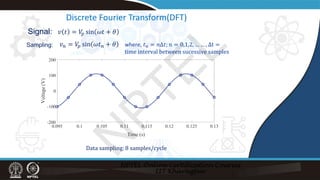
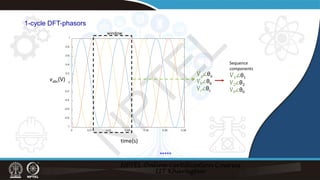
This document discusses different techniques for phasor estimation from discrete time signals, including the discrete Fourier transform (DFT). It focuses on explaining the one-cycle DFT method. The one-cycle DFT divides the signal into windows of one cycle and applies the DFT to each window to estimate the phasor. It is shown that with each new sample, the phasor estimate from the DFT advances by 45 degrees. The document also discusses applying the one-cycle DFT to signals with harmonic components and estimating sequence components from three-phase signals.


![Phasor estimation: 1-cycle DFT
Defining
𝑉𝑉𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟 =
2
𝑁𝑁
�
𝑛𝑛=0
𝑁𝑁−1
[𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛 cos(2𝜋𝜋
𝑛𝑛
𝑁𝑁
)] and 𝑉𝑉𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 =
2
𝑁𝑁
�
𝑛𝑛=0
𝑁𝑁−1
[𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛 sin(2𝜋𝜋
𝑛𝑛
𝑁𝑁
)]
Computed Phasor:
̇
𝑉𝑉 = 𝑉𝑉𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟 − 𝑗𝑗𝑉𝑉𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 𝑉𝑉 ∠𝜃𝜃
Where 𝑉𝑉 = 𝑉𝑉𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟
2
+ 𝑉𝑉𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖
2
,𝜃𝜃 = −tan−1(
𝑉𝑉𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖
𝑉𝑉𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟
)
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛 = 𝑉𝑉
𝑝𝑝 sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡𝑛𝑛 + 𝜃𝜃
Applying 1-cycle DFT ,
Voltage phasor, ̇
𝑉𝑉 =
2
𝑁𝑁
∑𝑛𝑛=0
𝑁𝑁−1
(𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁
𝑛𝑛
) ; 0 ≤ 𝑛𝑛 ≤ 𝑁𝑁 − 1 Where, N=number of samples in a cycle
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛 = 𝑛𝑛𝑡𝑡𝑡 𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑜𝑜𝑜 𝑣𝑣(𝑡𝑡)
�
𝑛𝑛=0
𝑁𝑁−1
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-5-320.jpg)




![=
2
𝑁𝑁
�
𝑛𝑛=0
𝑁𝑁−2
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛+1𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋𝑛𝑛
𝑁𝑁 +
2
𝑁𝑁
𝑣𝑣𝑁𝑁𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋 𝑁𝑁−1
𝑁𝑁
=
2
𝑁𝑁
�
𝑛𝑛=1
𝑁𝑁−1
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋𝑛𝑛
𝑁𝑁 𝑒𝑒𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁 +
2
𝑁𝑁
𝑣𝑣𝑁𝑁𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋 𝑁𝑁−1
𝑁𝑁
= ̇
𝑉𝑉1 −
2
𝑁𝑁
𝑣𝑣0 𝑒𝑒𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁 +
2
𝑁𝑁
𝑣𝑣𝑁𝑁𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁 𝑒𝑒𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁
̇
𝑉𝑉2 = [ ̇
𝑉𝑉1 +
2
𝑁𝑁
(𝑣𝑣𝑁𝑁 − 𝑣𝑣0)]𝑒𝑒𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁
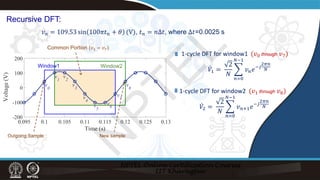
Recursive DFT:
̇
𝑉𝑉1 =
2
𝑁𝑁
�
𝑛𝑛=0
𝑁𝑁−1
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋𝑛𝑛
𝑁𝑁
=
2
𝑁𝑁
�
𝑛𝑛=1
𝑁𝑁−1
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁 +
2
𝑁𝑁
𝑣𝑣0
̇
𝑉𝑉2 =
2
𝑁𝑁
�
𝑛𝑛=0
𝑁𝑁−1
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛+1𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋𝑛𝑛
𝑁𝑁
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-18-320.jpg)
![The phasor at the 𝑟𝑟 + 1 𝑡𝑡𝑡 instant can be written as
Earlier phasor New Sample Outgoing Sample
̇
𝑉𝑉𝑟𝑟+1 = [ ̇
𝑉𝑉
𝑟𝑟 +
2
𝑁𝑁
(𝑣𝑣N+r − 𝑣𝑣𝑟𝑟)]𝑒𝑒𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁
New phasor
Recursive DFT:
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-19-320.jpg)
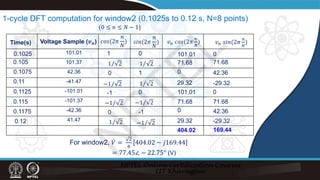
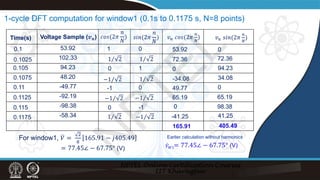
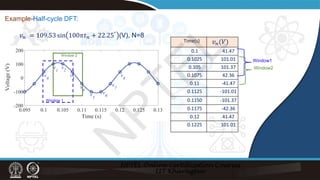
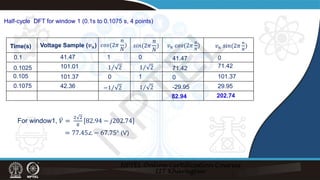
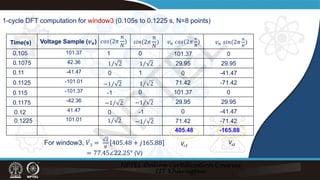
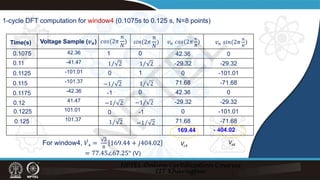
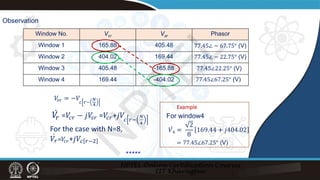
![Recursive DFT:
Example:
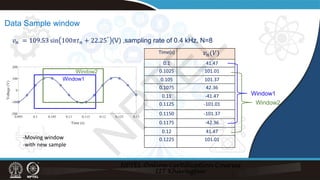
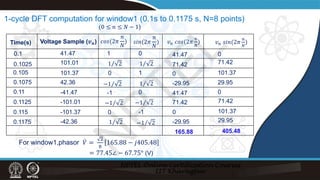
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛 = 109.53 sin 100𝜋𝜋𝑡𝑡𝑛𝑛 + 22.25° (V), N=8
Time(s)
0.1 41.47
0.1025 101.01
0.105 101.37
0.1075 42.36
0.11 -41.47
0.1125 -101.01
0.1150 -101.37
0.1175 -42.36
0.12 41.47
0.1225 101.01
̇
𝑉𝑉2
̇
𝑉𝑉1 = 77.45∠ − 67.75° (V)
= 77.45∠ − 22.75° (V)
̇
𝑉𝑉2 = [ ̇
𝑉𝑉1 +
2
8
(𝑣𝑣8 − 𝑣𝑣0)]𝑒𝑒𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋
8
Using recursive DFT:
=[77.45∠-67.75° +
2
8
(41.47-41.47)] 𝑒𝑒𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋
8
= 77.45∠ − 22.75° (V)
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛(𝑉𝑉)
𝑣𝑣0=
𝑣𝑣1=
𝑣𝑣2=
𝑣𝑣3=
𝑣𝑣4=
𝑣𝑣5=
𝑣𝑣6=
𝑣𝑣7=
𝑣𝑣8=
𝑣𝑣9=
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-20-320.jpg)

![𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛 = 𝑉𝑉
𝑝𝑝 sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡𝑛𝑛 + 𝜃𝜃
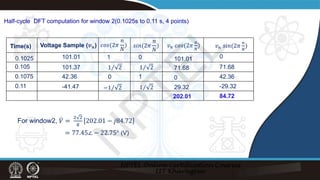
Half-cycle DFT for Phasor Calculation
1-cycle window
half-cycle window
̇
𝑉𝑉 =
2
𝑁𝑁
2
�
𝑛𝑛=0
𝑁𝑁
2
−1
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁
𝑛𝑛
; 0 ≤ 𝑛𝑛 ≤
𝑁𝑁
2
− 1
𝑉𝑉𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟 =
2
𝑁𝑁
2
�
𝑛𝑛=0
𝑁𝑁
2
−1
[𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛 cos(2𝜋𝜋
𝑛𝑛
𝑁𝑁
)]
Defining
Computed phasor: ̇
𝑉𝑉 = 𝑉𝑉𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟 − 𝑗𝑗𝑉𝑉𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 = 𝑉𝑉 ∠𝜃𝜃
Where, 𝑉𝑉 = 𝑉𝑉𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟
2
+ 𝑉𝑉𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖
2
,𝜃𝜃 = −tan−1(
𝑉𝑉𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖
𝑉𝑉𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟
)
𝑉𝑉𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖𝑖 =
2
𝑁𝑁
2
�
𝑛𝑛=0
(
𝑁𝑁
2)−1
[𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛 sin(2𝜋𝜋
𝑛𝑛
𝑁𝑁
)]
Signal
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-22-320.jpg)


![̇
𝑉𝑉1 = 𝑉𝑉∠𝜃𝜃
Using recursive DFT-
̇
𝑉𝑉2 = 𝑉𝑉∠(𝜃𝜃 +
2𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁
)
R𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒 ̇
𝑉𝑉1 = 𝑉𝑉𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝜃𝜃 = 𝑉𝑉𝑐𝑐𝑐
I𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚 ̇
𝑉𝑉1 = 𝑉𝑉𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝜃𝜃 = −𝑉𝑉𝑠𝑠𝑠
̇
𝑉𝑉3 = 𝑉𝑉∠(𝜃𝜃 +
4𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁
)
𝐼𝐼𝐼𝐼𝐼𝐼𝐼𝐼 ̇
𝑉𝑉𝑁𝑁
4
+1
= −𝑉𝑉
𝑠𝑠(
𝑁𝑁
4
+1)
= 𝑉𝑉 sin(𝜃𝜃 +
𝜋𝜋
2
)
𝑉𝑉
𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 = −𝑉𝑉
𝑐𝑐 𝑟𝑟−
𝑁𝑁
4
̇
𝑉𝑉𝑟𝑟 =𝑉𝑉
𝑐𝑐𝑟𝑟 − 𝑗𝑗𝑉𝑉
𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 =𝑉𝑉
𝑐𝑐𝑟𝑟+𝑗𝑗𝑉𝑉𝑐𝑐 𝑟𝑟−
𝑁𝑁
4
Let for window-1 we get,
R𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒𝑒 ̇
𝑉𝑉 = 𝑉𝑉
𝑐𝑐 I𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚 ̇
𝑉𝑉 = −𝑉𝑉
𝑠𝑠
and
Cosine Filter
and
̇
𝑉𝑉2 = [ ̇
𝑉𝑉1 +
2
𝑁𝑁
(𝑣𝑣𝑁𝑁 − 𝑣𝑣0)]𝑒𝑒𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁
and
= 𝑉𝑉cos 𝜃𝜃 = 𝑉𝑉𝑐𝑐𝑐
̇
𝑉𝑉𝑁𝑁
4
+1
= 𝑉𝑉∠ 𝜃𝜃 +
𝜋𝜋
2
,
̇
𝑉𝑉𝑁𝑁
4
+1
= 𝑉𝑉∠ 𝜃𝜃 +
2𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁
𝑁𝑁
4
,
For rth window
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-28-320.jpg)



![If �
𝑎𝑎 and �
𝑏𝑏 are the estimated values
�
𝑎𝑎 + �
𝑏𝑏𝑡𝑡0 − 𝑚𝑚0 = 𝜖𝜖1
�
𝑎𝑎 + �
𝑏𝑏𝑡𝑡1 − 𝑚𝑚1 = 𝜖𝜖2
�
𝑎𝑎 + �
𝑏𝑏𝑡𝑡𝑛𝑛−1 − 𝑚𝑚𝑛𝑛−1 = 𝜖𝜖𝑛𝑛−1
for 𝑚𝑚0, 𝑚𝑚2 … . 𝑚𝑚𝑛𝑛−1 are the measurements.
𝜖𝜖0, 𝜖𝜖2 … . 𝜖𝜖𝑛𝑛−1 are the errors (residues)
Where,
Least Square Estimation
1 𝑡𝑡0
1 𝑡𝑡1
. .
. .
1 𝑡𝑡𝑛𝑛−1
�
𝑎𝑎
�
𝑏𝑏
−
𝑚𝑚0
𝑚𝑚1
.
.
𝑚𝑚𝑛𝑛−1
=
𝜖𝜖0
𝜖𝜖1
.
.
𝜖𝜖𝑛𝑛−1
[A] [X] – [m] = [𝜖𝜖]
unknown
[𝜖𝜖]= [A][X] – [m]
n ×1
2 ×1
n ×2
n ×1
measurement
.
.
.
.
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-38-320.jpg)
![Least Square Estimation
[𝜖𝜖]= [A][X] – [m]
𝜖𝜖 𝑇𝑇 𝜖𝜖 = 𝐴𝐴𝑋𝑋 − 𝑚𝑚 𝑇𝑇 𝐴𝐴𝑋𝑋 − 𝑚𝑚
= [ 𝐴𝐴𝑋𝑋 𝑇𝑇
− 𝑚𝑚 𝑇𝑇
] [𝐴𝐴𝑋𝑋 − 𝑚𝑚]
= 𝐴𝐴𝑋𝑋 𝑇𝑇 𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 + 𝑚𝑚 𝑇𝑇[𝑚𝑚] − 𝐴𝐴𝑋𝑋 𝑇𝑇 𝑚𝑚 − 𝑚𝑚 𝑇𝑇 𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴
𝑚𝑚 𝑇𝑇 𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 = 𝑚𝑚𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 𝑇𝑇
𝑚𝑚 : n ×1 𝑚𝑚 𝑇𝑇
: 1 × n
[A]: n × 2
[X]: 2 × 1
𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 : n × 1
𝑚𝑚 𝑇𝑇
𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 : 1 × 1
For the 1 × 1 matrix,
= 𝐴𝐴𝑋𝑋 𝑇𝑇[𝑚𝑚]
= [𝑋𝑋]𝑇𝑇
[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇
[𝑚𝑚]
𝜖𝜖 𝑇𝑇[𝜖𝜖] = 𝑋𝑋𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇[𝐴𝐴𝑋𝑋] + 𝑚𝑚𝑇𝑇 𝑚𝑚 − 2 𝑋𝑋 𝑇𝑇 𝐴𝐴 𝑇𝑇[𝑚𝑚]
Here
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-39-320.jpg)
![Least Square Estimation
Differentiating the above equation w.r.t. [𝑋𝑋]
2[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇
𝐴𝐴 [X] − 2 𝐴𝐴 𝑇𝑇
[𝑚𝑚] = 0
[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇
𝐴𝐴 [𝑋𝑋] = 𝐴𝐴 𝑇𝑇
[𝑚𝑚]
𝑋𝑋 = 𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇
𝐴𝐴 −1
[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇
[𝑚𝑚]
𝜖𝜖 𝑇𝑇[𝜖𝜖] = 𝑋𝑋 𝑇𝑇 𝐴𝐴 𝑇𝑇[𝐴𝐴𝑋𝑋] + 𝑚𝑚𝑇𝑇 𝑚𝑚 − 2 𝑋𝑋 𝑇𝑇 𝐴𝐴 𝑇𝑇[𝑚𝑚]
unknown
when[𝐴𝐴] is a square matrix, the pseudo inverse becomes invese of [A]
𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓𝑓 𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡 𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 𝑎𝑎 + 𝑏𝑏𝑏𝑏 = 𝑚𝑚
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-40-320.jpg)

![Least Square Estimation for Phasor
𝑎𝑎01𝑋𝑋1 + 𝑎𝑎02𝑋𝑋2 = 𝑣𝑣0
𝑎𝑎11𝑋𝑋1 + 𝑎𝑎12𝑋𝑋2 = 𝑣𝑣1
.
.
𝑎𝑎(𝑛𝑛−1)1𝑋𝑋1 + 𝑎𝑎(𝑛𝑛−1)2𝑋𝑋2 = 𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛−1
[𝐴𝐴] =
𝑎𝑎01 𝑎𝑎02
𝑎𝑎11 𝑎𝑎12
. .
. .
𝑎𝑎(𝑛𝑛−1)1 𝑎𝑎(𝑛𝑛−1)2
[𝑋𝑋] =
𝑋𝑋1
𝑋𝑋2 [𝑚𝑚] =
𝑣𝑣0
𝑣𝑣1
.
.
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛−1
𝑎𝑎01 = sin(𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0) 𝑎𝑎02 = cos(𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0)
𝑎𝑎11 = sin(𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1) 𝑎𝑎12 = cos(𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1)
𝑎𝑎(n−1)1 = sin(𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡(n−1)) 𝑎𝑎 n−1 2 = cos(𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡(n−1))
.
.
.
.
.
.
𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤
𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤
unknowns
measurements
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-42-320.jpg)
![𝑋𝑋1 = 𝑉𝑉 𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐 𝜃𝜃 𝑋𝑋2 = 𝑉𝑉 𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 𝜃𝜃
𝑉𝑉 = 𝑋𝑋1
2
+ 𝑋𝑋2
2
Vrms =
𝑉𝑉
2
Number of unknowns = 2, we need at least 2 samples to obtain the phasor
or more can be included.
Say, with 1 cycle data in the window, for 50 Hz and sampling rate 0.4 kHz, 8 samples
Size of X = 2 x 1
Size of A = 8 x 2
Size of m = 8 x 1
𝜃𝜃 = tan−1
𝑋𝑋2
𝑋𝑋1
Least Square Estimation for Phasor
𝐴𝐴 𝑋𝑋 = [𝑚𝑚]
𝑋𝑋 = 𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇 [𝑚𝑚]
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-43-320.jpg)
![Time(s)
0.1 41.47
0.1025 101.01
0.105 101.37
0.1075 42.36
0.11 -41.47
0.1125 -101.01
0.1150 -101.37
0.1175 -42.36
0.12 41.47
0.1225 101.01
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛(𝑉𝑉)
t0
t1
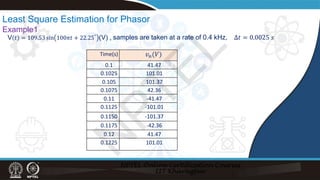
Least Square Estimation for Phasor
Example1..
[𝑚𝑚] =
41.47
101.01
[𝑋𝑋] =
𝑉𝑉 cos 𝜃𝜃
𝑉𝑉 sin 𝜃𝜃
𝜔𝜔 = 2𝜋𝜋𝜋𝜋 = 2𝜋𝜋 50 = 100𝜋𝜋
[𝐴𝐴] =
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0 cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1 cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1
=
0 1
1
2
1
2
assigning time for the calculation window, t0 = 0.0 s and t1 = 0.0025s
in [A]
For the corresponding samples as marked in the table
𝑋𝑋 = 𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇 [𝑚𝑚]
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-45-320.jpg)
![[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇[𝐴𝐴] =
0
1
2
1
1
2
0 1
1
2
1
2
=
0.5 0.5
0.5 1.5
[ 𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 ]−1=
3 −1
−1 1
𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇=
3 −1
−1 1
0
1
2
1
1
2
=
−1 1.4142
1 0
𝑋𝑋 =
−1 1.4142
1 0
41.47
101.01
=
101.37
41.47
Least Square Estimation for Phasor
Example1…
𝑋𝑋 = 𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇 [𝑚𝑚]
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-46-320.jpg)

![Time(s)
0.1 41.47
0.1025 101.01
0.105 101.37
0.1075 42.36
0.11 -41.47
0.1125 -101.01
0.1150 -101.37
0.1175 -42.36
0.12 41.47
0.1225 101.01
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛(𝑉𝑉)
t0
t1
[𝑚𝑚] =
101.01
101.37
[𝑋𝑋] =
𝑉𝑉 cos 𝜃𝜃
𝑉𝑉 sin 𝜃𝜃
𝜔𝜔 = 2𝜋𝜋𝜋𝜋 = 2𝜋𝜋 50 = 100𝜋𝜋
[𝐴𝐴] =
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0 cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1 cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1
=
0 1
1
2
1
2
with t0 = 0.0 s and t1 = 0.0025s for matrix A
For the corresponding samples as marked in the table
Least Square Estimation for Phasor
Example2- Different window
𝑋𝑋 = 𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇 [𝑚𝑚]
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-48-320.jpg)
![[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇
[𝐴𝐴] =
0
1
2
1
1
2
0 1
1
2
1
2
=
0.5 0.5
0.5 1.5
𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1 =
3 −1
−1 1
𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇=
3 −1
−1 1
0
1
2
1
1
2
=
−1 1.4142
1 0
𝑋𝑋 =
−1 1.4142
1 0
101.01
101.37
=
42.36
101.01
Least Square Estimation for Phasor
Example2..
𝑋𝑋 = 𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇 [𝑚𝑚]
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-49-320.jpg)

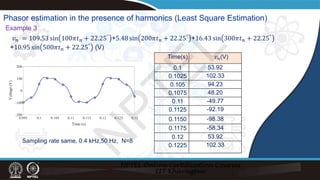
![Time(s) 𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛(V)
0.1 53.92
0.1025 102.33
0.105 94.23
0.1075 48.20
0.11 -49.77
0.1125 -92.19
0.1150 -98.38
0.1175 -58.34
0.12 53.92
0.1225 102.33
t0
t1 [𝑚𝑚] =
53.92
102.33
[𝑋𝑋] =
𝑉𝑉 cos 𝜃𝜃
𝑉𝑉 sin 𝜃𝜃
𝜔𝜔 = 2𝜋𝜋𝜋𝜋 = 2𝜋𝜋 50 = 100𝜋𝜋
[𝐴𝐴] =
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0 cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1 cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1
=
0 1
1
2
1
2
Only with 2 measurements:
Example 3:
𝑋𝑋 = 𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇 [𝑚𝑚]
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-52-320.jpg)
![[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇
[𝐴𝐴] =
0
1
2
1
1
2
0 1
1
2
1
2
=
0.5 0.5
0.5 1.5
𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1 =
3 −1
−1 1
𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇=
3 −1
−1 1
0
1
2
1
1
2
=
−1 1.4142
1 0
[𝑋𝑋] =
−1 1.4142
1 0
53.92
102.33
=
90.80
53.91
Example 3..
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-53-320.jpg)

![Time(s) 𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛(V)
0.1 53.92
0.1025 102.33
0.105 94.23
0.1075 48.20
0.11 -49.77
0.1125 -92.19
0.1150 -98.38
0.1175 -58.34
0.12 53.92
0.1225 102.33
[𝑚𝑚] =
53.92
102.33
94.23
48.20
−49.77
−92.19
−98.38
−58.34
[𝑋𝑋] =
𝑉𝑉 cos 𝜃𝜃
𝑉𝑉 sin 𝜃𝜃
𝜔𝜔 = 2𝜋𝜋𝜋𝜋 = 2𝜋𝜋 50 = 100𝜋𝜋
With 8 measurements (1-cycle window)
t0
t1
t2
t3
t4
t5
t6
t7
[𝐴𝐴] =
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0 cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1 cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡2
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡3
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡4
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡5
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡6
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡7
cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡2
cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡3
cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡4
cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡5
cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡6
cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡7
=
0 1
1
2
1
2
1
1
2
0
−
1
2
−1
−
1
2
−
0
1
2
−1
−
1
2
0
1
2
with t0 = 0.0 s and t1 = 0.0025s … t7 =0.175 s
for matrix A
Example 3:
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-55-320.jpg)
![𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇
𝐴𝐴 −1
𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇
=
=
101.37
41.47
0 0.1768 0.25 0.1768 0 −0.1768 −0.25 −0.1768
0.25 0.1768 0 −0.1768 −0.25 −0.1768 0 0.1768
𝑉𝑉 = 𝑋𝑋1
2
+ 𝑋𝑋2
2 = 109 ⋅ 53 (𝑉𝑉) 𝑉𝑉(𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟𝑟) = 77.45 (V)
𝜃𝜃 = tan−1
𝑋𝑋2
𝑋𝑋1
= 22.250
Estimated phasor is 77.45∠22.25° (V)
This is correct the phasor.
𝑋𝑋 = 𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇
𝐴𝐴 −1
[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇
[𝑚𝑚]
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-56-320.jpg)
![Estimation of harmonic component (using Least Square Estimation)
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛 = 𝑉𝑉1 sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡𝑛𝑛 + 𝜃𝜃1 +𝑉𝑉2 sin 2𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡𝑛𝑛 + 𝜃𝜃2
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛 = 𝑉𝑉1 𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡n 𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐 𝜃𝜃1 + 𝑉𝑉1 sin 𝜃𝜃1 cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡n +𝑉𝑉2 𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 2𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡n 𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐 𝜃𝜃2 + 𝑉𝑉2 sin 𝜃𝜃2 cos 2𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡n
Say we need 2nd harmonic component to be estimated with fundamental
A =
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0 cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0 sin 2𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0 cos 2𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡0
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1 cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1 sin 2𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1 cos 2𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡1
⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮
⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮
sin 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡n−1 cos 𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡n−1 sin 2𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡n−1 cos 2𝜔𝜔𝑡𝑡n−1
𝑚𝑚 =
𝑣𝑣0
𝑣𝑣1
⋮
⋮
𝑣𝑣n
𝑉𝑉1 = 𝑋𝑋1
2
+ 𝑋𝑋2
2 V1rms =
𝑉𝑉1
2
𝜃𝜃1 = tan−1
𝑋𝑋2
𝑋𝑋1
𝑋𝑋 =
𝑉𝑉1 𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐 𝜃𝜃1
𝑉𝑉1 𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 𝜃𝜃1
𝑉𝑉2 𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐 𝜃𝜃2
𝑉𝑉2 𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠𝑠 𝜃𝜃2
𝑉𝑉2 = 𝑋𝑋3
2
+ 𝑋𝑋4
2 𝜃𝜃2 = tan−1
𝑋𝑋4
𝑋𝑋3
V2rms =
𝑉𝑉2
2
𝑋𝑋2
𝑋𝑋1
𝑋𝑋3
𝑋𝑋4
2nd harmonic
𝑋𝑋 = 𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇 [𝑚𝑚]
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-57-320.jpg)
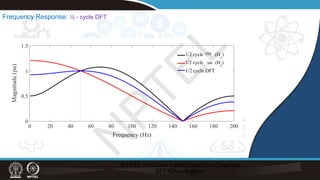
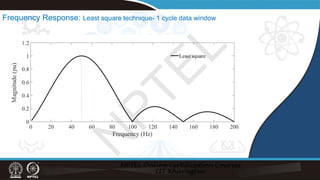
![Remarks
Least square estimation- provides phasors like DFT
It can manage with less number of samples for pure sinusoid
But with harmonics– it is able to filter out with 1-cycle of data
—similar to 1-cycle DFT
- We can incorporate harmonics also and get the magnitude and phase.
To reduce computation- matrix- [A] is fixed for a given window size and
signal sampling rate—so also the 𝐴𝐴𝑇𝑇𝐴𝐴 −1[𝐴𝐴]𝑇𝑇
∗∗∗∗∗
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-58-320.jpg)



![Frequency Response: 1-cycle DFT (8 points, 50 Hz signal)
Sample No. Delays Sin(-∆θ)
0 7 1.0 0
1 6
2 5 0 -1
3 4
4 3 -1 0
5 2
6 1 0 1
7 0
z-Transform of cosine filter
Hc(ω) =
1
4
[1.0𝑧𝑧7 +
1
2
𝑧𝑧6 + 0.0𝑧𝑧 −
1
2
𝑧𝑧4 − 1.0𝑧𝑧3 −
1
2
𝑧𝑧2 + 0.0𝑧𝑧1 +
1
2
𝑧𝑧0]
Hs(ω) =
1
4
[0.0𝑧𝑧7 −
1
2
𝑧𝑧6 − 1.0𝑧𝑧5 −
1
2
𝑧𝑧4 − 0.0𝑧𝑧3 +
1
2
𝑧𝑧2 + 1.0𝑧𝑧1 +
1
2
𝑧𝑧0]
Window N=8
∆θ =
2π𝑛𝑛
𝑁𝑁
̇
𝑉𝑉 =
2
𝑁𝑁
�
𝑛𝑛=0
𝑁𝑁−1
(𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁
𝑛𝑛
)
50 Hz signal, Sampling rate 0.4 kHz, ∆t=0.0025 s
z-Transform of sine filter
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-62-320.jpg)


![Frequency Response: 1-cycle DFT
Power System Relaying Committee IEEE working group report, Understanding microprocessor based technology applied to relaying,
Feb2004
L. Wang, Frequency Response of Phasor based microprocessor relaying algorithms, IEEETransactions on Power Delivery, vol 14, no.1,
1999, page 98
For DC component, 𝜔𝜔=0
Hc (0) =
1
4
1.0 +
1
2
+ 0.0 −
1
2
− 1.0 −
1
2
+ 0.0 +
1
2
= 0
Hs (0) =
1
4
[0.0 −
1
2
− 1.0 −
1
2
− 0.0 +
1
2
+ 1.0 +
1
2
] = 0
For second harmonic, 𝜔𝜔=2𝜋𝜋 2 50 =200𝜋𝜋
Hc (200𝜋𝜋) =0
Hs (200𝜋𝜋) = 0
x x
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-65-320.jpg)
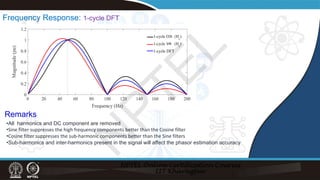
![Frequency Response: ½ - cycle DFT
Sample No. Delays Sin(-∆θ)
0 3 1.0 0
1 2
2 1 0 -1
3 0
Using z-Transform
Hc(ω) =
1
4
[1.0𝑧𝑧3 +
1
2
𝑧𝑧2 + 0.0𝑧𝑧1 −
1
2
𝑧𝑧0]
Hs(ω) =
1
4
[0.0𝑧𝑧3 −
1
2
𝑧𝑧2 − 1.0𝑧𝑧1 −
1
2
𝑧𝑧0]
̇
𝑉𝑉 =
2
𝑁𝑁
2
�
𝑛𝑛=0
𝑁𝑁
2
−1
𝑣𝑣𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗
2𝜋𝜋
𝑁𝑁
𝑛𝑛
∆θ =
2π𝑛𝑛
𝑁𝑁
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-67-320.jpg)



![Presence of Decaying DC in current signal:
v(t)
R L
v t = V sin ωt + θ
i t = 𝐼𝐼𝑚𝑚[sin ωt + θ − θz − sin θ − θz e−
t
τ]
Here, θz = tan−1(
X
R
) =tan−1(
ωL
R
)
θ − θz = nπ ; zero transient, n=0,1,2,3..
θ − θz =
nπ
2
; maximum transient, n=1,3,5..
Thus, for different faults, fault inceptions, the relay will see different amount of decaying DC
The decaying DC will result in larger magnitude of phasor, leading to incorrect relay
decision
i t
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-73-320.jpg)
![Solution: Elimination of Decaying DC using Mimic Filter :
i(t)
R’ L’
Let decaying dc, i t = e−
t
τ
Vo s = sL′
+ R′
I s
ℒ−1 Vo(s) = ℒ−1[
sL′+R′
s+
1
τ
]
= L′
ℒ−1
s+
1
𝜏𝜏
s+
1
τ
= L′
u(t)
𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤𝑤, 𝜏𝜏 =
L′
R′
Vo(t)
Mimic impedance where u(t)– unit impulse
This implies, decaying DC in the output has vanished
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-74-320.jpg)

![Elimination of Decaying DC using Digital Mimic Filter :
• With a mimic circuit consisting of R-L in impedance form K(1+sτ), then the exponentially decaying component at the output will
vanish, provided its time constant is equal to τ.
• The differentiator circuit, as with s-term, can be emulated by digital FIR filter: (1-z-1)
• The impedance can be represented as: K[(1+ τ) - τ z-1]
• K has to be set in such a way that, at rated frequency (50/60 Hz), the filter gain will be 1.
• The corresponding gain
f= 50/60 Hz
Gain(f) = |K[(1+ τ)- τ𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗𝑗𝑗∆𝑡𝑡
]| = 1
• Solving this equation for K, we obtain 𝐾𝐾2
=
1
1 + τ − τ cos 2𝜋𝜋/𝑁𝑁 2 + τ sin 2𝜋𝜋/𝑁𝑁 2
• Thus using mimic filter, the current sample at pth instant can be obtained as,
𝑖𝑖′ 𝑝𝑝 = 𝐾𝐾 1 + τ ∗ 𝑖𝑖 𝑝𝑝 − τ ∗ 𝑖𝑖(𝑝𝑝 − 1)
N = number of samples per cycle
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-76-320.jpg)
![Fault current response using Digital Mimic Filter with phase shift compensation:
𝜙𝜙𝑠𝑠𝑠 = tan−1
𝜏𝜏 sin ⁄
2𝜋𝜋 𝑁𝑁
1 + 𝜏𝜏 − 𝜏𝜏 cos ⁄
2𝜋𝜋 𝑁𝑁
Phase shift with mimic filter,
𝜏𝜏 = decaying time constant
N = number of samples per cycle
G. Benmouyal, "Removal of DC-offset in current waveforms using digital mimic filtering," IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 621-630, April
1995.
Gain(f) = |K[(1+ τ)- τ𝑒𝑒−𝑗𝑗𝑗𝑗∆𝑡𝑡
]| = 1
N
P
T
E
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2material-230718082216-0c63940c/85/Week-2-Material-pdf-77-320.jpg)



