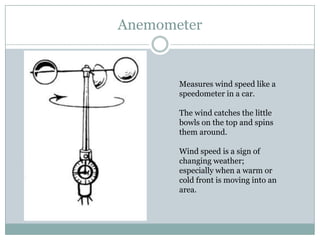
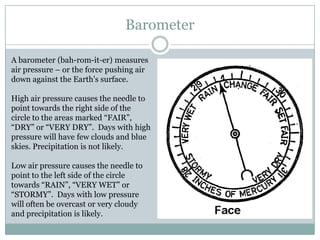
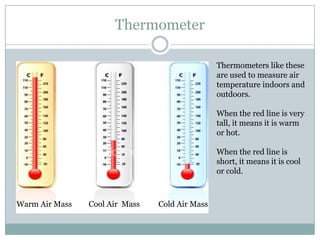
This document describes several common weather instruments and what each measures. An anemometer measures wind speed, a barometer measures air pressure, a hygrometer measures humidity, a rain gauge measures precipitation, a thermometer measures temperature, and a wind vane measures wind direction. These tools are important for collecting weather data and understanding current and changing conditions.