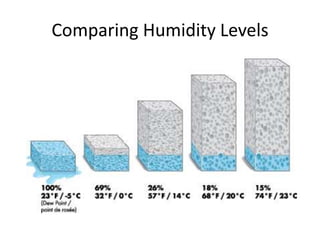
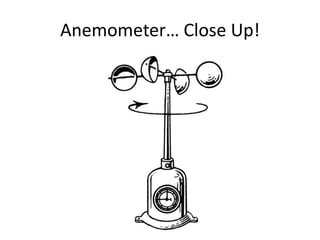
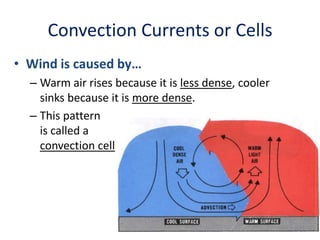
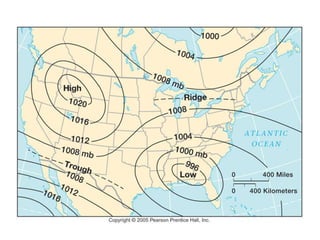
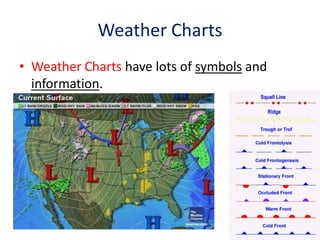
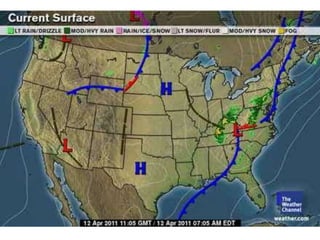
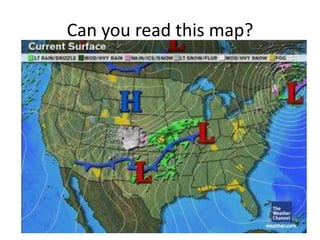
The document explains various weather instruments, including thermometers, psychrometers, anemometers, and barometers, detailing how each measures temperature, humidity, wind speed, and air pressure. It outlines concepts like convection currents, isobars, and pressure systems, emphasizing their roles in weather forecasting. Additionally, it discusses interpreting weather charts and maps to predict weather conditions.