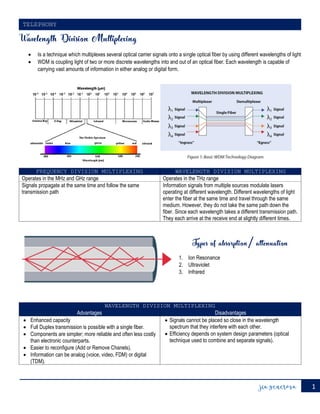
Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) is a technique that multiplexes multiple optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths of light. Each wavelength can carry vast amounts of digital or analog information. In WDM, information signals from multiple sources modulate lasers operating at different wavelengths. The different wavelength signals enter the fiber at the same time through the same medium but take different transmission paths and arrive at the receiver end at slightly different times. WDM has advantages like enhanced capacity, full duplex transmission with a single fiber, and simpler more reliable components compared to electronic counterparts. However, the signals cannot be placed too close in wavelength spectrum to avoid interference.
![2Jia GENEROSA
CWDM vs. DWDM
Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing
• Multiplex few onto a single fiber
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
• Multiplex many onto a single fiber.
• Spacing between adjacent frequency is less than 200 GHz.
Example 1.] At 1550 nm and 100 GHz frequency separation, the wavelength separation is approximately 0.8 nm. Three adjacent
wavelengths each separated by 100 GHz correspond to 1550 nm, 1549.2 nm and 1548.4 nm.
Components
1. Wavelength-Division Multiplexers and Demultiplexers
a. Multiplexer or Combiners
✓ Combine signals with different wavelengths in a way that allows them to pass through a single optical fiber
without interfering with one another.
b. Demultiplexers or Splitters
✓
2. Wavelength Division Data Drop
✓ Similar to demultiplexers or multiplexers except they are located at intermediate points in the system.
✓ Devices that separate a wavelength from a fiber cable.
3. Wavelength Division Routers
✓ Directs signals of a particular wavelength to a specific destination while not separating all the wavelengths
present in the cable.
4. Wavelength Division Couplers
a. Diffraction Grating Prism
✓ Wavelength are separated by refracting them at different angles.
b. Dichrofilter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/telephonywavelengthdivisionmultiplexing-200330031156/85/Wavelength-Division-Multiplexing-Wayne-Tomasi-2-320.jpg)
