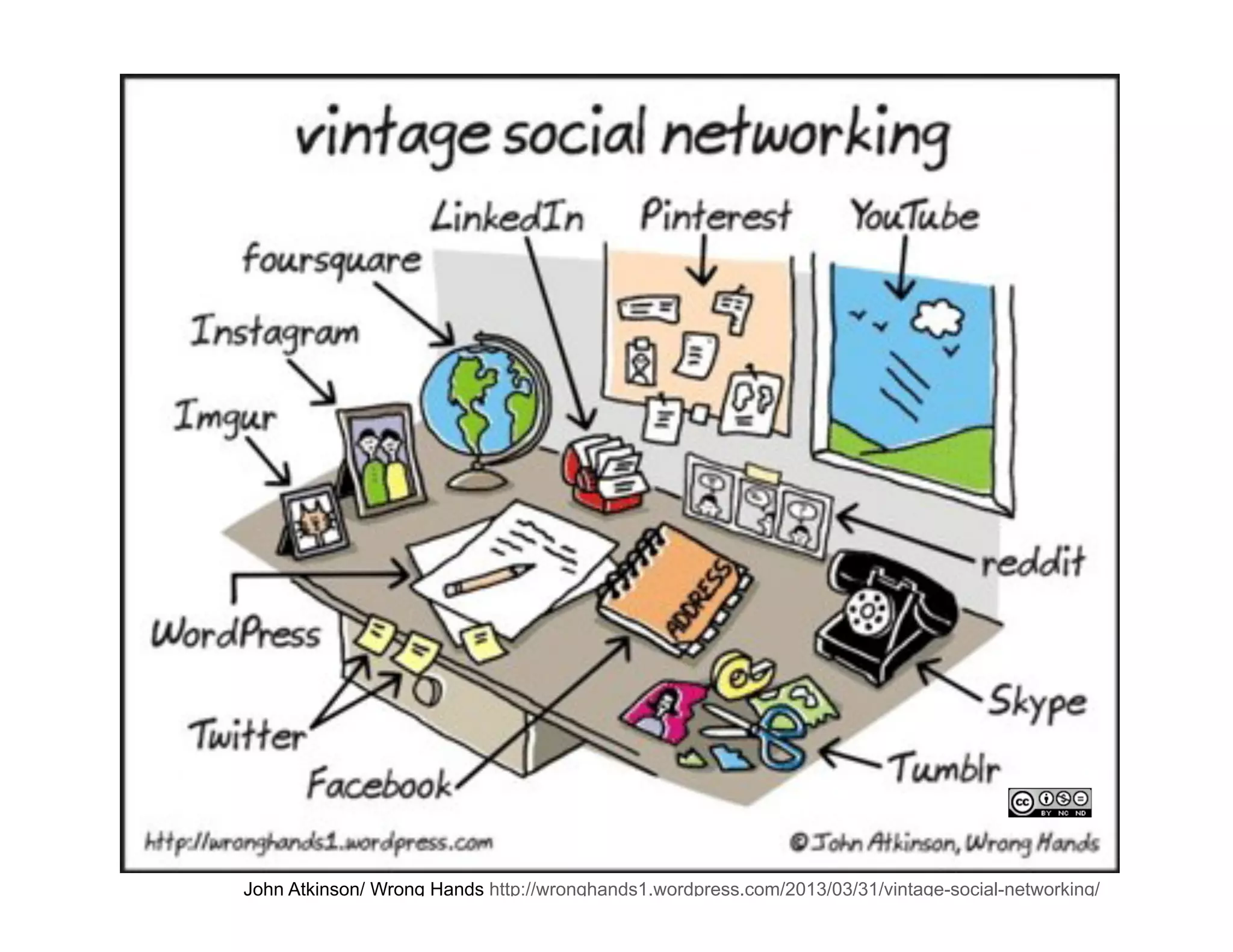
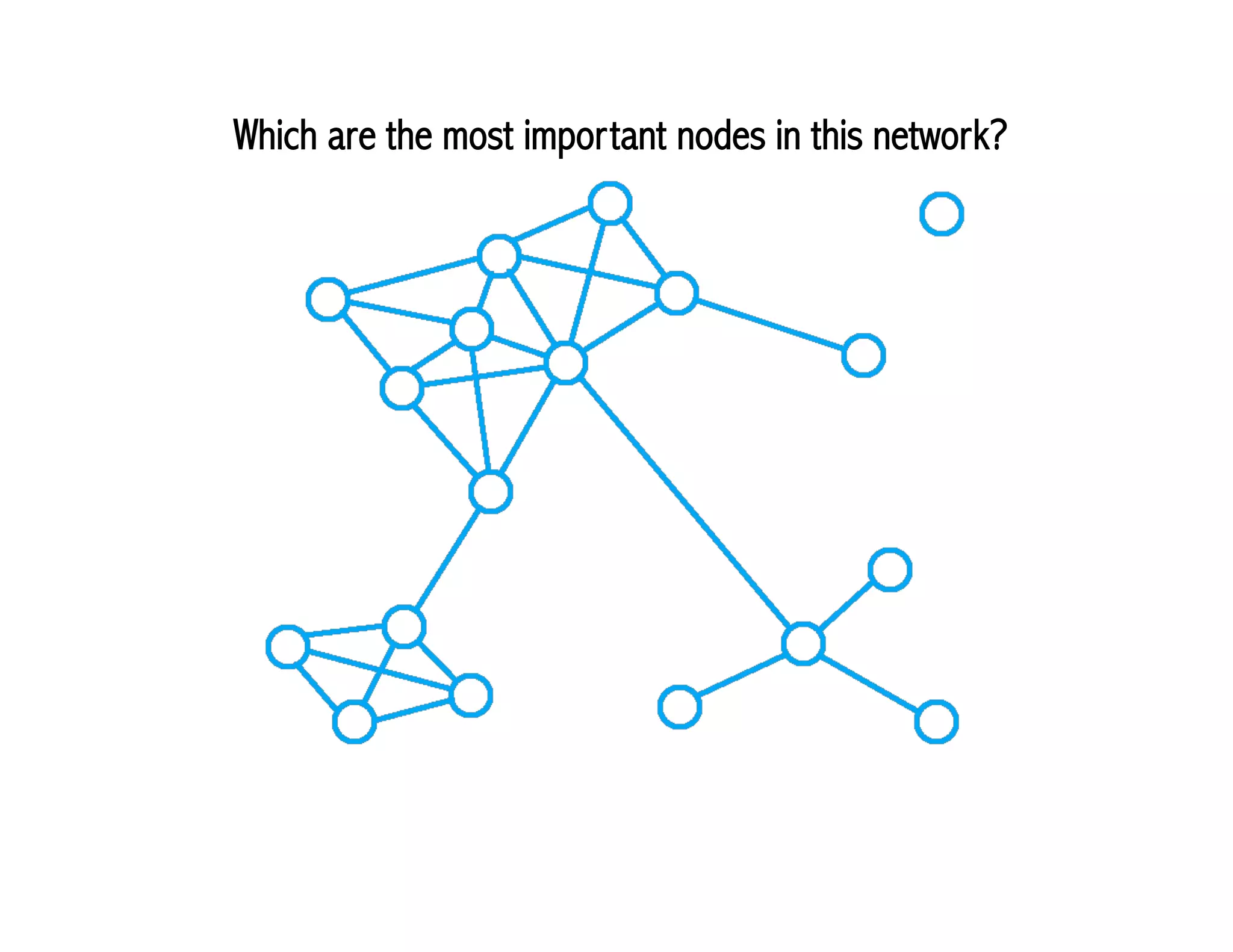
This document provides an agenda for a class on social media that includes discussions on various social media terms and concepts. It outlines activities for students, such as defining social media and discussing the differences between social media "visitors" and "residents". It also lists various readings and resources for students to explore key topics in social media research, such as network analysis, tie strength, and strategic planning for social media initiatives. The document provides links to external resources and materials to support the activities and assignments for the class.