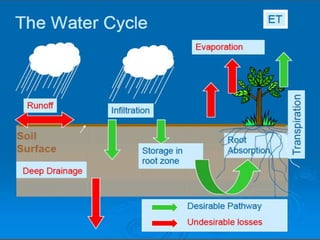
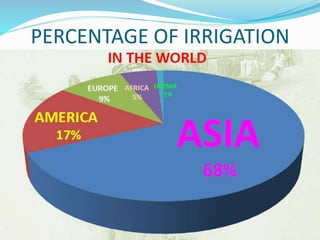
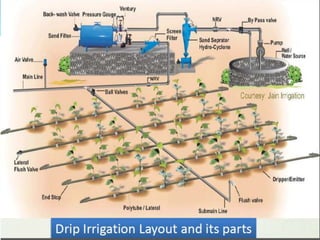
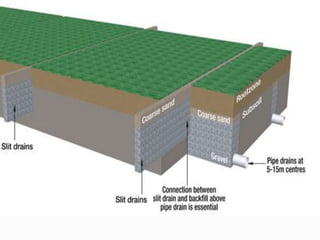
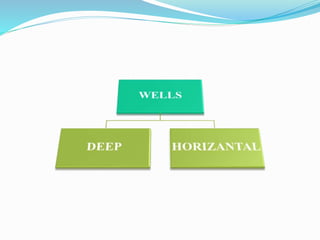
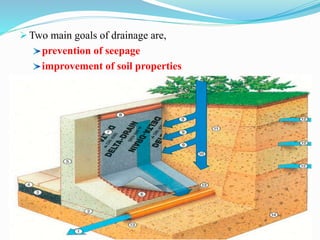
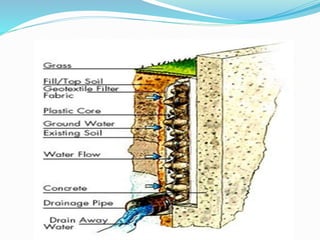
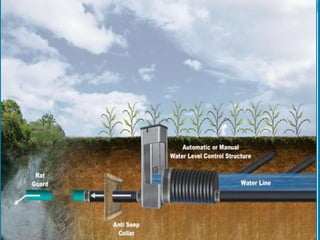
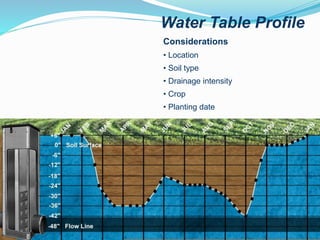
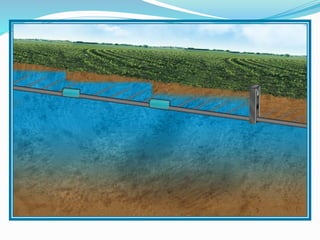
This document provides information about irrigation, including its definition, purposes, history, types, and components. It defines irrigation as the artificial application of water to soil, usually used to assist growing crops in dry areas or during low rainfall. Ancient Mesopotamian engineers built elaborate dam and canal systems to distribute water for agricultural and domestic needs. Modern irrigation systems include surface, center pivot, lateral move, and localized drip/sprinkler methods. Proper drainage of excess water is also important for soil health and equipment access. The document discusses drainage system design considerations based on soil, water table, and crop factors.