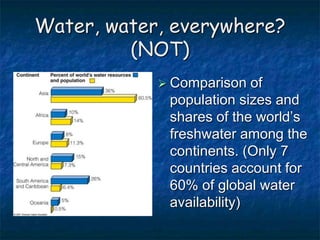
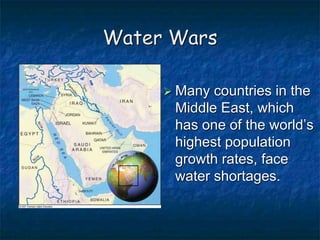
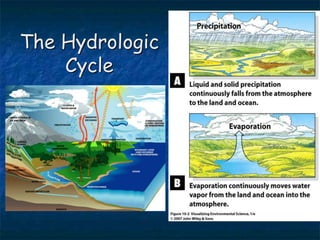
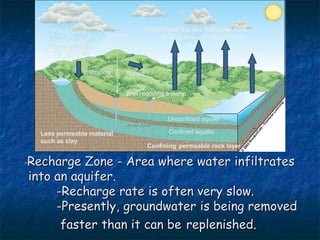
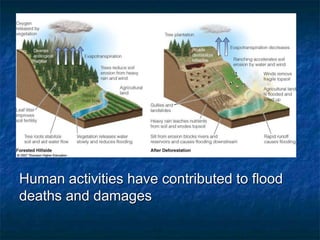
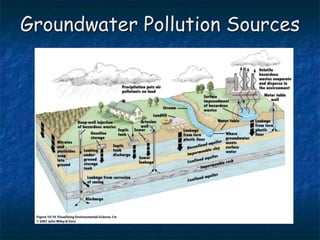
This document summarizes key topics related to freshwater resources and water pollution. It discusses the properties and importance of water, noting that only 1% of Earth's water is available freshwater and many regions will face shortages by 2025. Issues covered include too much/too little water, water conflicts, the hydrologic cycle, surface and groundwater, causes of water pollution from various sources, and approaches to water conservation and pollution control. The document emphasizes the need for sustainable water management given growing demands on limited supplies.