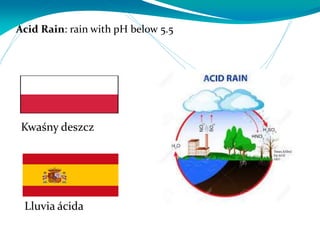
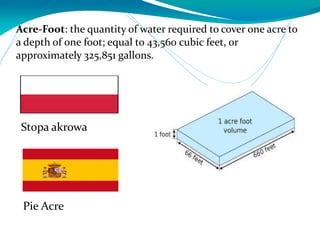
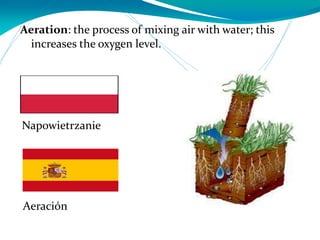
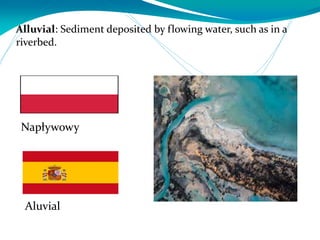
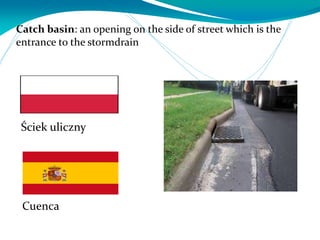
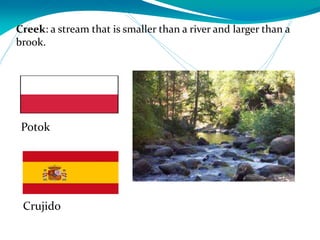
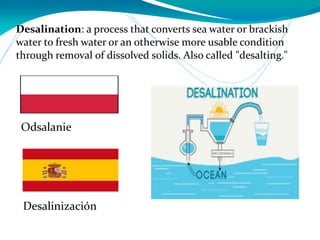
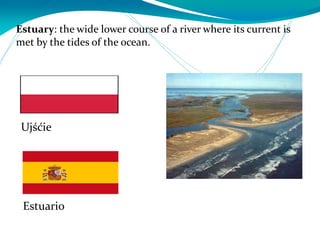
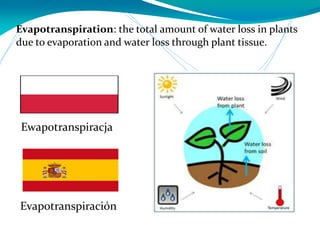
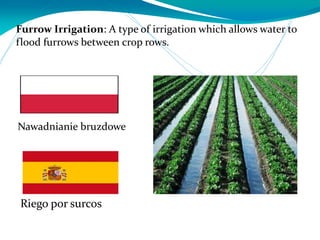
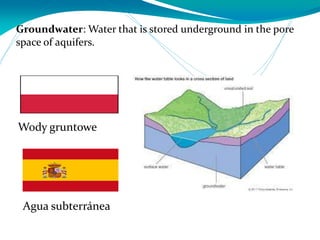
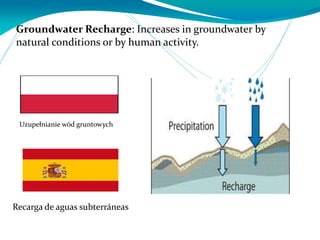
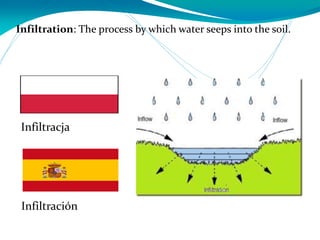
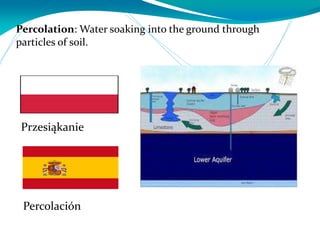
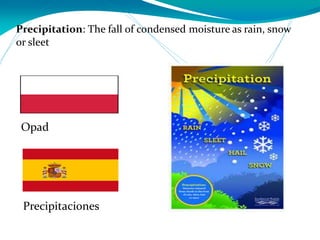
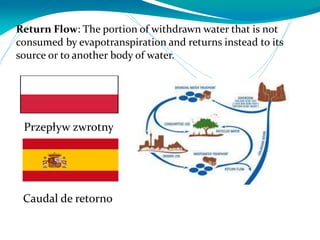
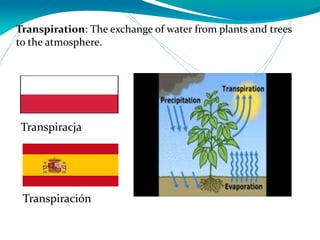
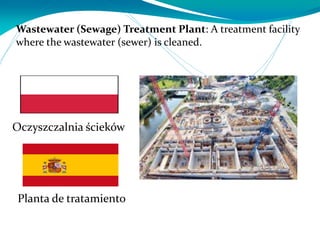
This document provides definitions for various water-related terms in English, Polish and Spanish. It includes over 50 terms related to water quality, treatment, distribution, hydrology and other water-science topics. The terms are translated phrase-by-phrase into the other two languages to serve as a tri-lingual glossary for water professionals, students or others interested in water resources.