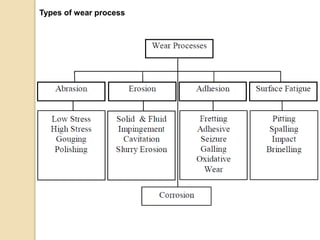
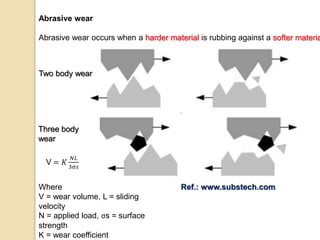
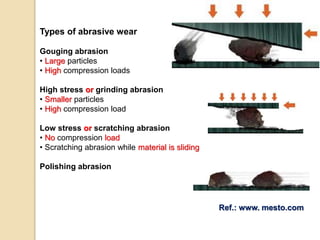
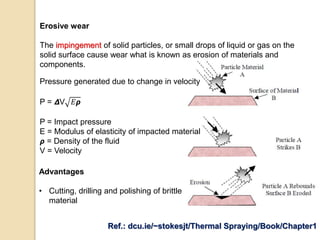
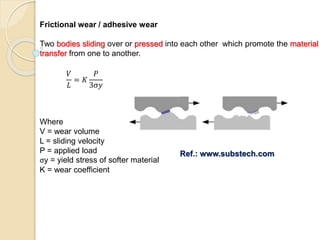
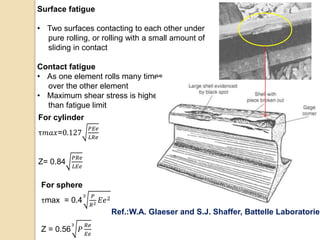
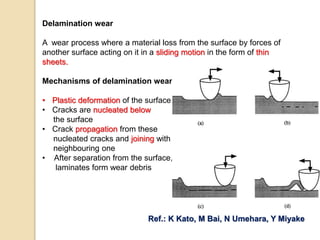
Wear occurs when two solid surfaces are in contact and sliding or rolling against each other, resulting in material removal from one or both surfaces. The main factors that affect wear are surface geometry, applied load, sliding velocity, environment, material properties, and lubricant properties. There are several types of wear processes, including abrasive, erosive, frictional, surface fatigue, delamination, and chemical wear. Abrasive wear involves harder materials rubbing against softer ones, while erosive wear is caused by particle or fluid impingement. Frictional wear involves material transfer between sliding surfaces. Surface fatigue occurs from repeated rolling and sliding contact stresses. Delamination and chemical wear remove material in thin sheets or through environmental reactions, respectively