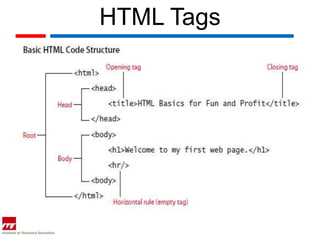
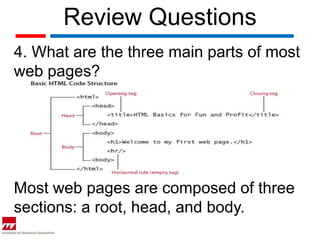
HTML is the backbone of the web and is used to create structured web pages. It uses tags denoted by < > to designate formats, styles, and logical/structural information. The basic structure of an HTML document includes the <html>, <head>, and <body> tags. HTML5 introduces new semantic tags like <header> and <footer> and supports native playback of video and audio with the <video> and <audio> tags. HTML documents can be created and edited using simple text editors.