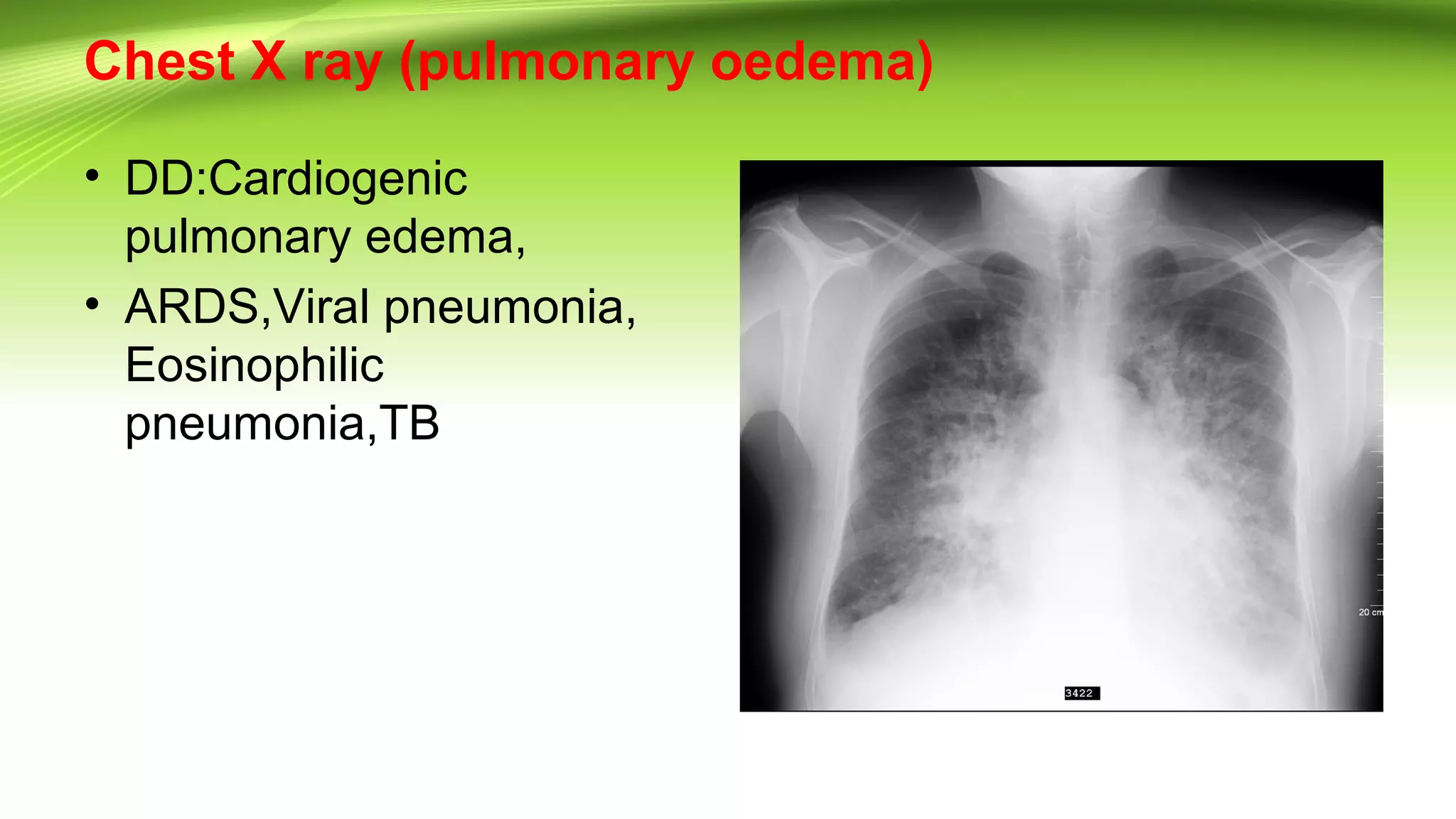
Pulmonary edema is fluid accumulation in the lungs that impairs gas exchange and can cause respiratory failure. Cardiac failure occurs when the heart cannot maintain adequate cardiac output or can only do so with elevated filling pressure. Left ventricular failure can be systolic, with reduced contractility, or diastolic, with impaired relaxation. Common causes include coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, and valvular heart disease. Treatment involves oxygen, diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and management of triggers like infections, arrhythmias, and electrolyte imbalances.