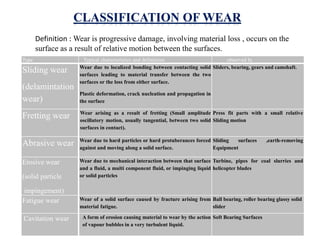
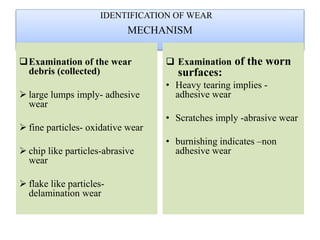
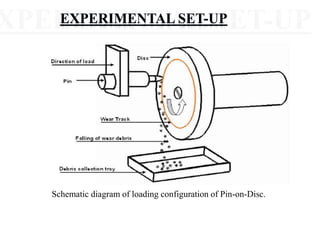
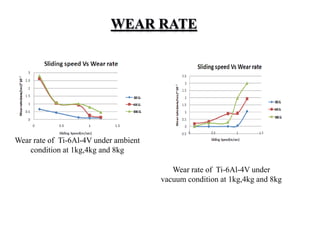
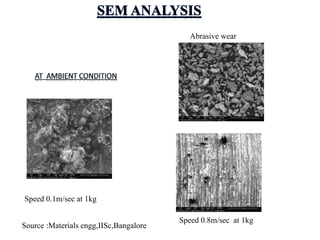
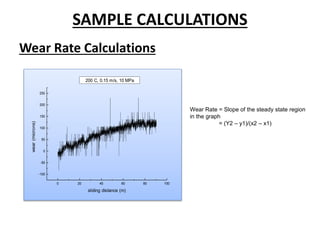
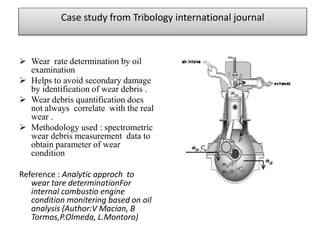
This presentation discusses various types of wear measurement. It defines wear as progressive damage involving material loss that occurs on surfaces due to relative motion. The types of wear discussed include sliding wear, fretting wear, abrasive wear, erosive wear, fatigue wear, and cavitation wear. The Archard wear equation relating wear volume to load and material properties is presented. Methods for identifying wear mechanisms by examining wear debris and worn surfaces are described. A pin-on-disc apparatus for measuring wear rates and a case study using oil analysis to determine wear rates are also summarized.