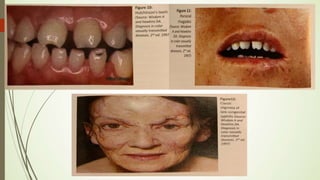
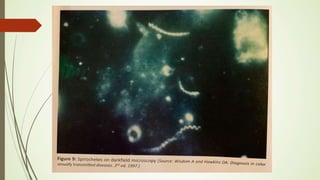
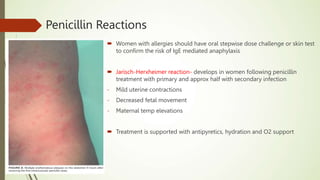
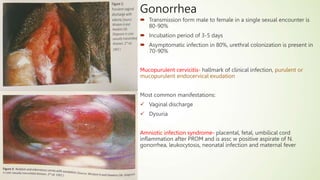
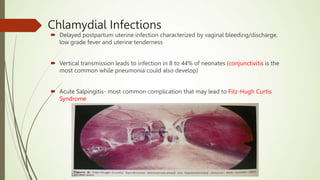
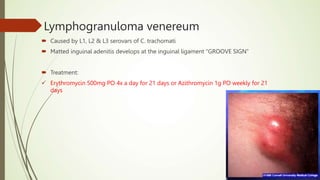
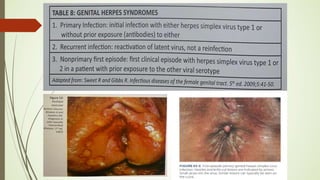
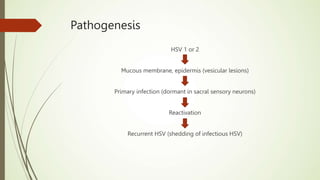
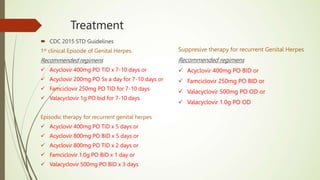
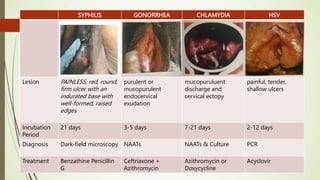
This document discusses sexually transmitted infections including syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and HSV. It provides details on the pathogenesis, transmission, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of each STI. For syphilis, gonorrhea and chlamydia, it outlines the recommended screening, diagnostic tests including NAAT and culture, and CDC-recommended treatment regimens for pregnant and non-pregnant patients. Complications of untreated STIs for both mother and fetus are also discussed.