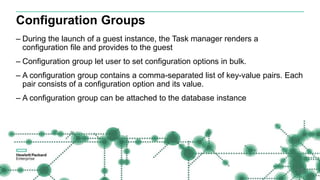
This document provides an overview of OpenStack Trove:
- Trove is a database as a service that provisions and manages relational and non-relational databases. It exposes a REST API and stores data in an infrastructure database.
- Key components include the Trove API service, Task Manager, and Conductor service. The Task Manager handles operations like instance creation while the Conductor updates status in the infrastructure database.
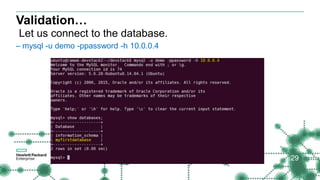
- The document then covers installing and configuring Trove on DevStack, including validation steps to create a database instance, database, and user. It also discusses debugging techniques like checking logs and running commands with the debug option.