The document discusses various topics related to assessment in schools including intelligence, learning outcomes, educational achievement, taxonomies of educational objectives, multiple intelligences, standards, and domains of learning. It provides definitions for key concepts like intelligence, learning, achievement, Bloom's taxonomy, and standards. It also outlines the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains of learning objectives and outcomes.

![Intelligence Are you brainless? Jar Jar Binks : I speck! Qui-Gon Jinn: The ability to speak does not make you intelligent. What is Intelligence? [2-8 to 2-15]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2learningobjectives-100219202910-phpapp02/75/Week2-Learning-Objectives-2-2048.jpg)



![Educational Achievement What does achievement mean [see 2-7] Being able to recall important facts and information on demand. Being able to perform discrete skill like reading, writing, speaking, or computing. view from behavior psychology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2learningobjectives-100219202910-phpapp02/75/Week2-Learning-Objectives-6-2048.jpg)
![Educational Achievement What does achievement mean [see 2-7] Understanding concepts & principles. Ability to think independently, formulate questions, inquire, solve problems, create new processes, evaluate ones thinking & that of others Exercise discernment and judgment in matters of taste and preference view from Philosophy & Cognitive Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2learningobjectives-100219202910-phpapp02/75/Week2-Learning-Objectives-7-2048.jpg)
![Taxonomy of Educational Objectives Cognitive Domain : Knowledge outcomes, intellectual ability & skills Affective Domain: Attitudes, Interests, Values, Emotions, Social norms Psychomotor Domain : (motor skills) Physical Performance, Ability & Behaviors [pg. 55; Appendix G ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2learningobjectives-100219202910-phpapp02/75/Week2-Learning-Objectives-8-2048.jpg)
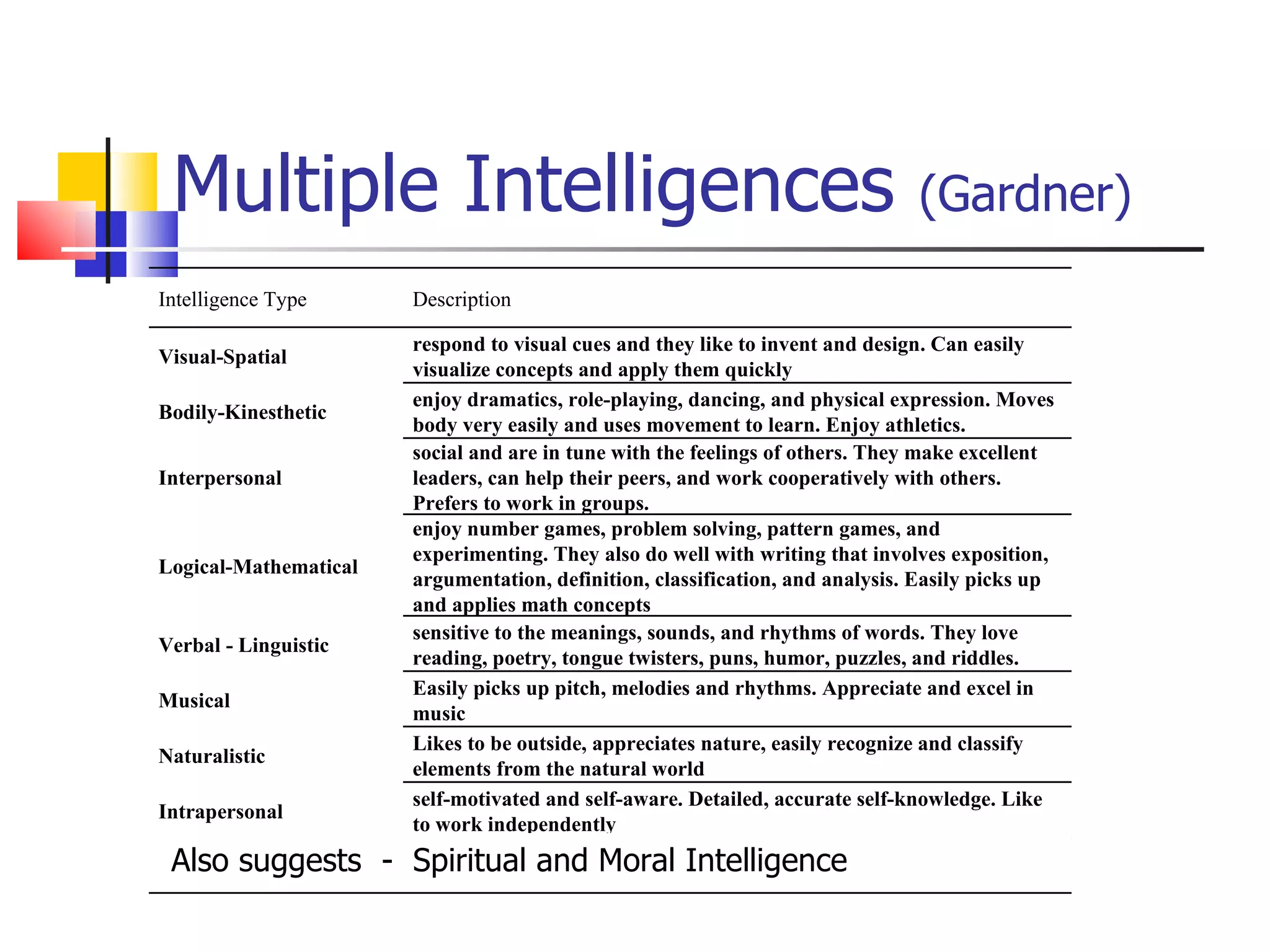





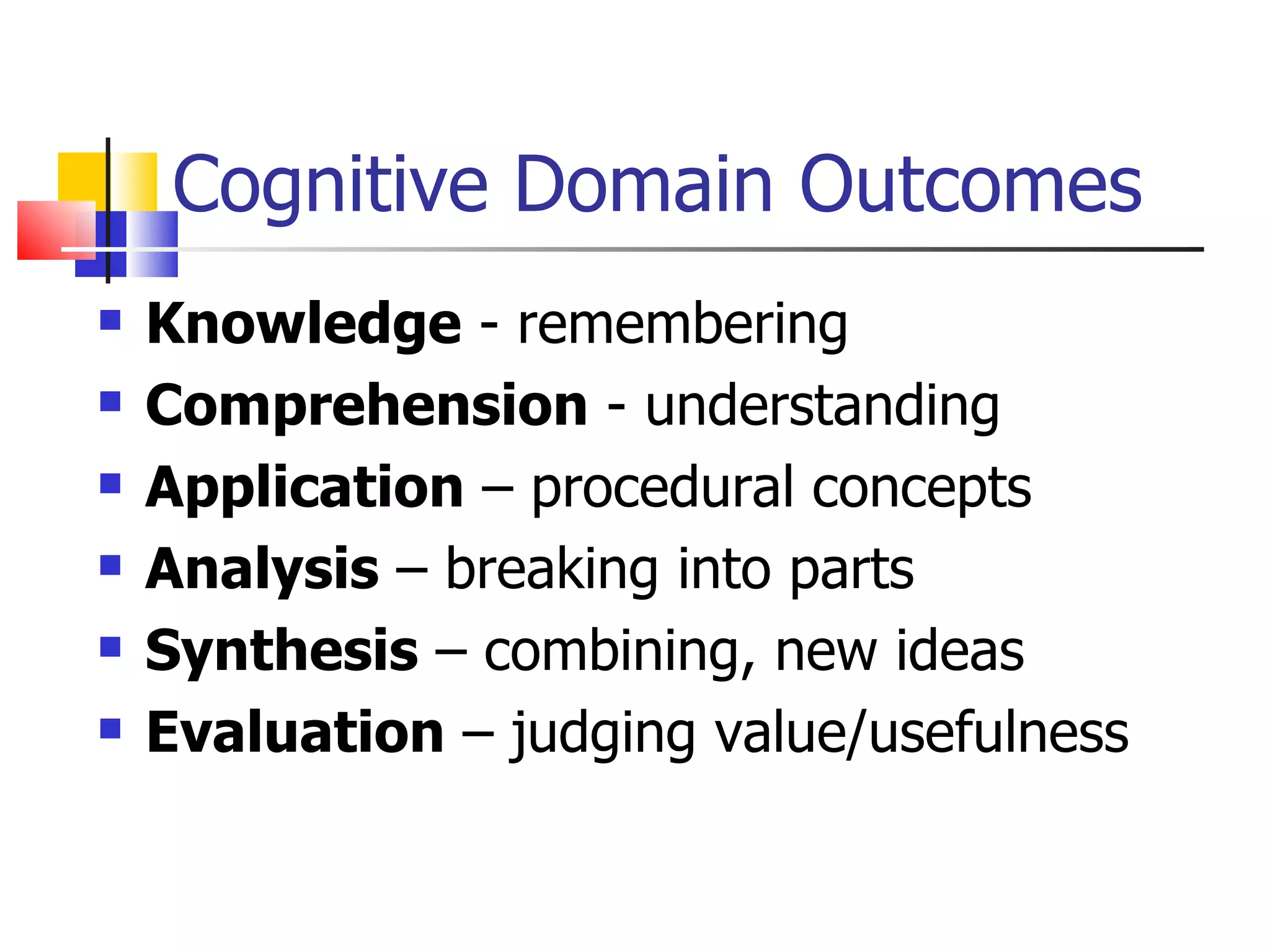
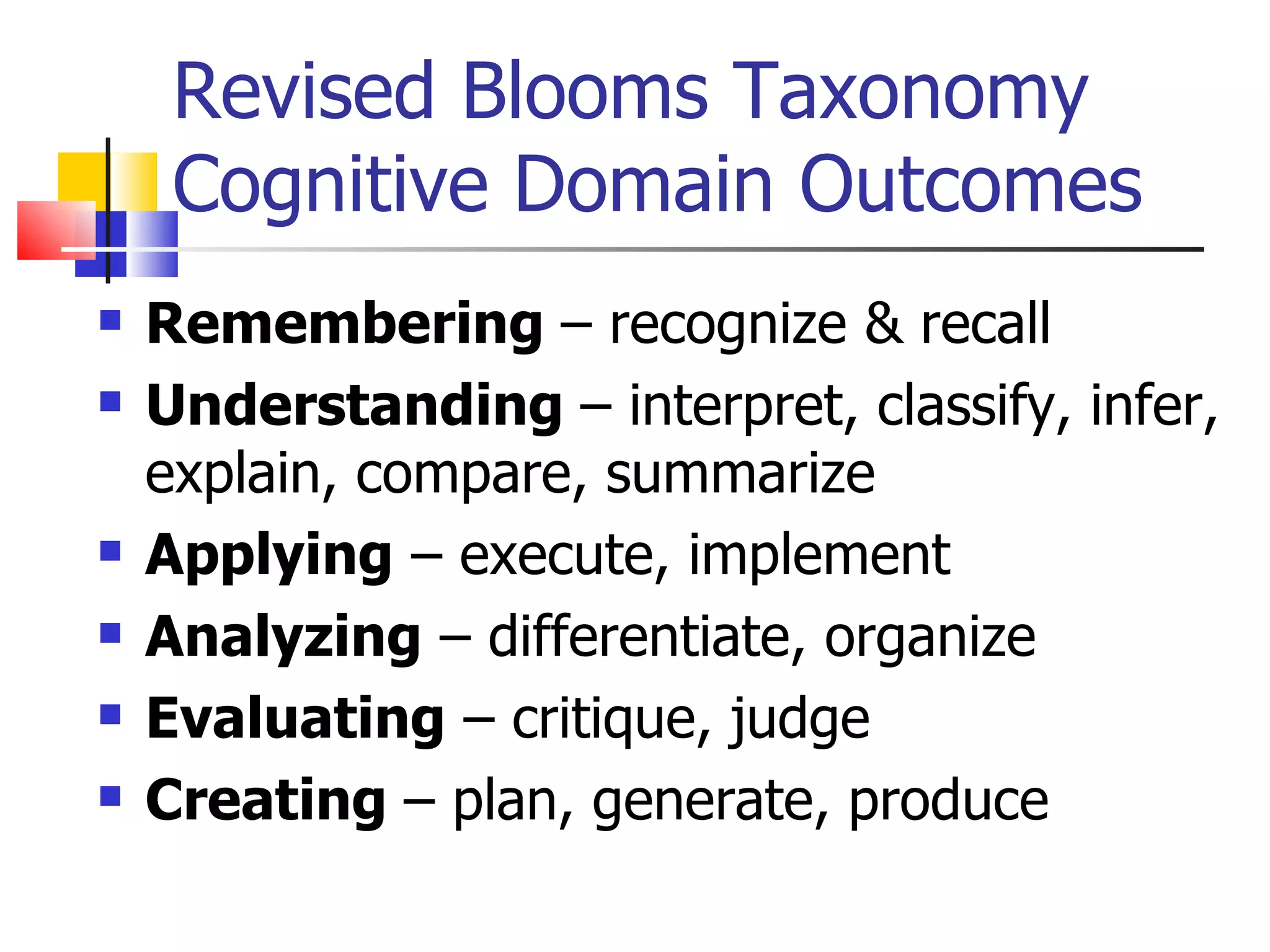
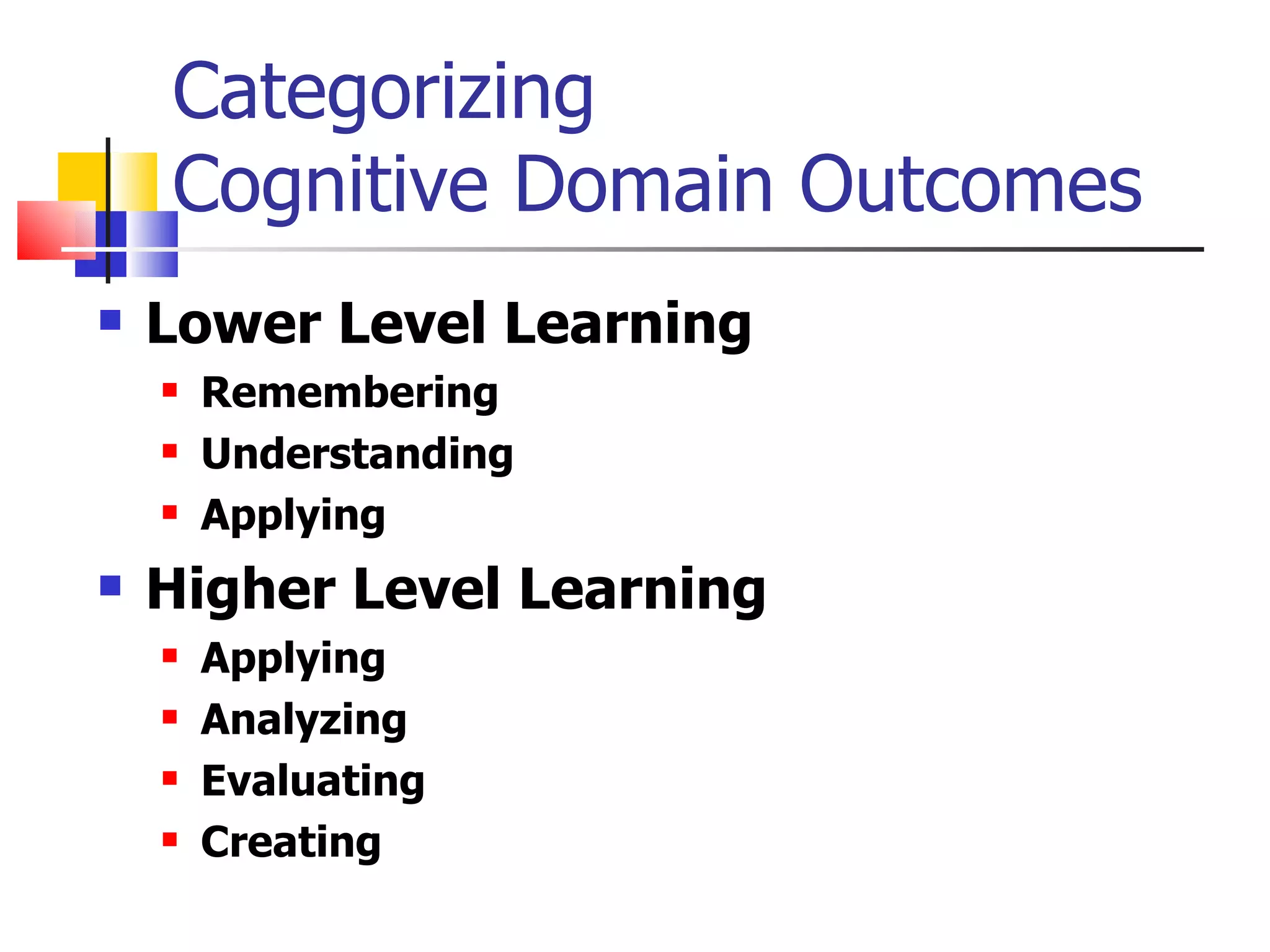
![Types of Knowledge [2-21] Factual – terms, details Conceptual – classifications, principles Procedural – skills, techniques, method MetaCognitive – strategies, self-knowledge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2learningobjectives-100219202910-phpapp02/75/Week2-Learning-Objectives-18-2048.jpg)




