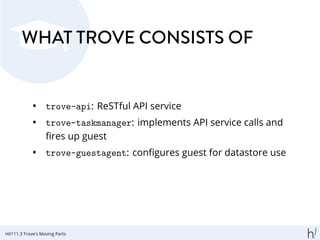
The document provides an overview of OpenStack's database as a service (DBaaS) called Trove, detailing its history, architecture, key components, and operational instructions. Trove allows users to manage various database systems within the OpenStack framework, shifting the control of infrastructure to the cloud. It includes functionalities for creating instances, databases, and managing configurations effectively.





































![CREATING A USER AND
ENABLING DATABASE ACCESS
trove user-create
<instanceid >
<username >
<password >
[--host=<host >]
[--databases=<db1>,<db2>,...]
HX111.4 Working With Trove](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perconalive2014-slides-trove-140416030950-phpapp01/85/Hands-On-Trove-Database-as-a-Service-in-OpenStack-42-320.jpg)
![GRANTING USER ACCESS
trove user-grant-access
<instanceid >
<username >
<password >
<db1>,<db2>,...
[--host=<host >]
HX111.4 Working With Trove](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perconalive2014-slides-trove-140416030950-phpapp01/85/Hands-On-Trove-Database-as-a-Service-in-OpenStack-43-320.jpg)

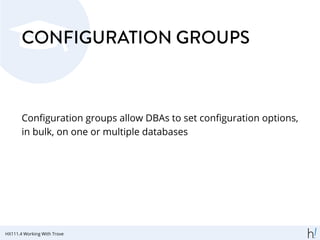
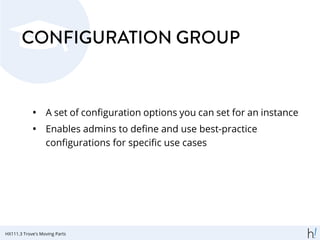
![CREATING A CONFIGURATION
GROUP
trove configuration -create <name>
'{ <values > }'
[--description <description >]
HX111.4 Working With Trove](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perconalive2014-slides-trove-140416030950-phpapp01/85/Hands-On-Trove-Database-as-a-Service-in-OpenStack-46-320.jpg)











