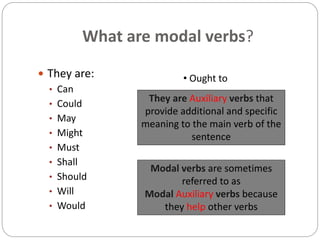
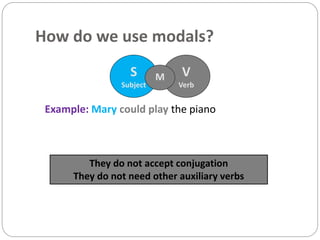
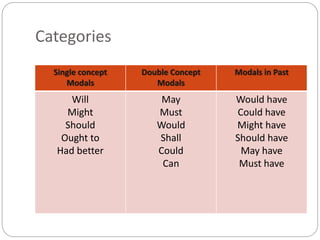
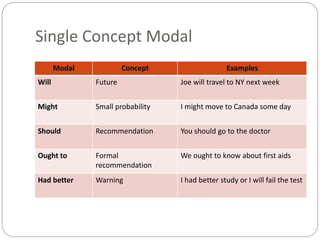
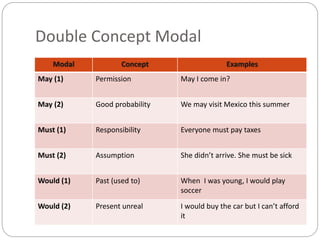
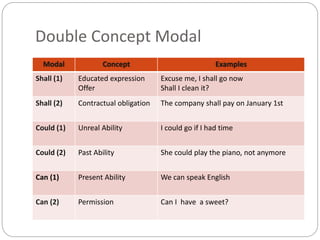
Modal verbs are used to express ideas like ability, permission, obligation, possibility, and necessity. The modal verbs include can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would, and ought to. They are sometimes called auxiliary verbs because they help convey additional meaning about the main verb. Modal verbs do not conjugate or require other helping verbs. They are categorized as single concept modals, which have one meaning, double concept modals, which can have two meanings depending on context, and modals used in the past. Different modal verbs express different concepts like ability, permission, advice, degrees of certainty, criticism, and obligation.