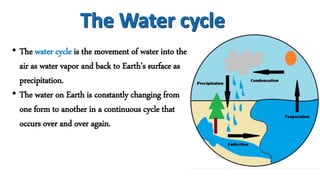
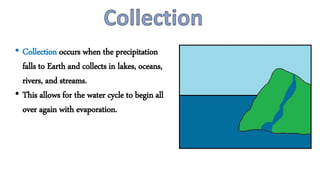
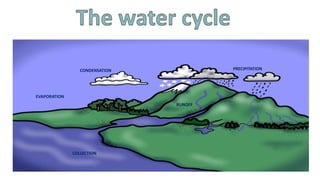
The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface. Water evaporates from bodies of water and condenses into clouds due to heat from the sun. Clouds release water through precipitation in forms like rain, snow, sleet, and hail. Precipitation collects in bodies of water through runoff and infiltration, allowing the cycle to repeat as water evaporates again.