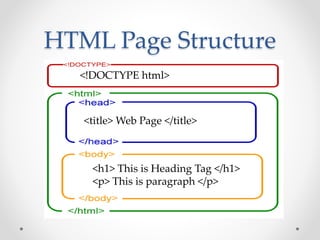
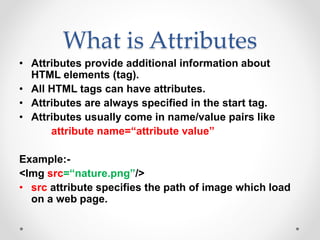
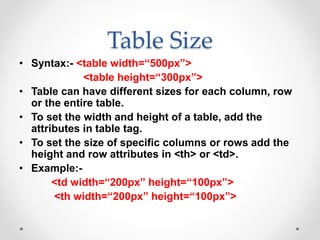
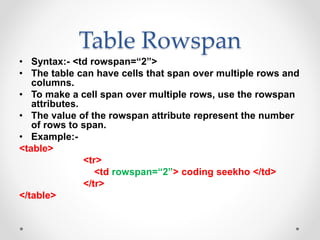
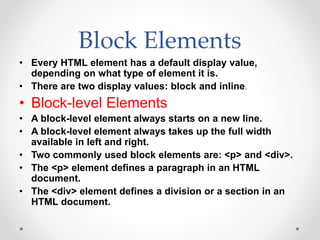
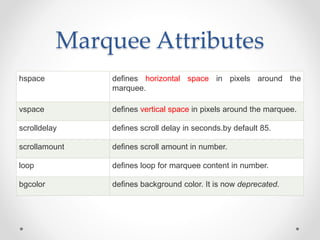
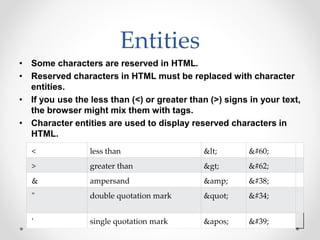
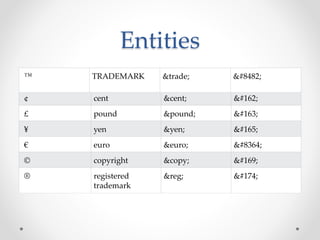
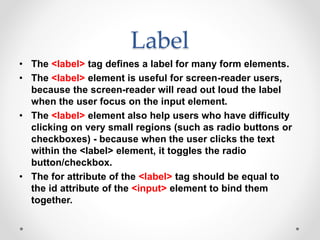
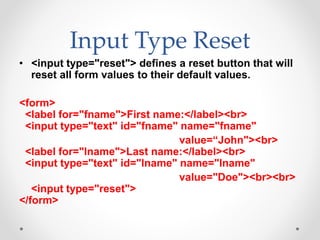
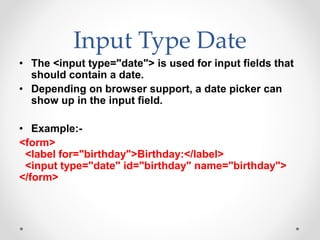
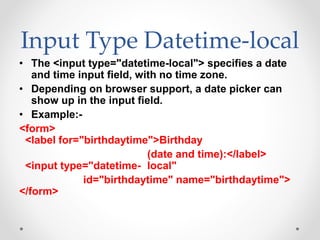
Tim Berners-Lee invented HTML in 1991 to define the structure of web pages. HTML uses tags like <h1> and <p> to define headings and paragraphs. Browsers read HTML tags and display web page content but not the tags themselves. HTML documents have a basic structure including <html>, <head>, <title>, and <body> tags. Common text formatting tags include <b>, <i>, <u> for bold, italic, and underline.