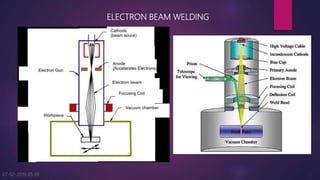
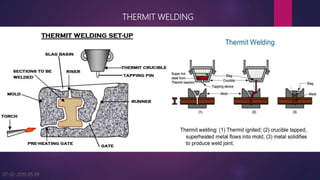
The document discusses two welding processes: electron beam welding and thermit welding. Electron beam welding uses a concentrated beam of electrons to melt and fuse base metals in a vacuum chamber, allowing for high purity welds of dissimilar metals. However, it has high costs and downtime for pumping the vacuum chamber. Thermit welding uses an exothermic reaction between aluminum and a metal oxide to produce enough heat to melt metals for welding without external energy. The reaction separates into a superheated metal and aluminum oxide slag. Thermit welding is used to join shafts, railway tracks, and machinery frames.