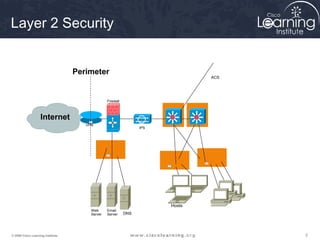
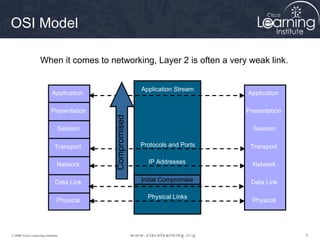
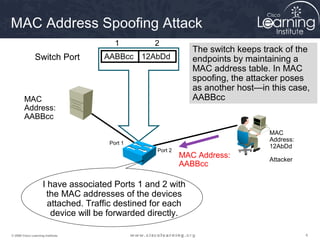
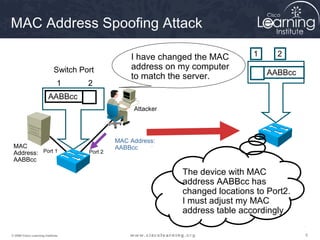
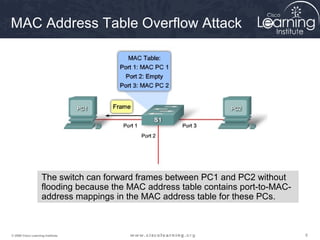
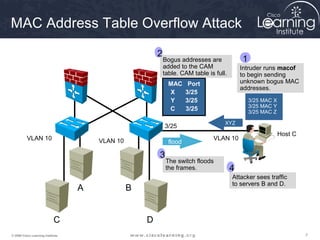
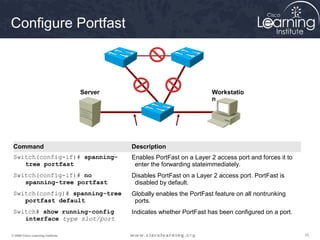
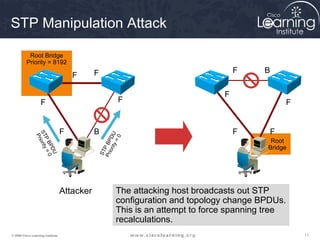
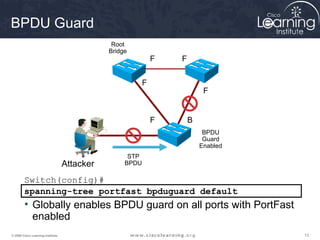
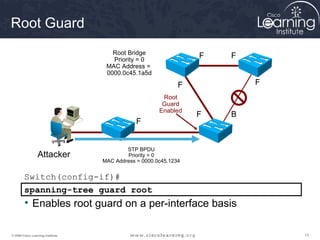
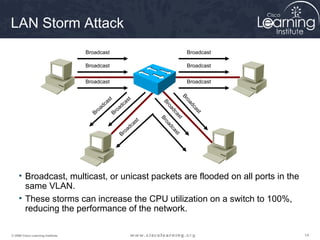
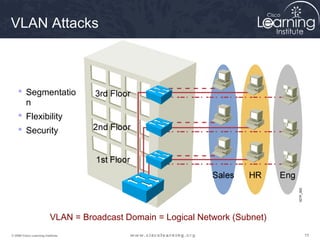
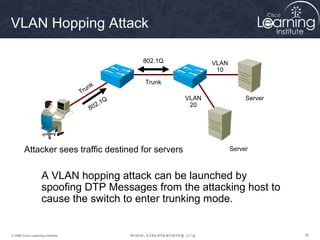
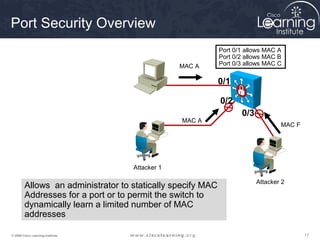
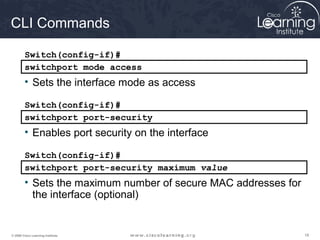
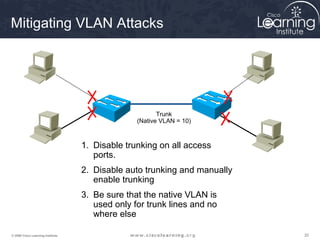
This document discusses techniques for securing the local area network layer 2, including mitigating MAC address spoofing, STP manipulation, broadcast storms, and VLAN hopping attacks. It provides examples of how these attacks work and recommends configuration options like port security, BPDU guard, root guard, and controlling trunking to enhance network security. Specific commands are shown to enable these security features on Cisco switches to prevent common layer 2 attacks.