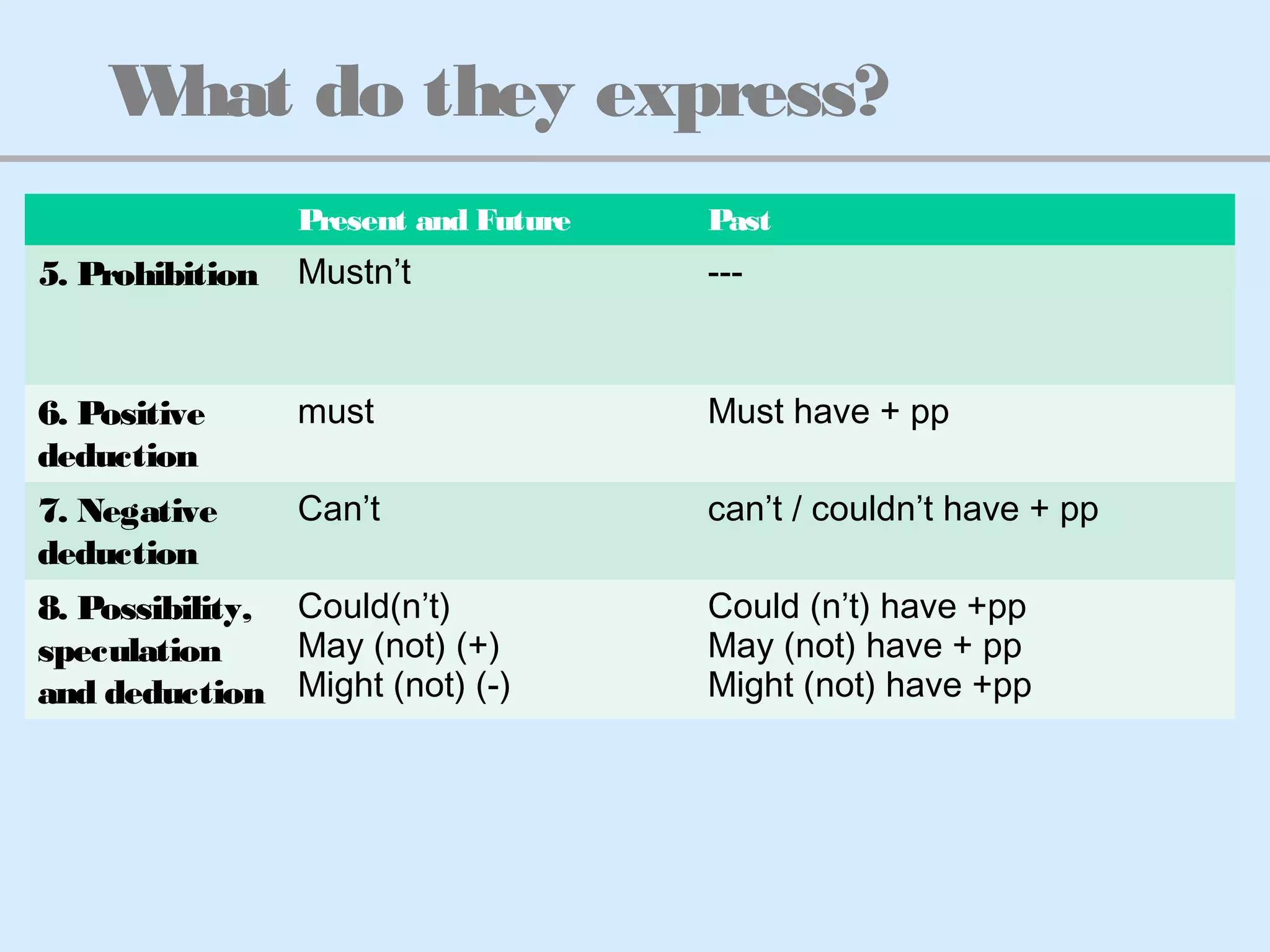
The document discusses modal verbs and semi-modal verbs in English. It provides definitions and examples of modal verbs like can, could, must, may, might, should, ought to, and needn't. It explains that modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that add meaning to the main verb and do not conjugate. The document also covers semi-modal verbs like be able to and have to, noting they require auxiliary verbs in questions and negatives and show subject-verb agreement. It provides examples of how modal verbs are used to express meanings like ability, obligation, possibility and more in both the present/future and past tenses.