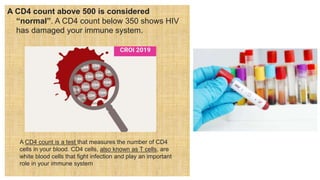
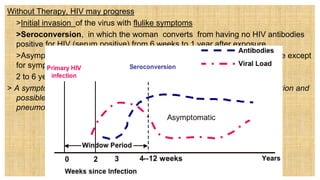
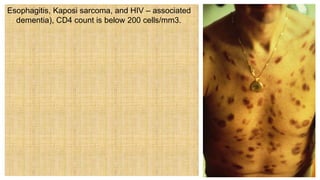
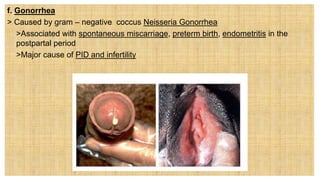
1. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) range in severity from easily treated infections like trichomoniasis to life-threatening infections like HIV.
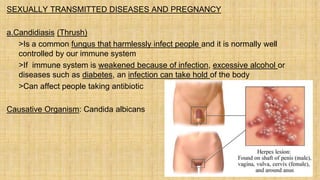
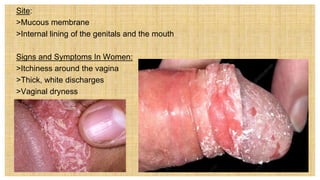
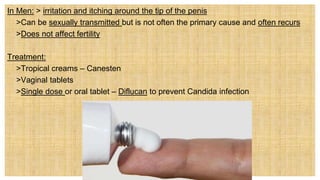
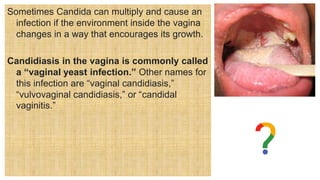
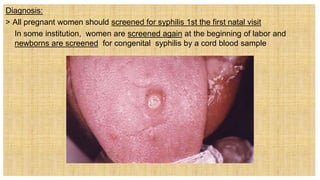
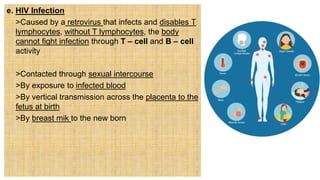
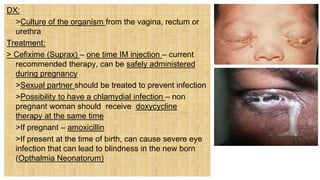
2. The document discusses several common STIs that can affect pregnant women including candidiasis, chlamydia, syphilis, human papillomavirus, and HIV.
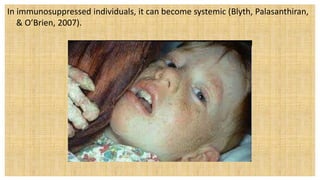
3. Left untreated, STIs can cause complications for both the mother and fetus, including pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, spontaneous abortion, preterm labor, stillbirth, and congenital infections in newborns. Proper screening and treatment are important for preventing adverse outcomes.