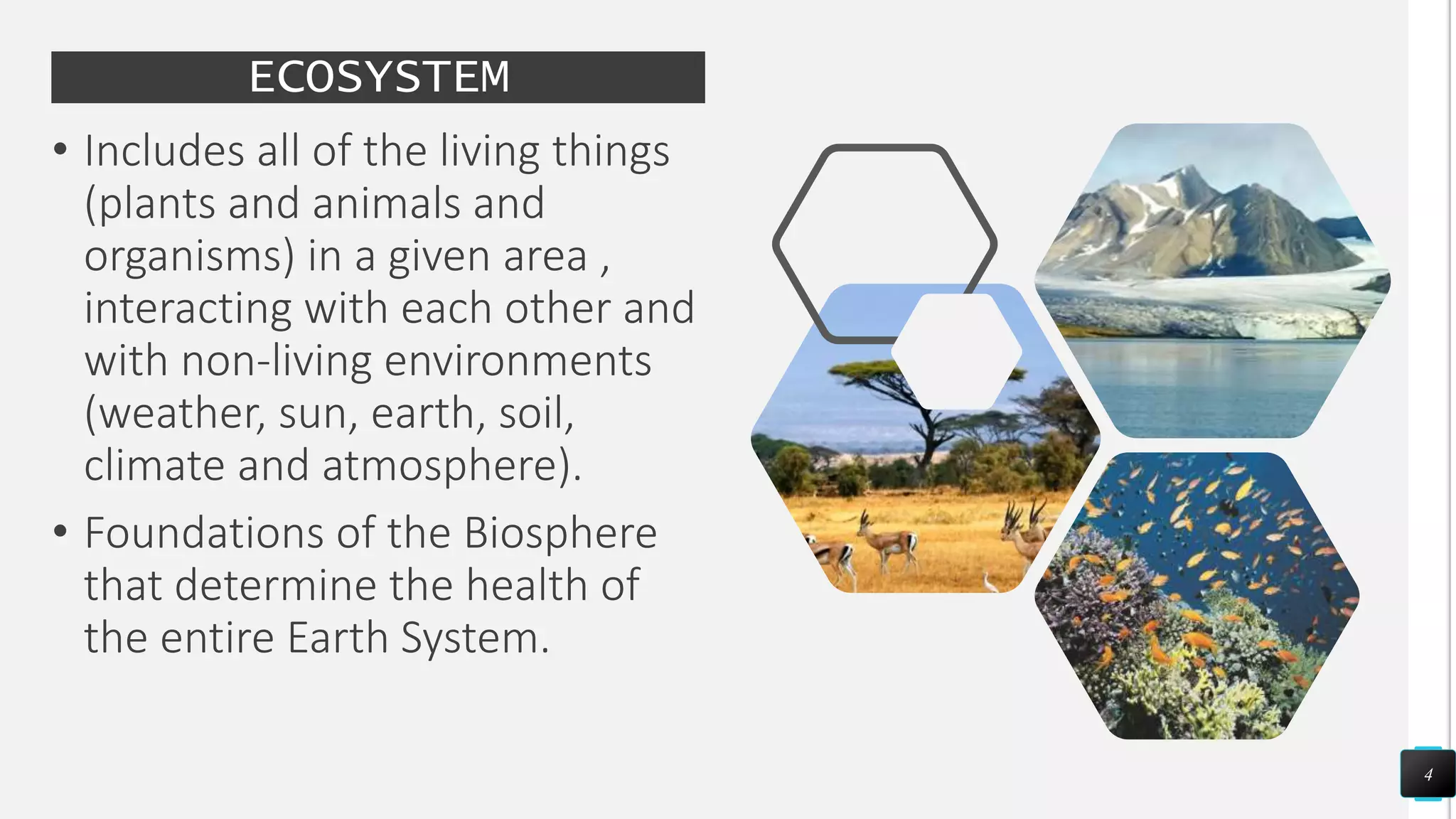
An ecosystem includes all living and non-living components in a given area that interact. It consists of organisms like plants and animals, as well as non-living factors like climate and soil. There are different types of ecosystems like deserts, coral reefs, and urban areas. Organisms within ecosystems interact through competition, predation, and symbiosis. Competition occurs between organisms seeking the same resources, predation involves one organism consuming another, and symbiosis describes long-term interactions that can be mutualistic, parasitic, or commensal. Biomes are large areas with similar climates that support certain global plant and animal communities. Climate strongly influences the formation of different biomes like forests and grasslands.