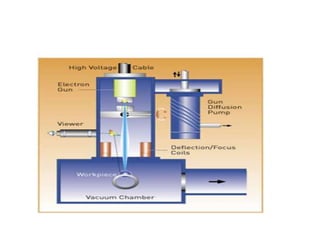
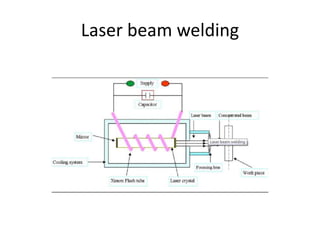
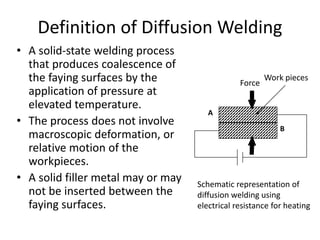
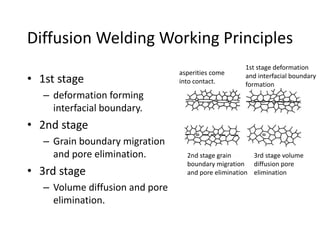
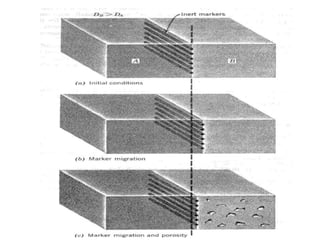
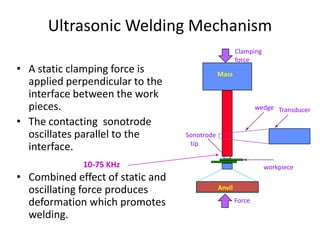
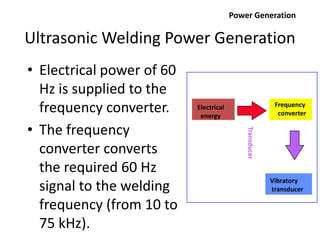
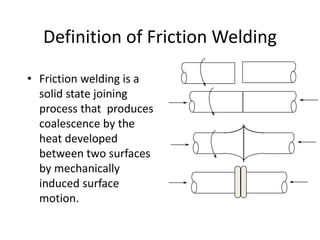
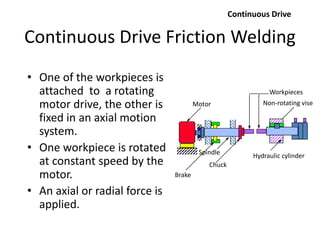
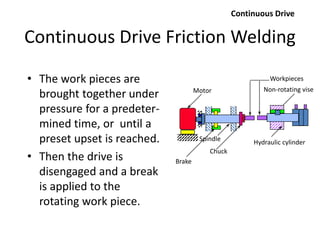
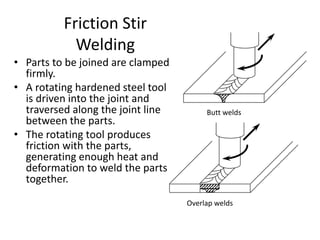
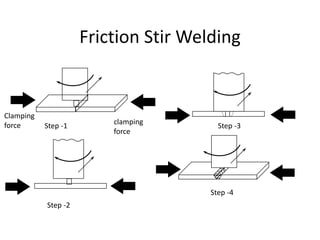
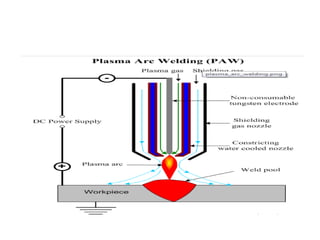
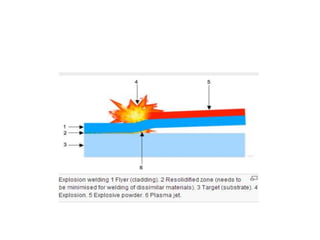
Electron beam welding uses a beam of electrons accelerated by high voltage to melt and join materials. It can achieve deep penetration with minimal heat input. It produces a clean, homogeneous weld in a vacuum environment without filler metals or shielding gas. However, it requires expensive equipment and a vacuum chamber. Laser beam welding uses a focused laser beam to melt materials. It has high travel speeds but requires precise part fit-up and positioning. Solid state welding joins materials without melting through processes like friction, diffusion, or ultrasonic welding. This reduces heat effects but is limited in applications. Plasma welding uses an arc struck in an externally-supplied ionized gas to produce high temperature for welding metals.