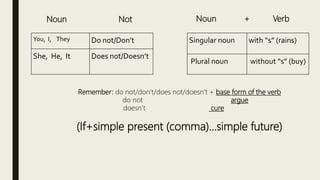
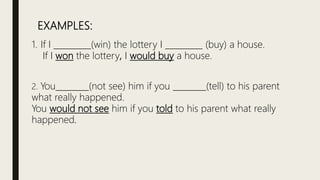
This document provides information about using different types of conditionals to express arguments:
- Zero conditional uses present tense and refers to general truths and habits (e.g. "If you leave the object, it drops").
- First conditional uses present tense and simple future to refer to likely future situations (e.g. "If you don't hurry, you will be late").
- Second conditional uses past tense and "would" to talk about unlikely or improbable situations (e.g. "If I won the lottery, I would buy a house").
- Third conditional uses past perfect tense to describe actions that could have been different if past conditions were different (e.g. "If