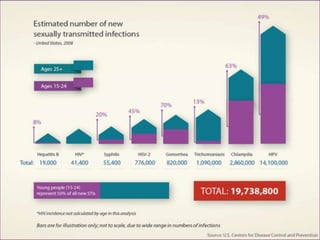
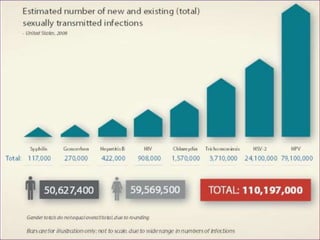
This document provides an overview of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), including:
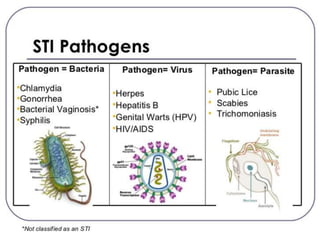
STDs are passed through sexual contact and can also spread through other means like childbirth or blood transfusions. Common pathogens that cause STDs include bacteria, parasites, and viruses. STDs have an array of symptoms and are diagnosed through tests of blood, urine, or fluid samples. While treatment involves antibiotics or antiviral drugs, prevention relies on screening and reducing risk factors like unprotected sex or multiple partners. The document outlines the types of STDs, their effects on both men and women, risk factors, and resources for further information.