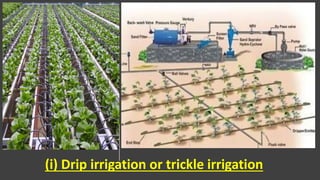
Surface irrigation methods like furrow and border strip irrigation distribute water over soil surfaces using gravity. Furrow irrigation involves making small channels along slopes for water to flow down, while border strip irrigation uses longer borders oriented with slopes. These methods are suited for row crops but often result in non-uniform water distribution and issues like waterlogging or salinity if not properly managed through drainage and controlling water amounts. Drip and sprinkler irrigation use pipes and emitters to supply water directly to plant roots, allowing more control and efficiency. The appropriate irrigation method depends on factors like crop type, water source, and land characteristics.