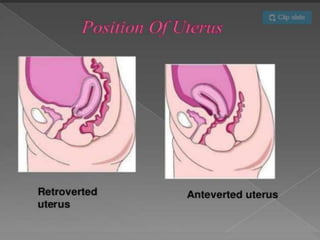
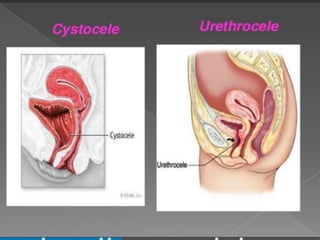
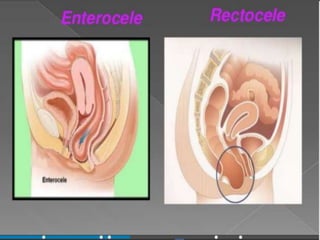
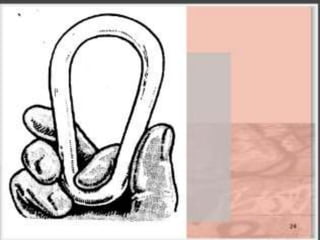
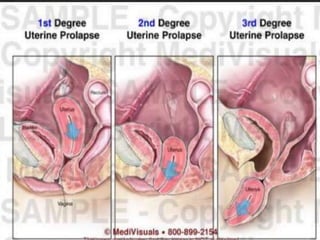
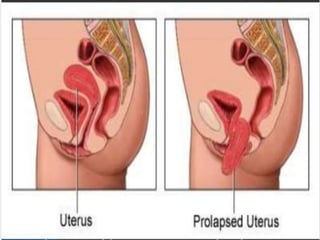
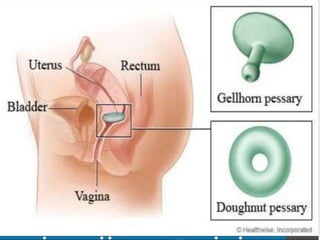
Uterine prolapse occurs when the uterus descends from its normal position due to weakened pelvic muscles and tissues. It is often caused by pregnancy, childbirth, obesity, menopause, or chronic conditions like coughing or constipation. Symptoms range from a feeling of heaviness to organs protruding from the vagina. Treatment options include pelvic floor exercises, pessaries, hormone therapy, and surgery to repair damaged tissues or remove the uterus. Surgical risks include infection, incontinence, and prolapse recurrence.








![PREVENTIVE
Adequate antenatal and intranatal care:
To avoid injury to the supporting structures during
vaginal delivery either spontaneous or instrumental
Adequate postnatal care: To encourage early
ambulation and pelvic floor exercises[kegel exercise]
during puerperium .
General measures : To avoid strenuous activities,
chronic cough , constipation and heavyweight lifting.
Limiting and spacing pregnancies help avoid pelvic
relaxation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uterineprolapse-190430145448/85/Uterine-prolapse-12-320.jpg)




![IMMEDIATE
Hemorrhage within 24hours following
surgery[primary]or between 5th and 10th day
[secondary].
Retention of urine.
Infection leading to cystitis.
Wound sepsis.
Vault cellulits .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uterineprolapse-190430145448/85/Uterine-prolapse-18-320.jpg)
![ Dyspareunia .
Recurrence of prolapse.
Vesicovaginal fistula[VVF] following bladder injury.
Cervical stenosis – hematometra .
Infertility.
Cervical incompetency.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uterineprolapse-190430145448/85/Uterine-prolapse-19-320.jpg)