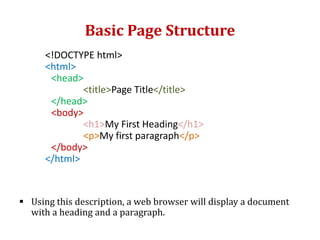
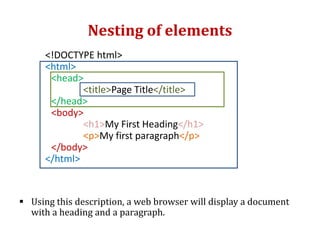
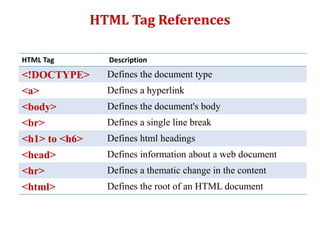
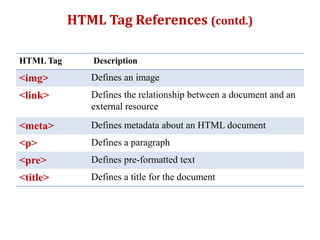
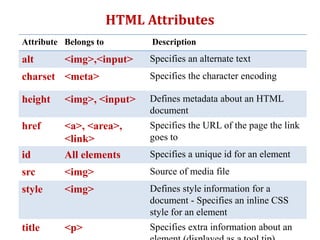
HTML is a markup language used to define the structure and layout of web pages. HTML uses tags to label different parts of a web page like headings, paragraphs, links, and images. The basic structure of an HTML page includes <html>, <head>, and <body> tags. Common HTML tags are <h1> for main headings, <p> for paragraphs, <a> for links, <img> for images, and <div> and <span> for dividing content. HTML documents are displayed in web browsers which use the HTML tags to render the page elements properly.