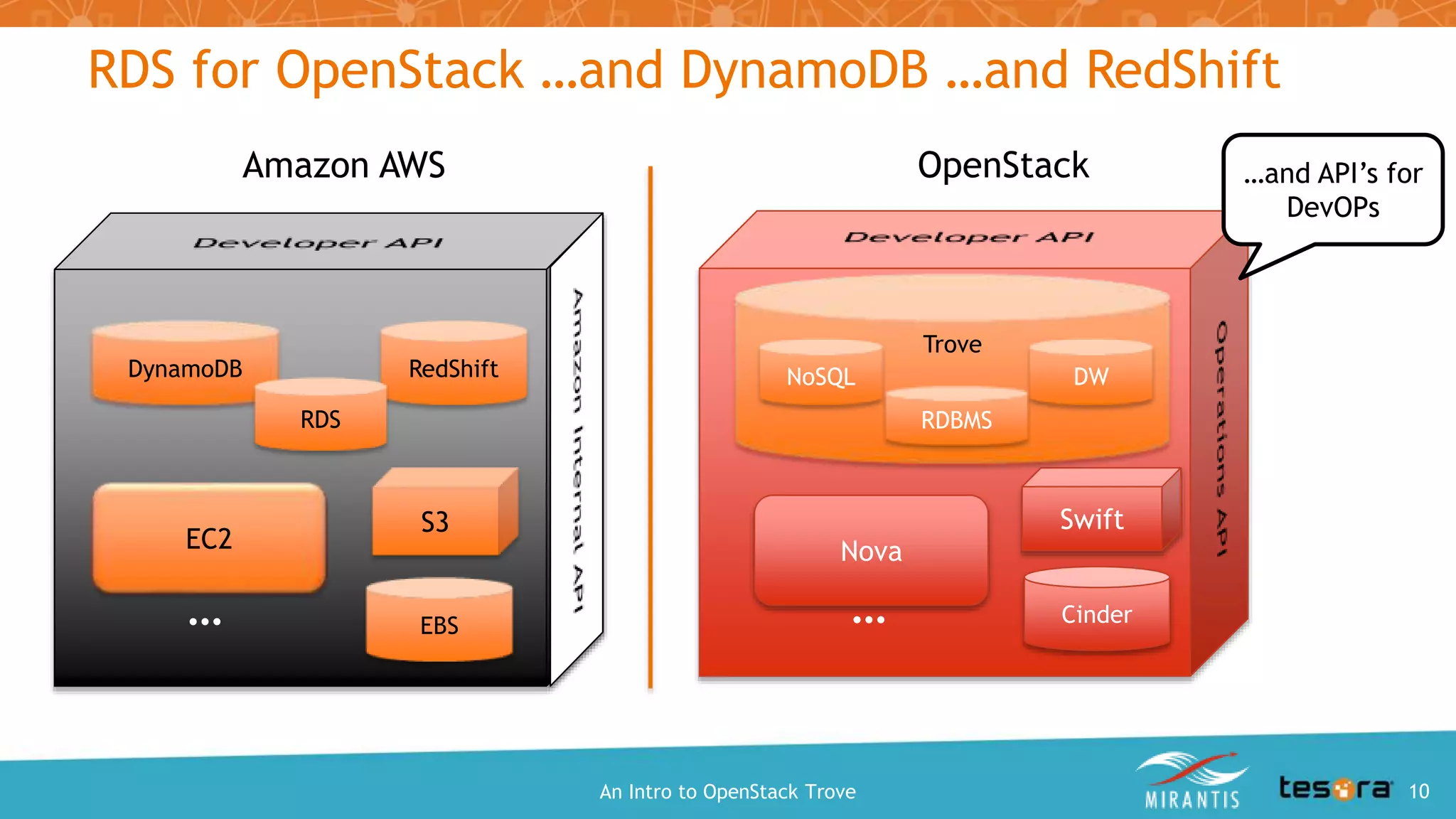
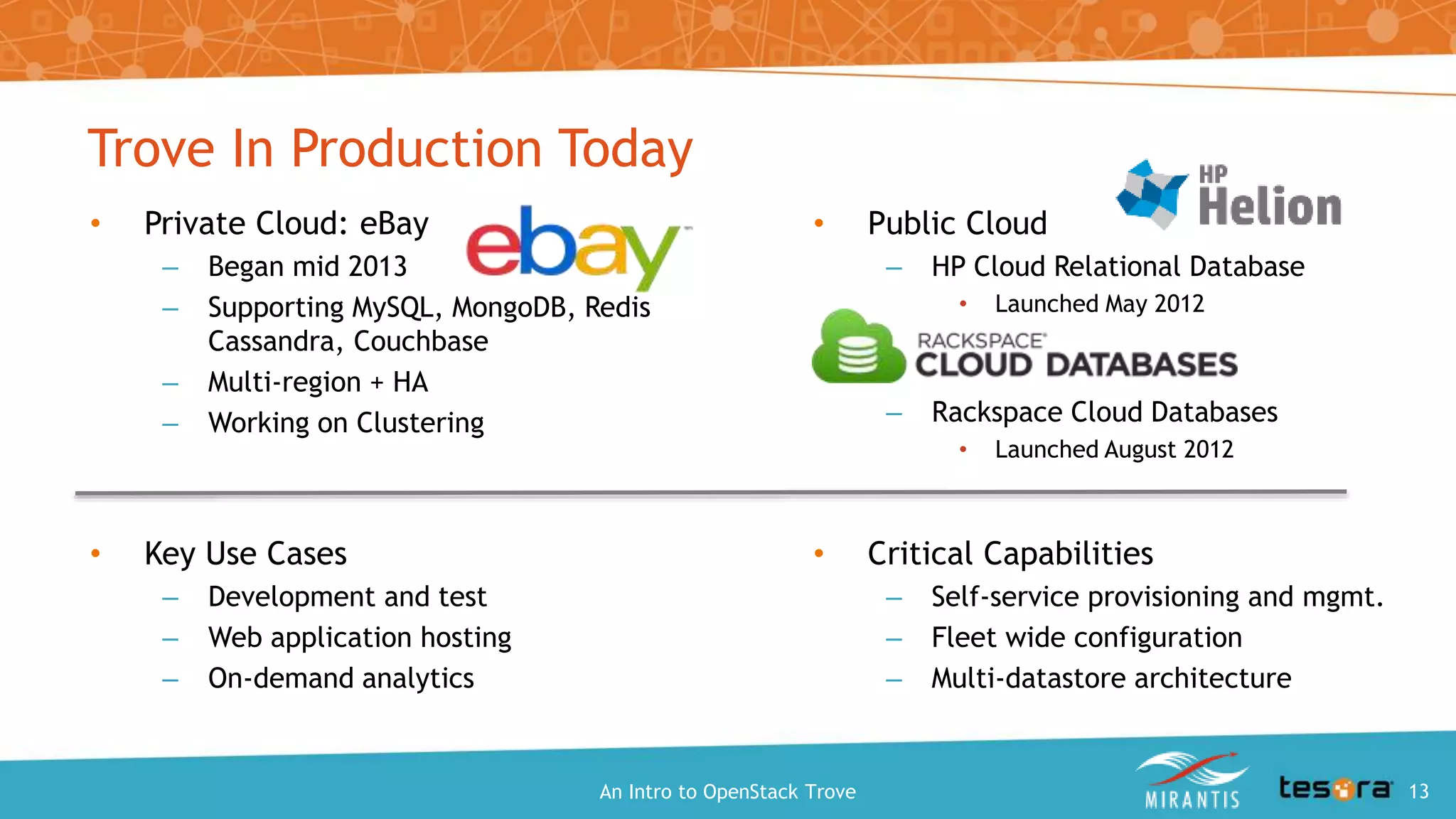
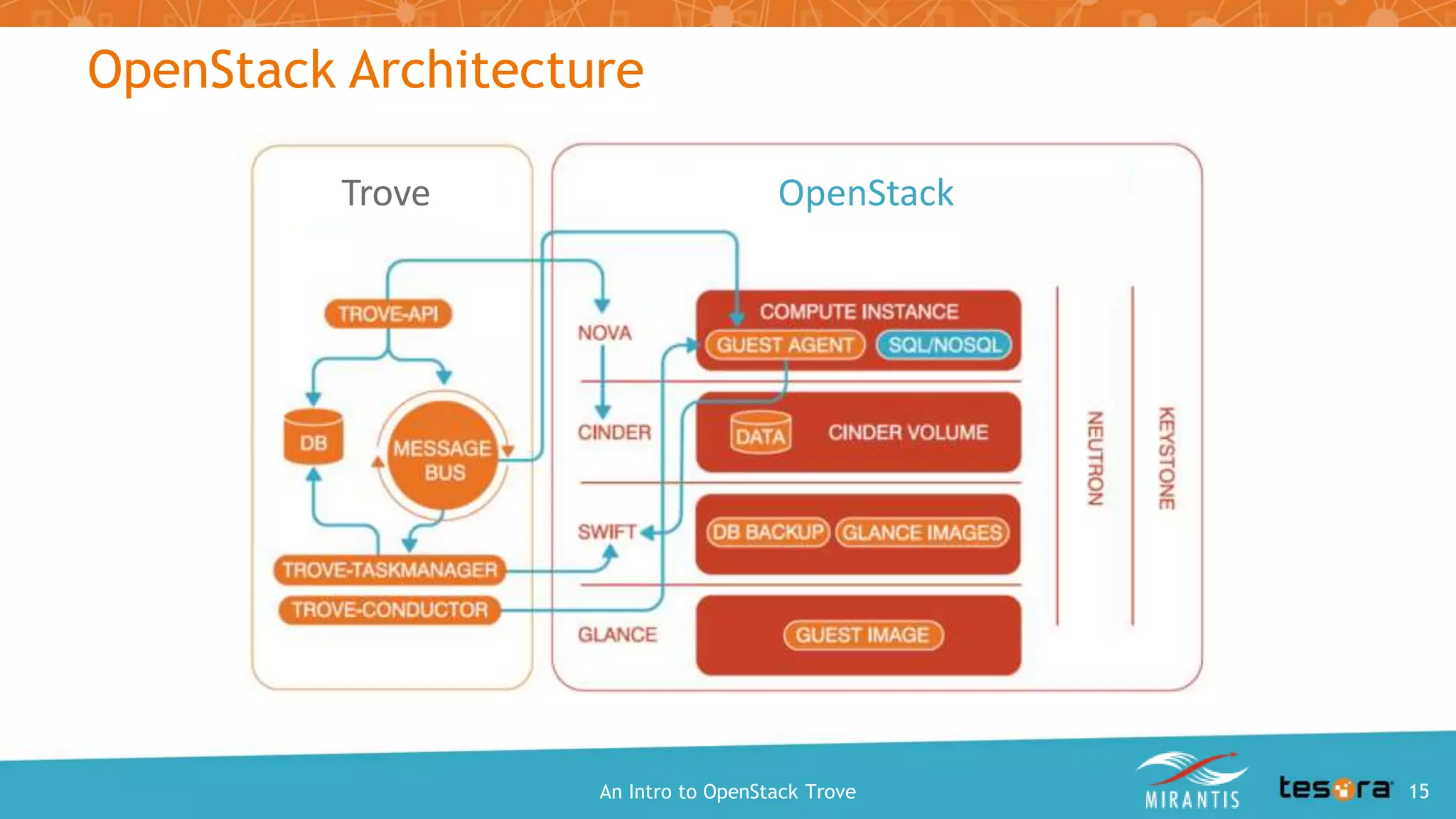
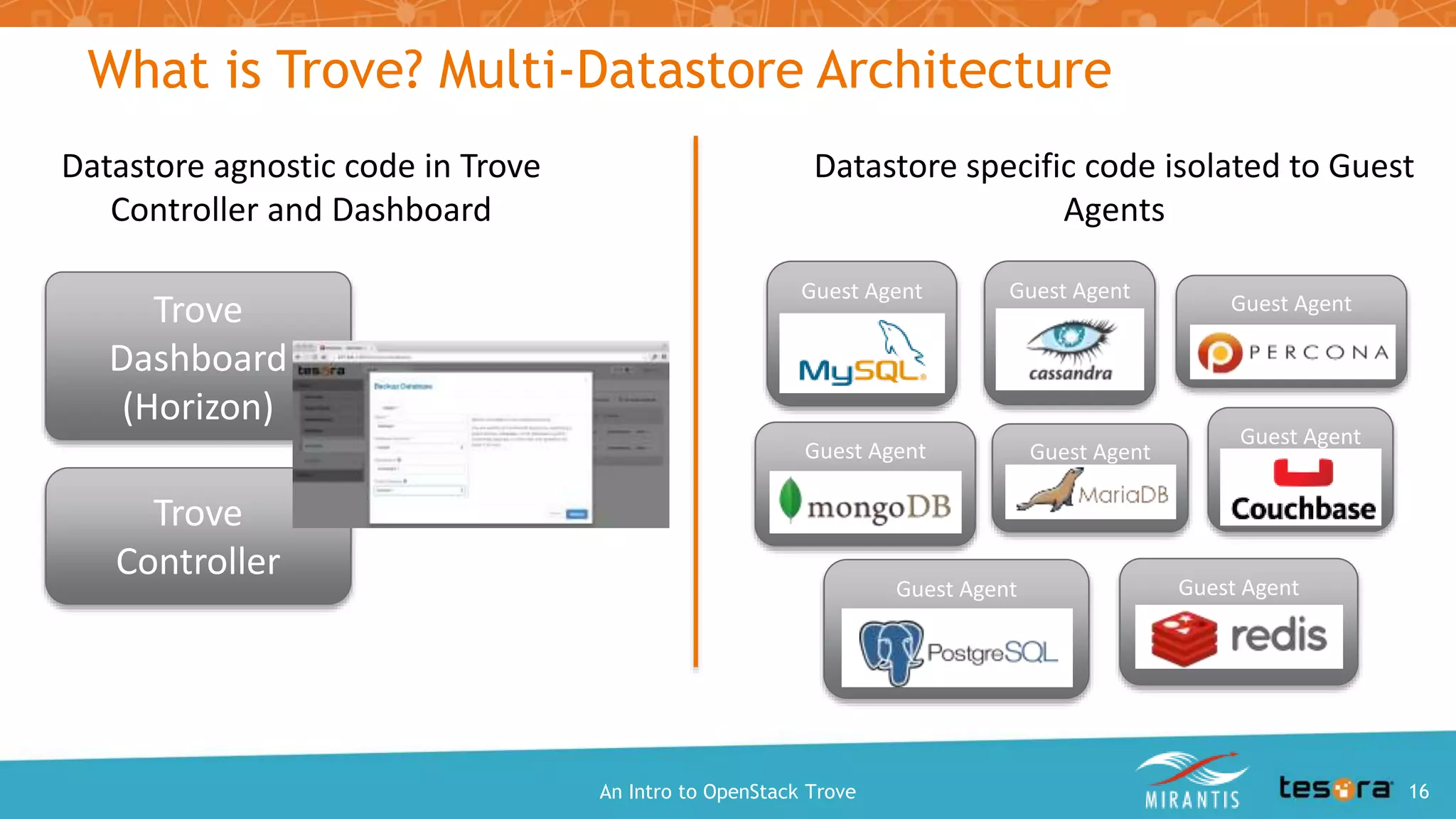
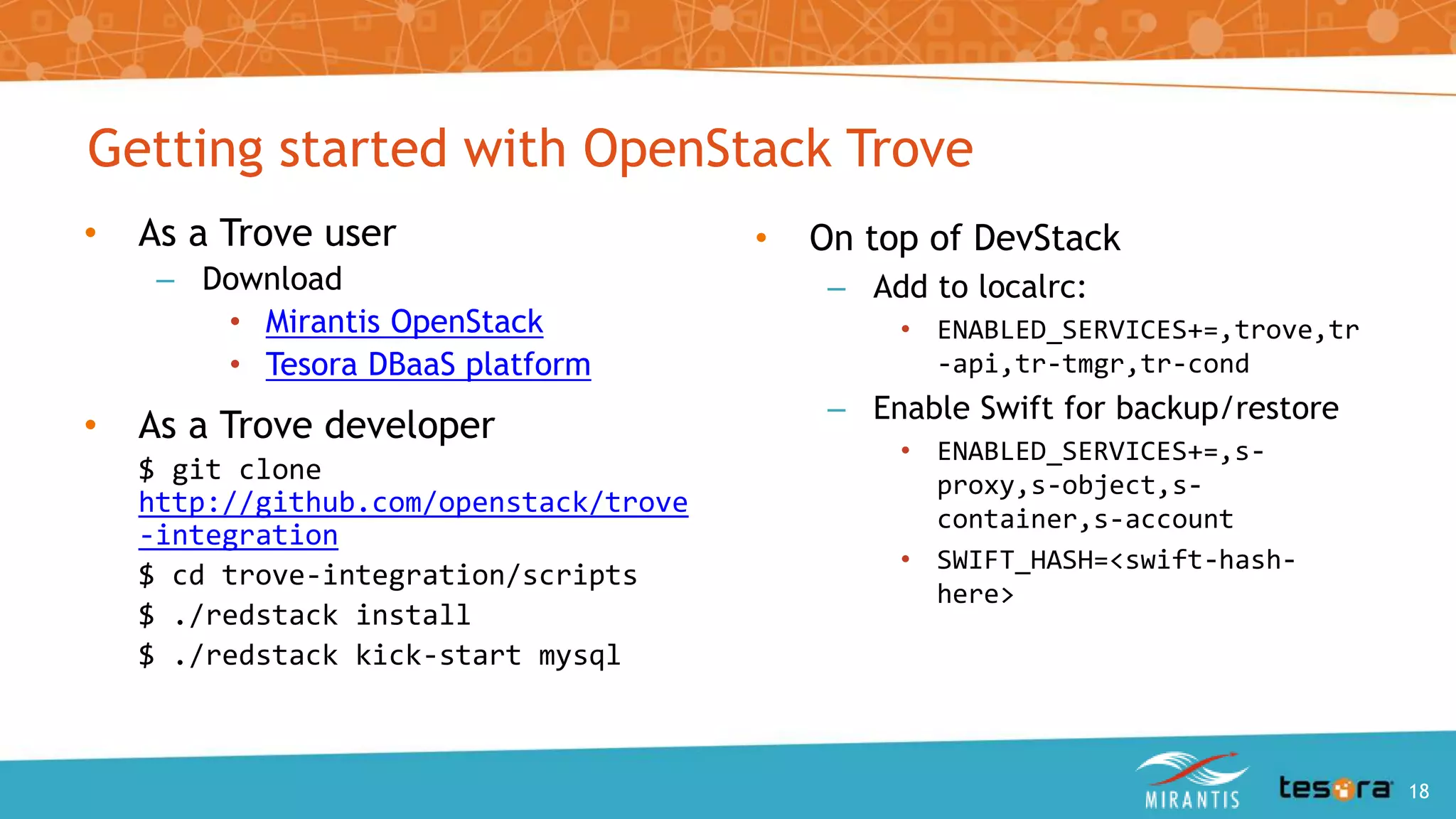
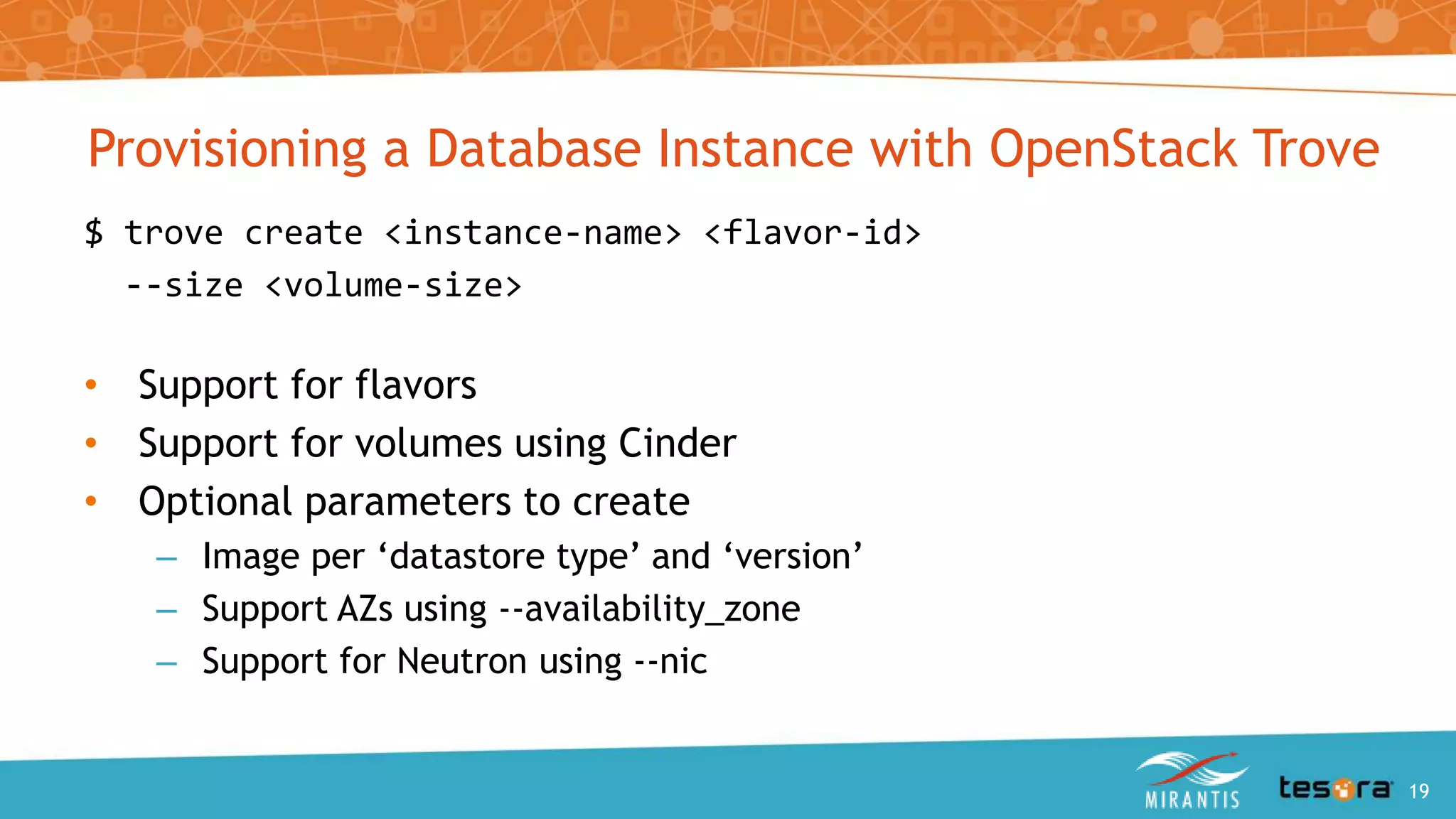
This document provides an introduction and overview of OpenStack Trove, which is a Database as a Service (DBaaS) component of OpenStack. It discusses what OpenStack Trove is, its architecture, supported databases, features like provisioning, backups and replication. It also covers getting started with Trove and the roles of Mirantis and Tesora in providing enterprise-hardened Trove solutions.