Herpesvirus
- 2. Herpesvirus family: General introduction: • Most important human pathogens with both broad and specific host range. • Ability to establish lifelong persistence with periodic reactivation. • Frequent reactivation occurs in immunocompromised patients. Common human pathogens: 1. Herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 2. Vericella-zoster virus 3. Cytomeghalovirus 4. Epstein-Barr virus 5. Herpes virus type-6 6. Herpes virus type-7 7. Herpes virus type-8 8. Herpes B-virus of monkey can infects human. ©sunilbhandariv@gmail.com
- 3. Classification of Herpesvirus Family 3 Broad categories *Lymphoreticular system: spleen, lymphnodes, lymphatic vessels, thymus, and bone marrow. ©sunilbhandariv@gmail.com
- 4. Morphology: 1. Core: Single linear DNA (ds) in the form of torus. 2. Capsid: surrounds core: Icosahedral, 100nm dm, constructed of 160 capsomeres. 3. Teguments: • Between capsid and envelope • Amorphous or asymmetrical features • Consists of viral enzymes needed for cellular process and some against hosts cells immediate responses. 3. Envelope: • Outer layer of virion • Composed of altered hosts N-membrane • Consists dozen of unique viral glycoproteins which appears as short spikes embedded in envelopes. ©sunilbhandariv@gmail.com
- 5. Herpes simplex virus Herpes simplex virus causes disease by direct cytopathologic effects. The infection is initiated by direct contact and depends on the infected tissues whether oral, genital, or brain, etc. The infection occurs by inoculation of virus into susceptible mucosal surfaces, such as the oropharynx, conjunctiva, or cervix or through small abrasions on the skin. Persists in three different ways: 1. Neuroinvasiveness (the ability of virus to invade the brain) 2. Neurotoxicity (ability to multiply in the brain and destroy the brain) 3. Latency (ability to remain in a nonreplicating stage in the dorsal root ganglia of the central nervous system, or CNS) are the properties of HSV. ©sunilbhandariv@gmail.com
- 6. The virus replicates in the infected cells and infects the innervating neuron. Subsequently, the viruses travel by retrograde transport (axonal transport) to the ganglion, such as the trigeminal ganglion (brain) for HSV-1 and the sacral ganglion(spine) for HSV-2. The virus then returns back to the initial site of infection and produce vesicular lesions. Thin walled umbilicated vesicles—the roof of which breaks down, leaving tiny superficial ulcers—are the typical lesions caused by HSV. The vesicle fluid contains infectious virions. ©sunilbhandariv@gmail.com
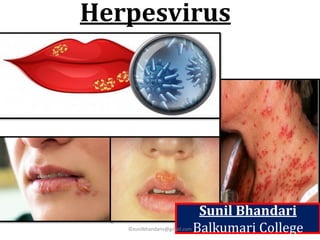
- 11. Clinical syndrome of HSV infections: Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 cause many clinical entities, and infections may be primary or recurrent. The clinical manifestations depend on (a) The age of patient (b) Immune status of the host (c) Previous immunity of the patient to autologous or heterologous viruses (d) Antigenic type of the virus (e) Anatomical site of involvement. • Generally, HSV-1 produces the lesions above the waist, and HSV-2 produces lesions below the waist. • HSV-1 infection is normally associated with orofacial infections and encephalitis, whereas HSV-2 is associated with genital infections. ©sunilbhandariv@gmail.com
- 15. Clinical syndrome of HSV-2 infections: 1. Genital herpes: - Most primary genital infections are asymptomatic. - In symptomatic men, the herpetic vesicles appear in the glans penis, the prepuce, shaft of the penis, and sometimes on the scrotum, thighs, and buttocks. - In women, the vesicles appear on the external genitalia, labia majora, labia minora, vaginal vestibule, and introitus. - The vesicles subsequently rupture, leaving behind extremely painful ulcers. - In both gender, the primary infection may be associated with constitutional symptoms, such as fever, headache, malaise, and myalgia. ©sunilbhandariv@gmail.com
- 16. 2. Neonatal infection: Neonatal infection is a most serious and usually fatal disease caused mostly by HSV-2. It usually occurs due to: • Shedding of HSV-2 from the cervix during vaginal delivery. • An ascending in-utero infection during a primary infection of the mother. • Can be acquired postnatally from family members or hospital staff. ©sunilbhandariv@gmail.com Since CMI is poorly developed in neonates, the virus causes a disseminated disease with involvement of liver, lung, as well as the organs of the CNS. The condition has a high mortality of 80%. Progression of the infection to the CNS results in mental retardation or neurological disabilities even with treatment, or may finally lead to death.
- 17. 3. Aseptic meningitis: Aseptic meningitis may occur as a complication of genital HSV-2 infection. • Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes (meninges) surrounding your brain and spinal cord. • The swelling from meningitis typically triggers symptoms such as headache, fever and a stiff neck. ©sunilbhandariv@gmail.com
- 19. 3. Direct antigen detection Direct enzyme immunoassay and direct fluorescent antibody test are useful to demonstrate HSV antigens directly in vesicular fluid, tissue smear, or biopsy. ©sunilbhandariv@gmail.com
- 20. 5. Serodiagnosis : • Antibodies appears in 4-7 days after infection. • They reach a peak in 2-4 weeks. • Immunofluorescence, ELISA, Neutralization test (Nt-test) 6. Molecular Diagnosis: Specimens: vesicular fluid, skin scraping, CSF, and other specimens • DNA probe and PCR are useful for demonstration of viral genome. • PCR shows a higher sensitivity (95%) for detection of HSV-1 DNA in the CSF specimen. • PCR is also used to detect asymptomatic shedding or HSV in skin lesions, but is not cost-effective • The DNA maps of restriction enzyme fragments of HSV-1 and HSV-2 are unique. ©sunilbhandariv@gmail.com
- 21. Treatment of HSV-infection: • Several antiviral drugs have proved effective against HSV infections, including: Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, and Vidarabine, Famciclovir • All are inhibitors of viral DNA synthesis. • Acyclovir: It is a synthetic acyclic purine nucleotide analog, which is most commonly used to treat HSV infection. Acyclovir is useful: ■ To diminish shedding of viruses, ■ To decrease rate of clinical recurrences ■ To suppress recurrent genital infections. • Oral therapy with acyclovir is usually recommended for primary orolabial and genital HSV infections • Intravenous acyclovir is recommended for life-threatening and serious HSV infections, such as encephalitis, infections in immunocompromised patients. ©sunilbhandariv@gmail.com
