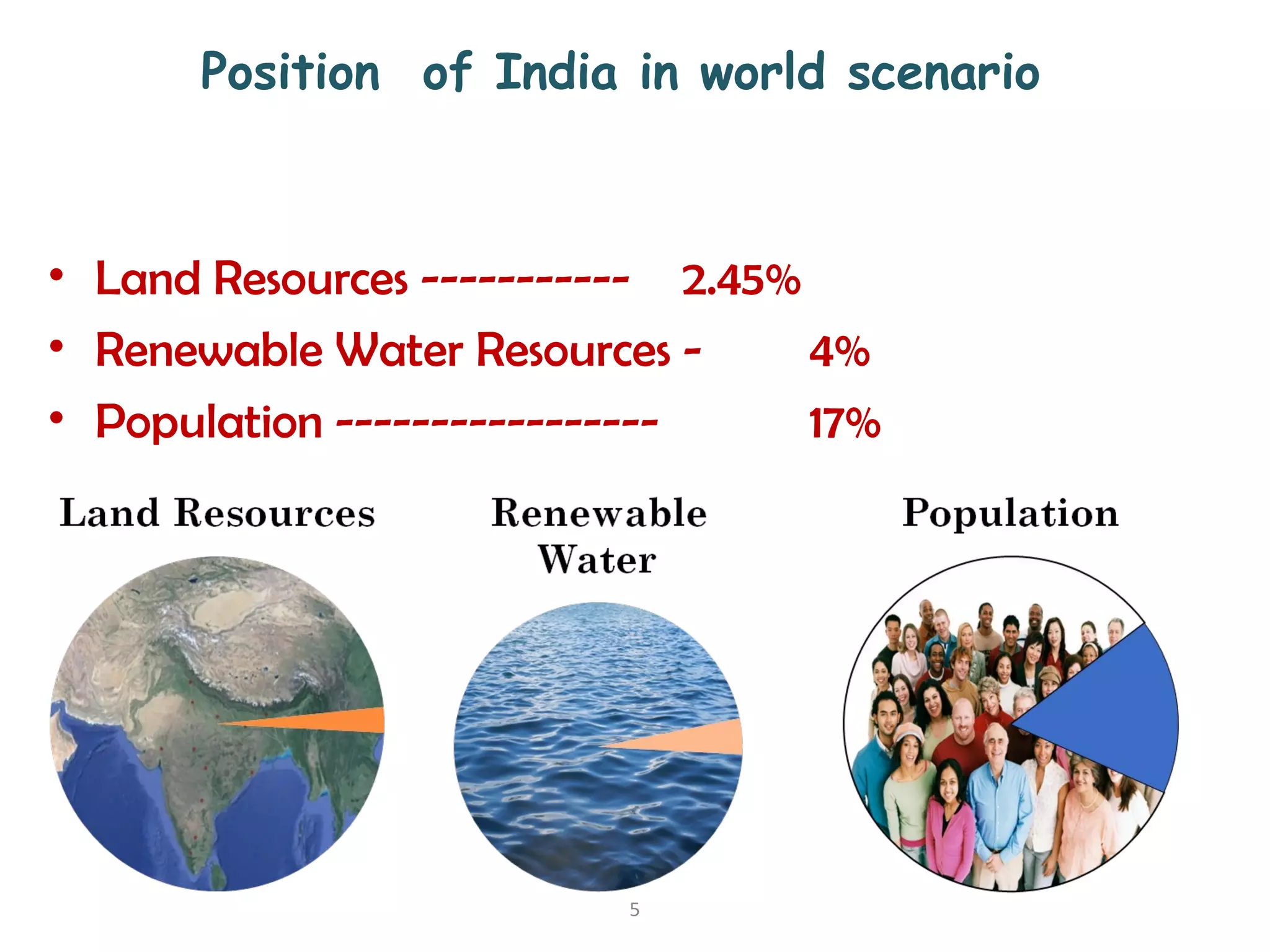
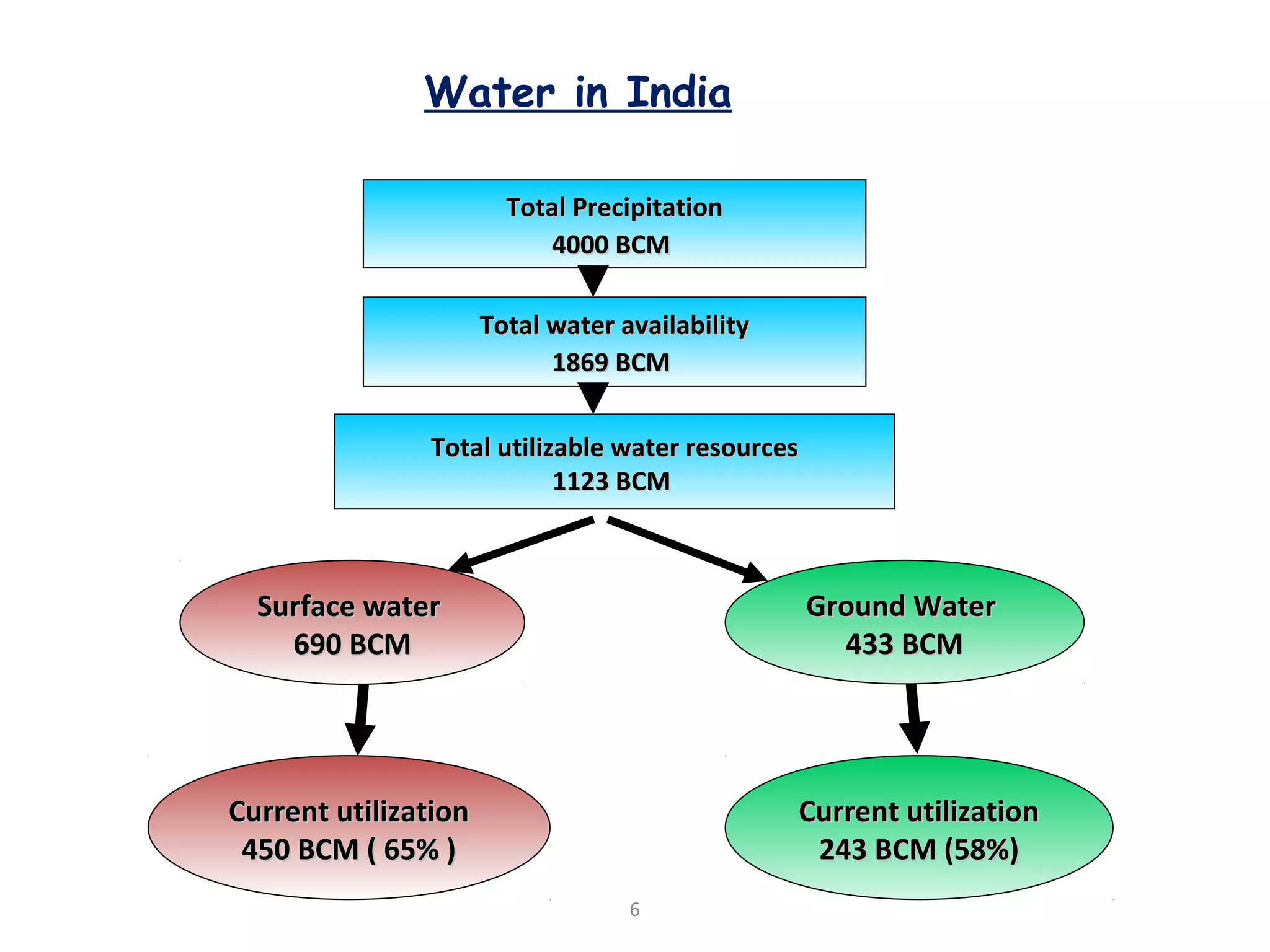
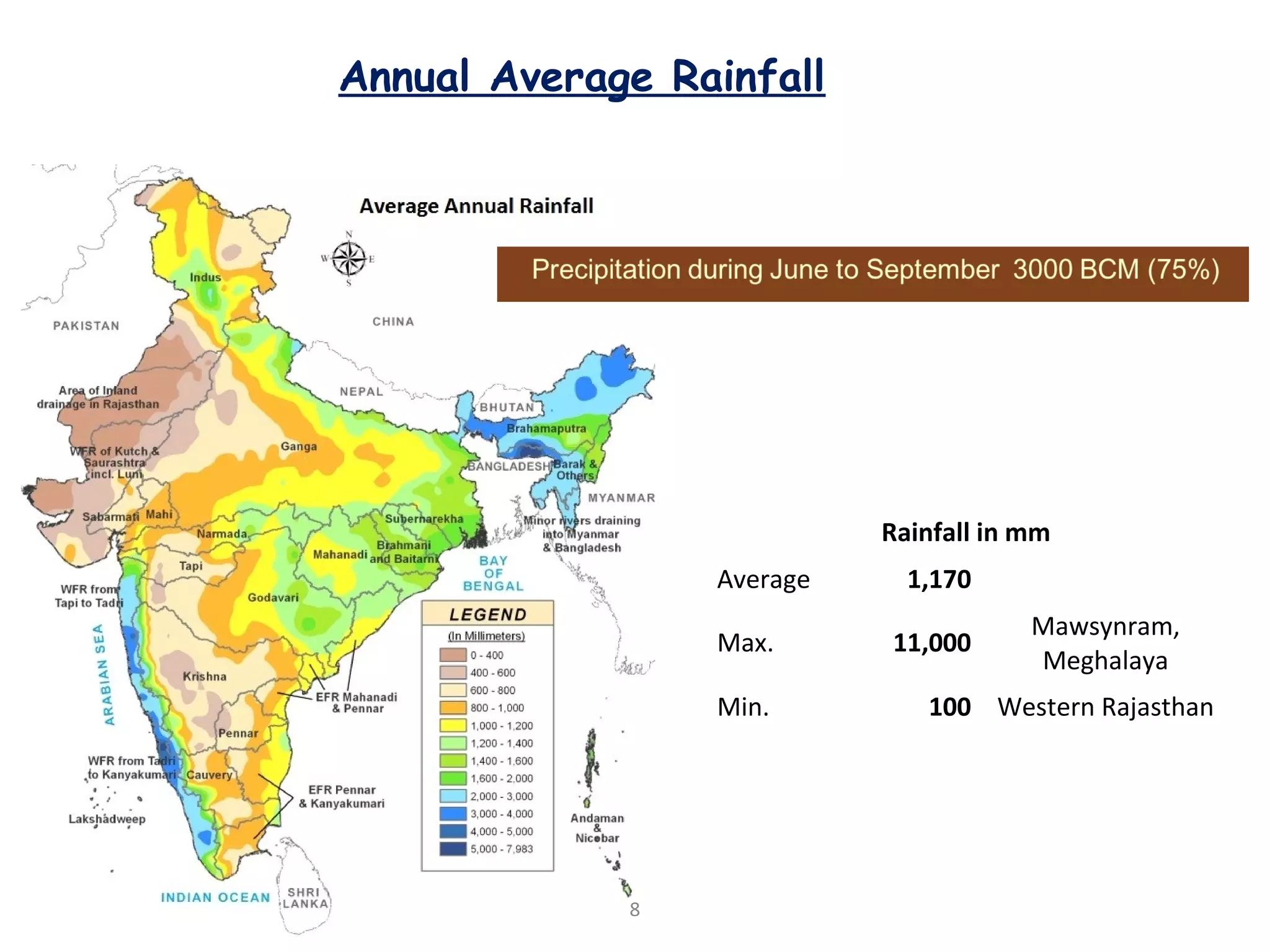
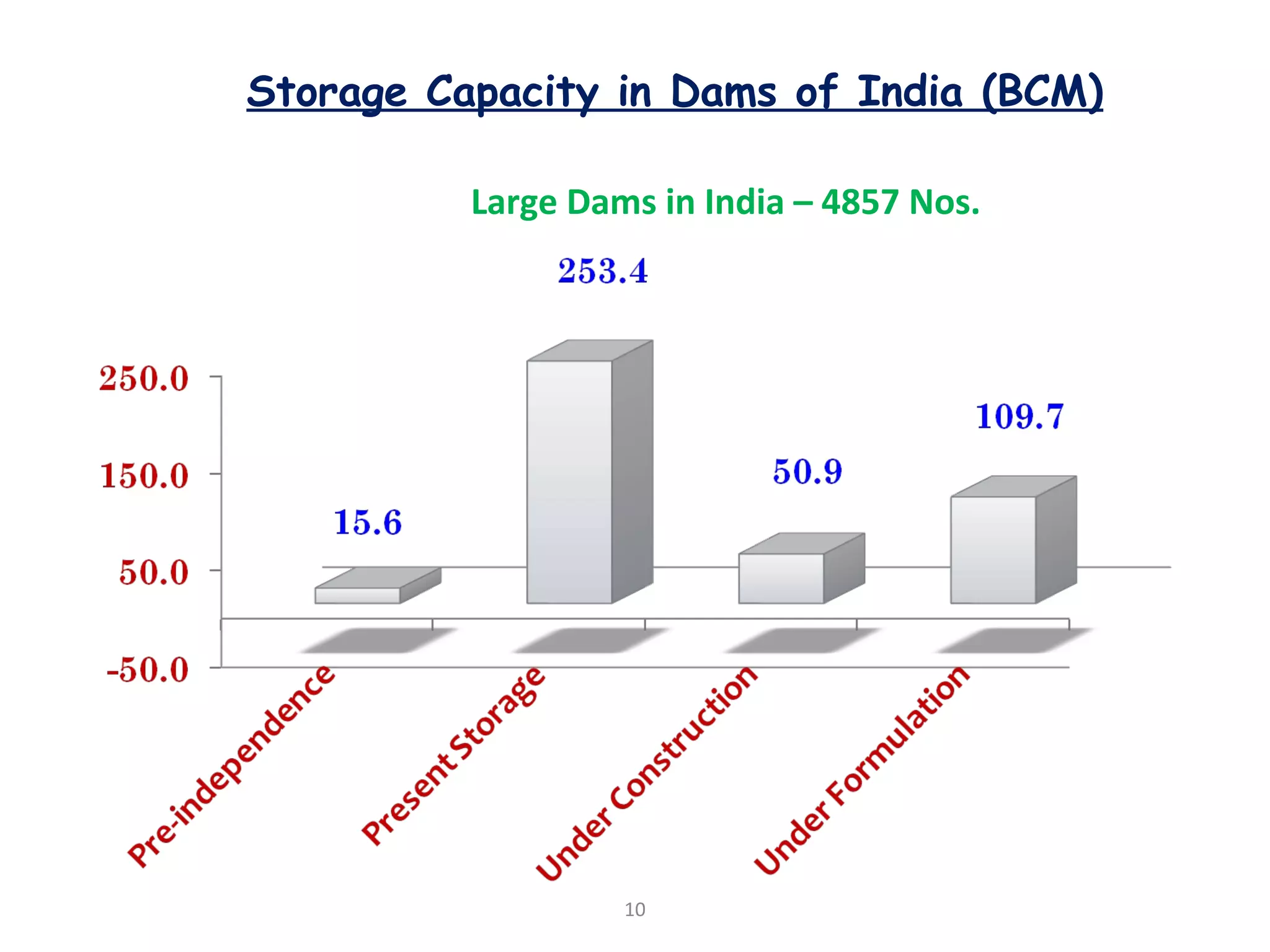
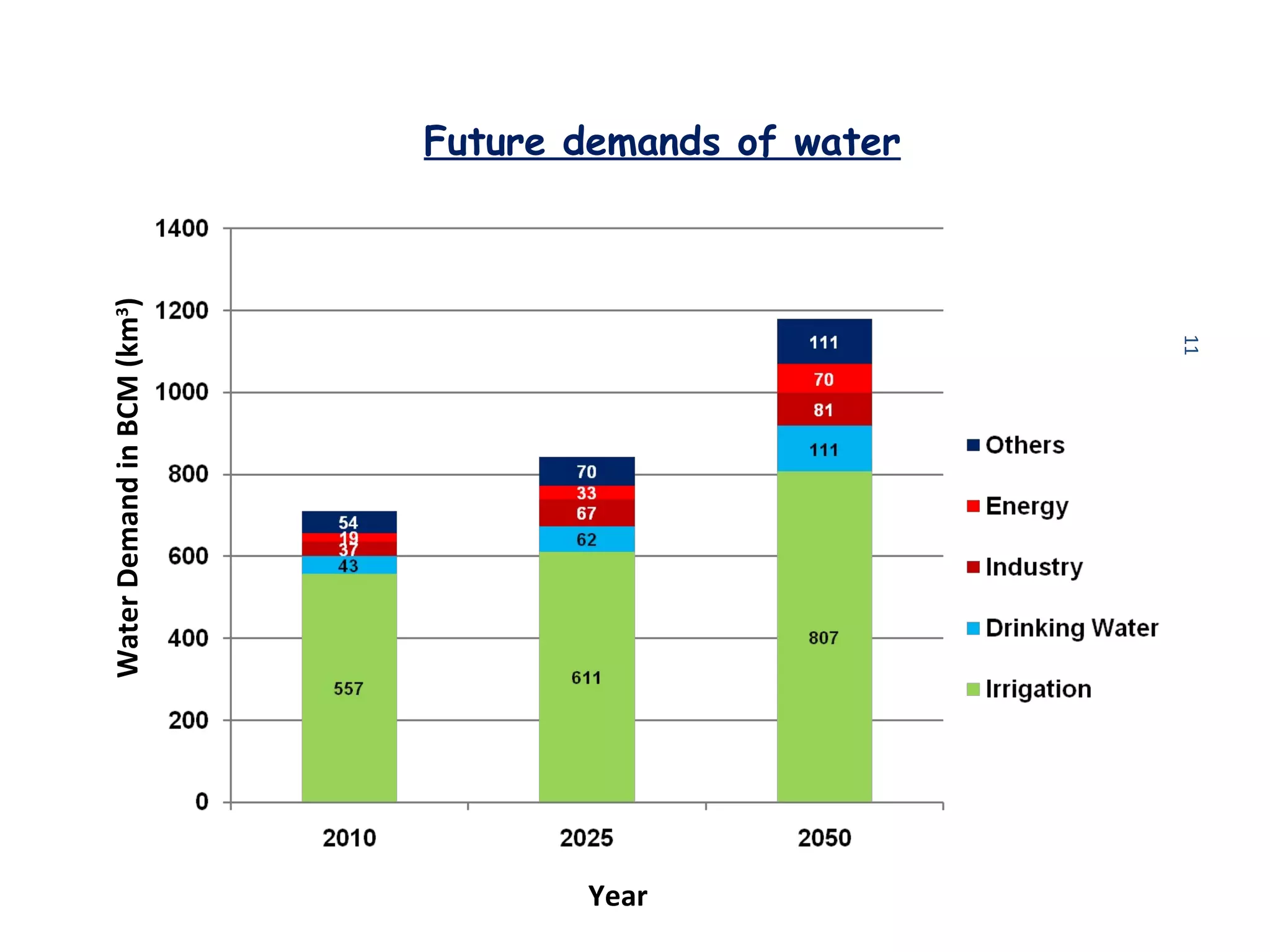
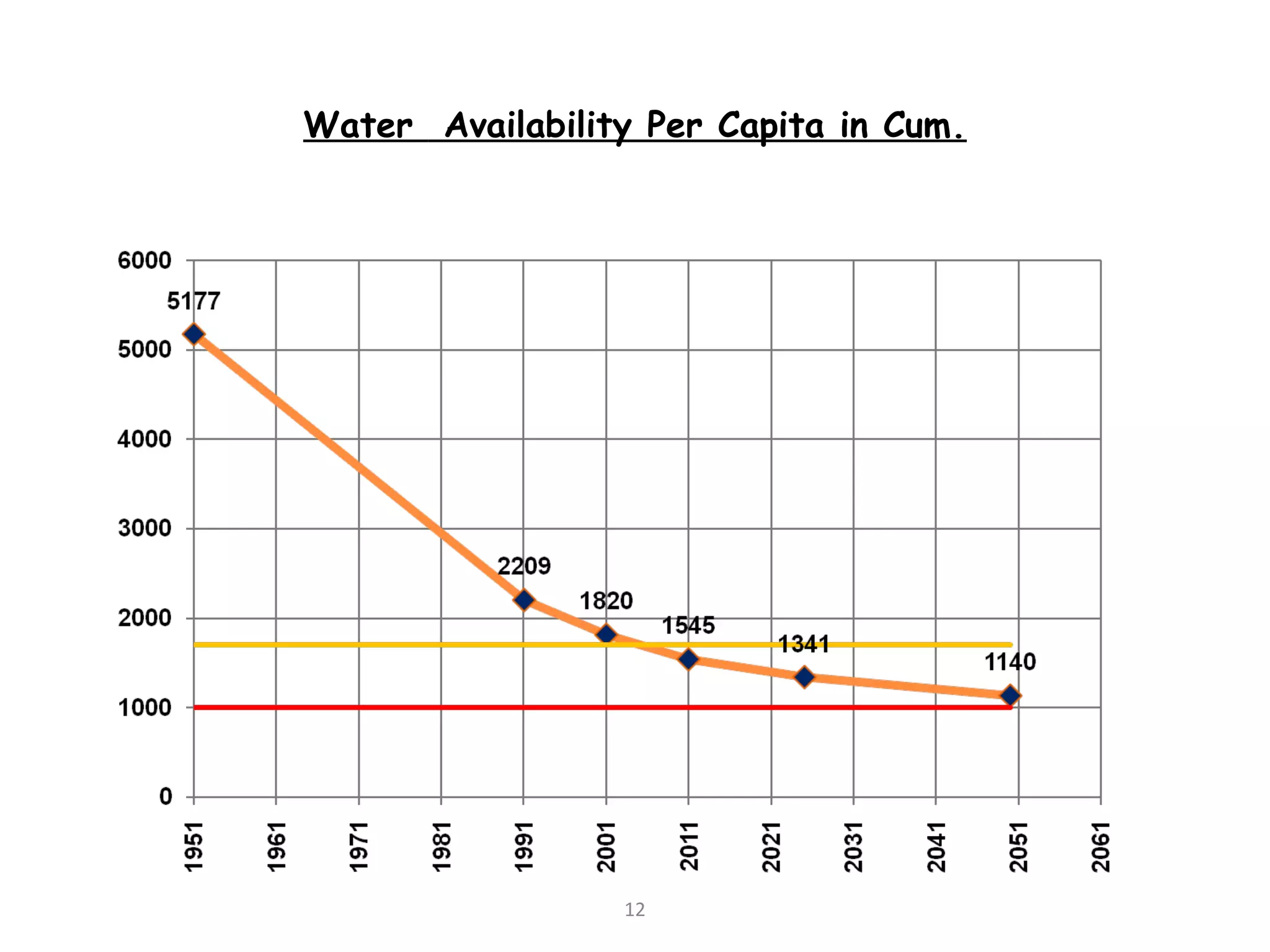
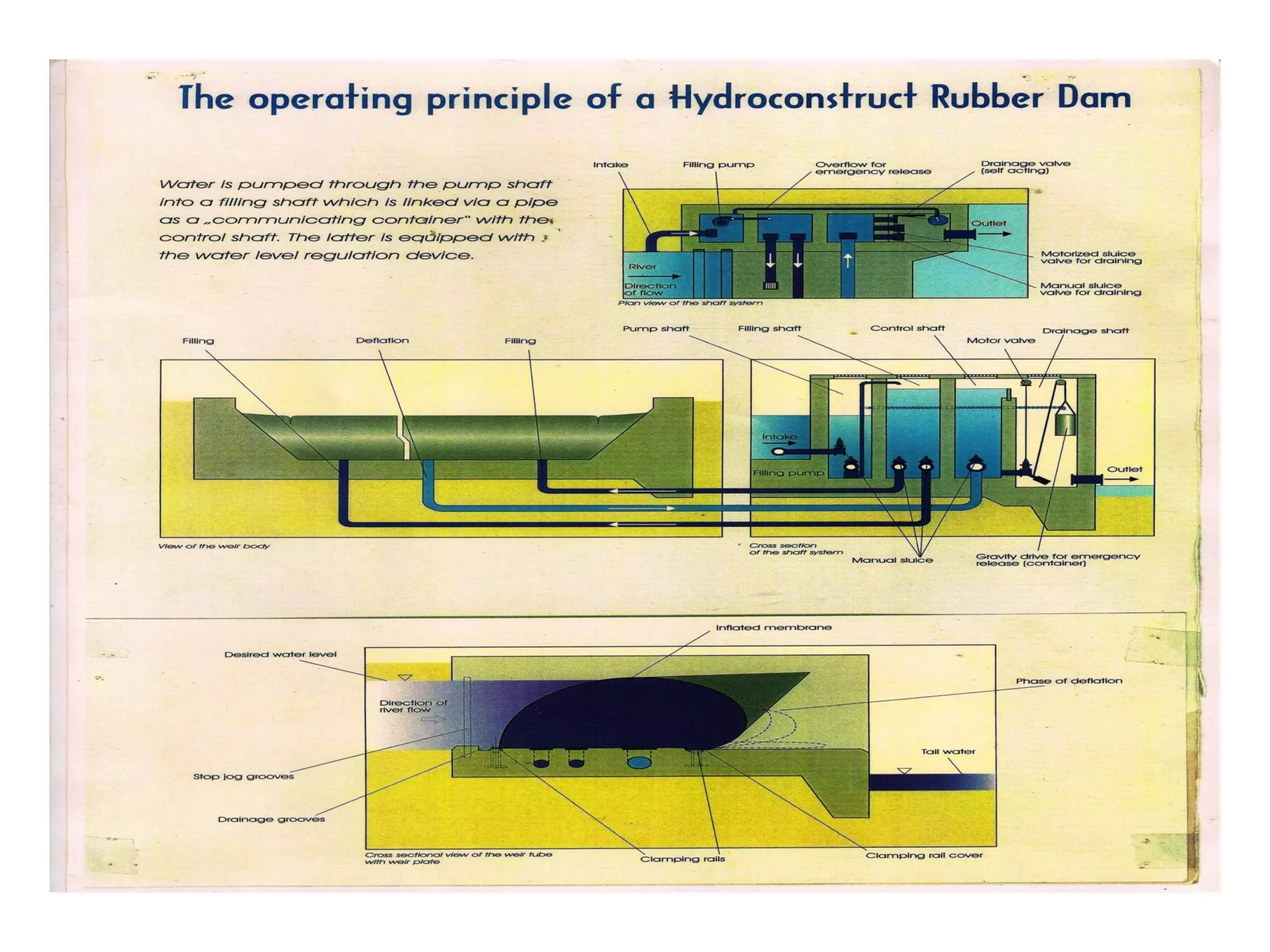
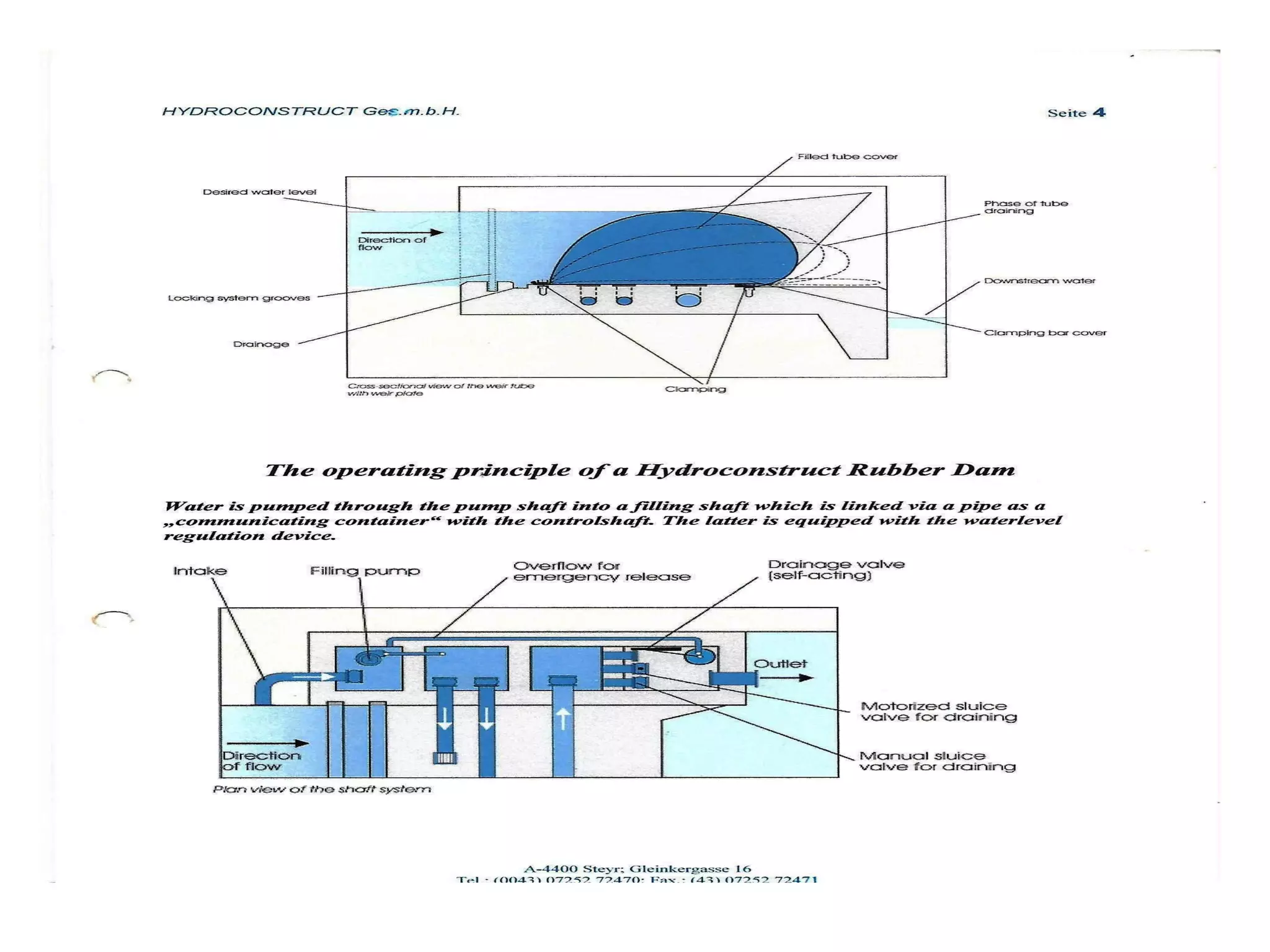
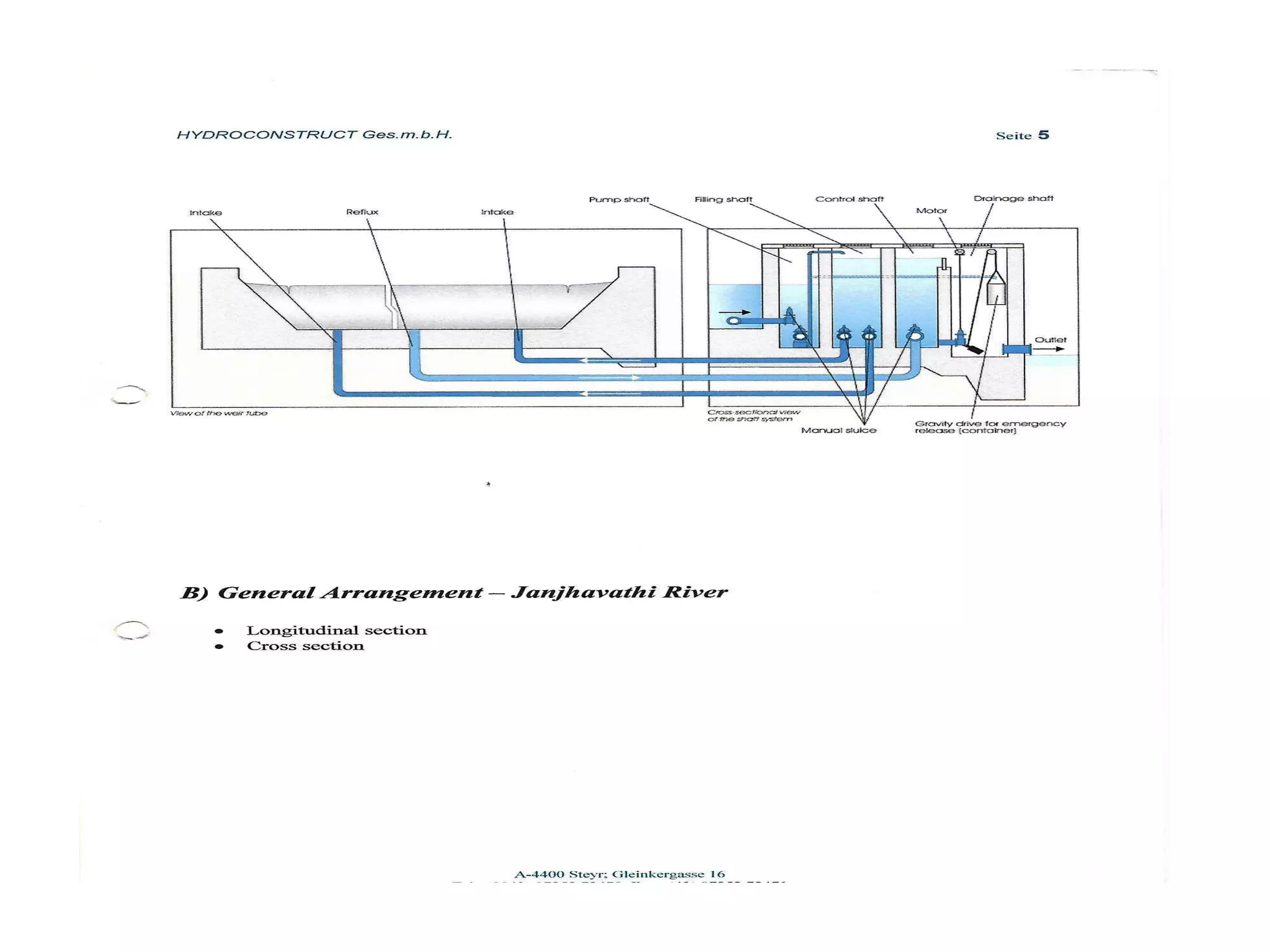
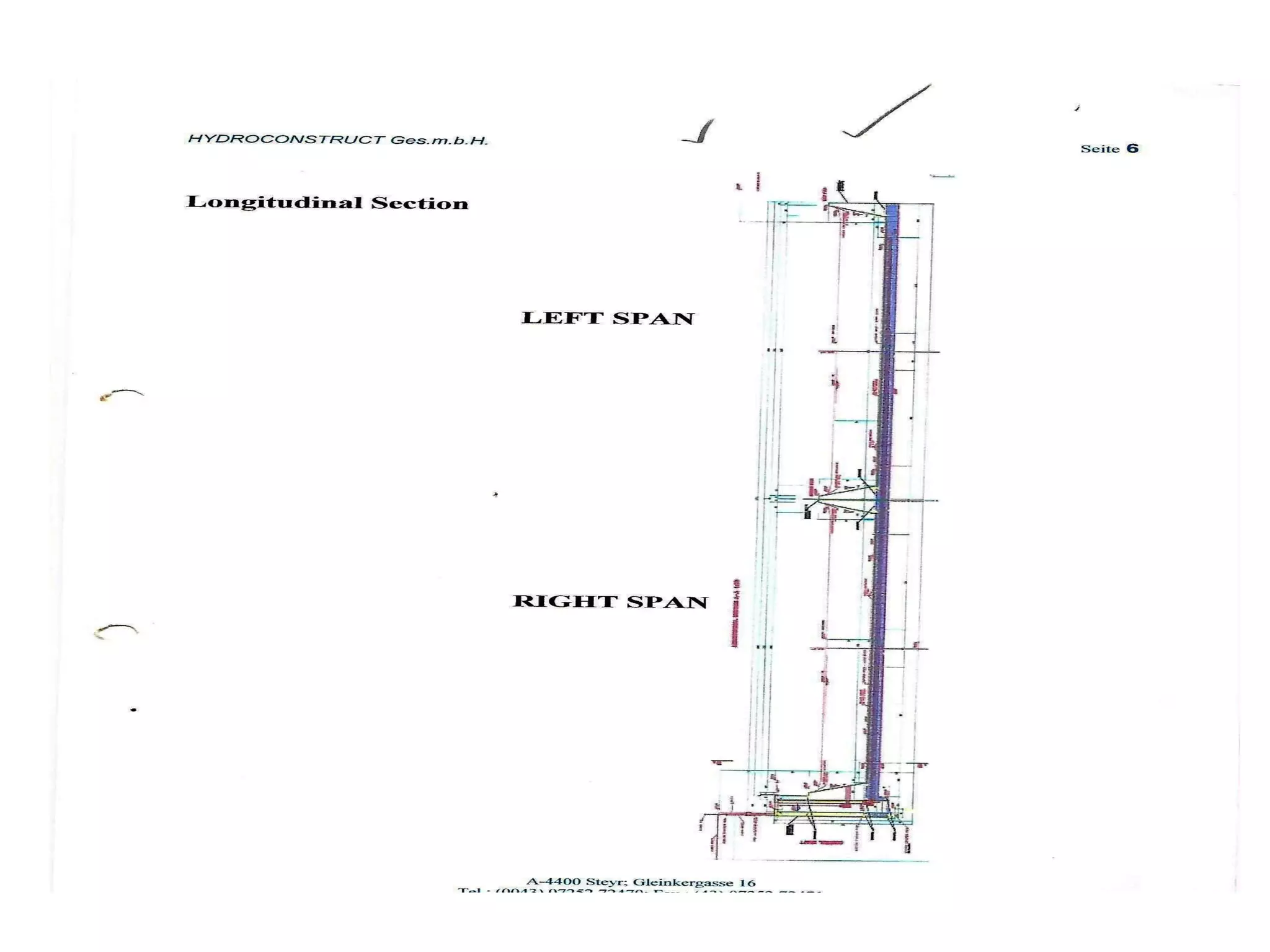
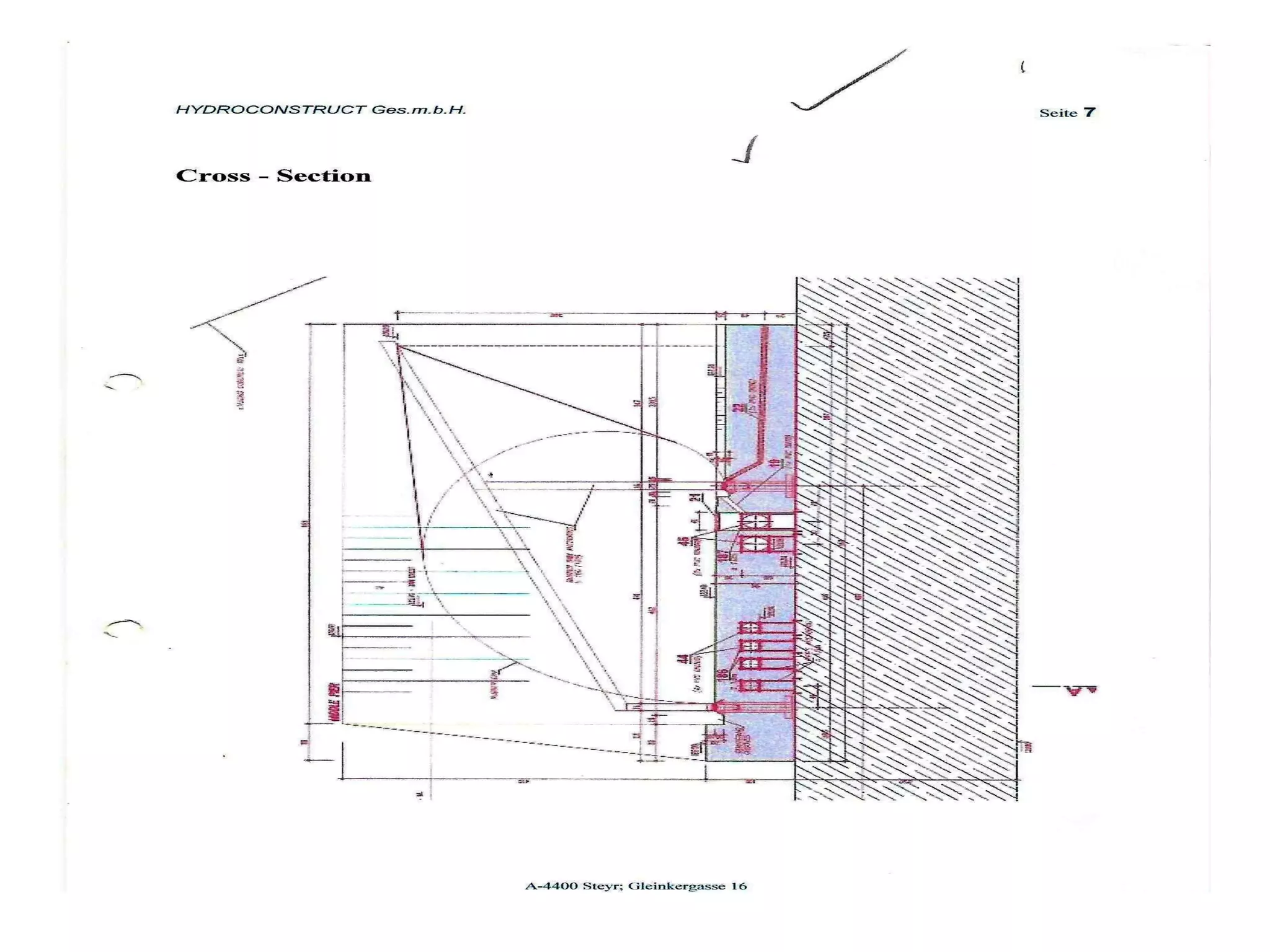
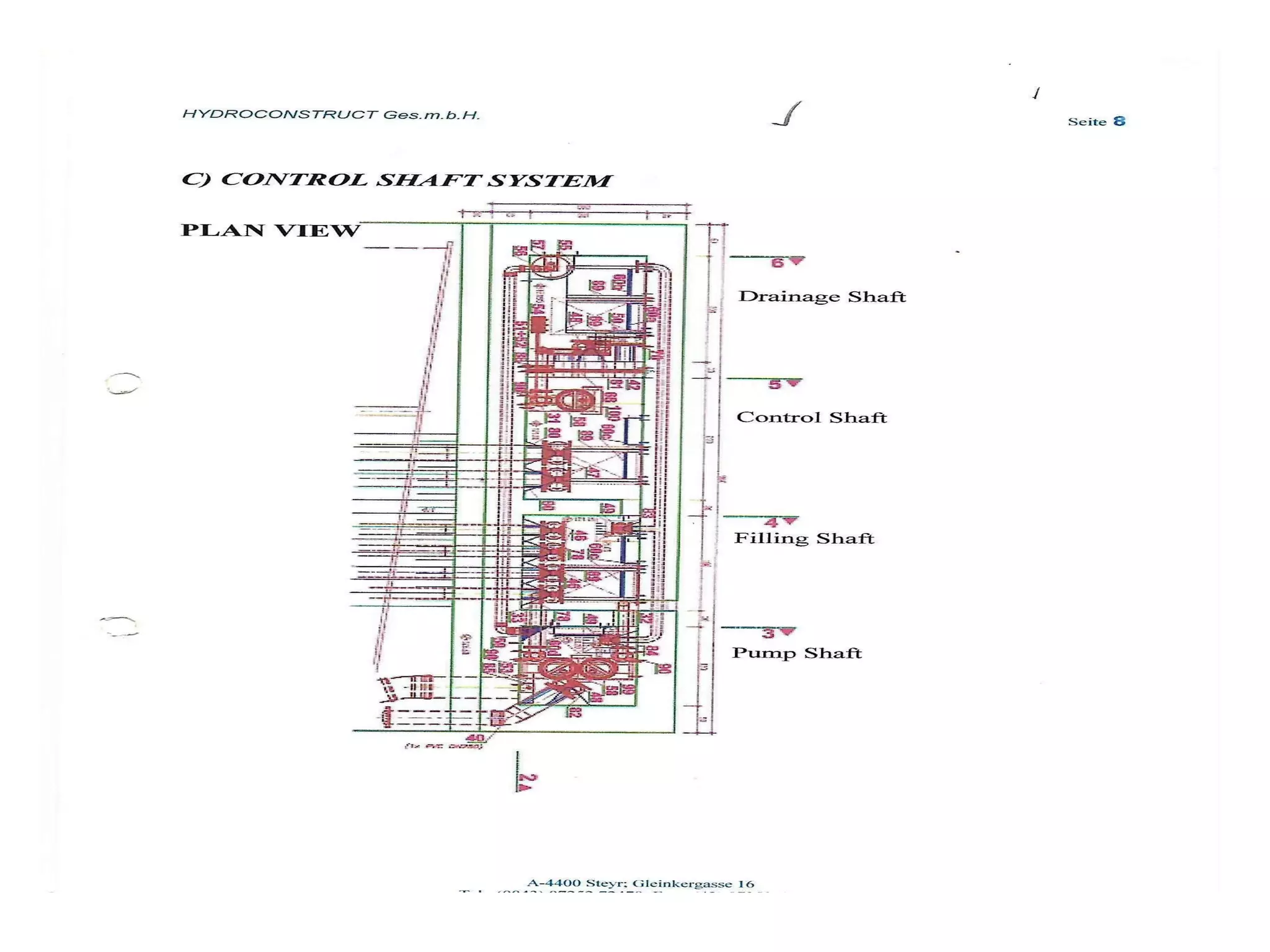
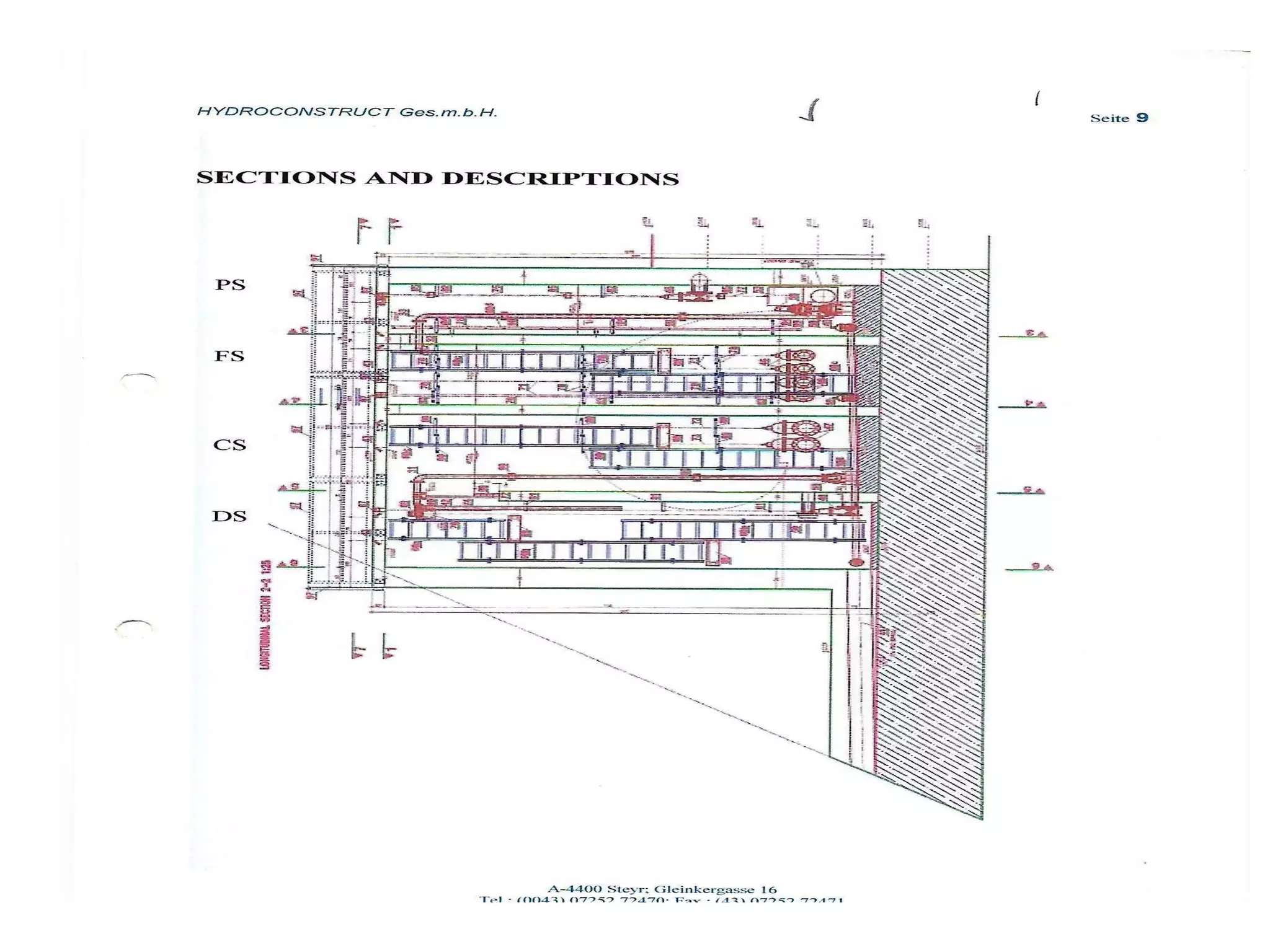
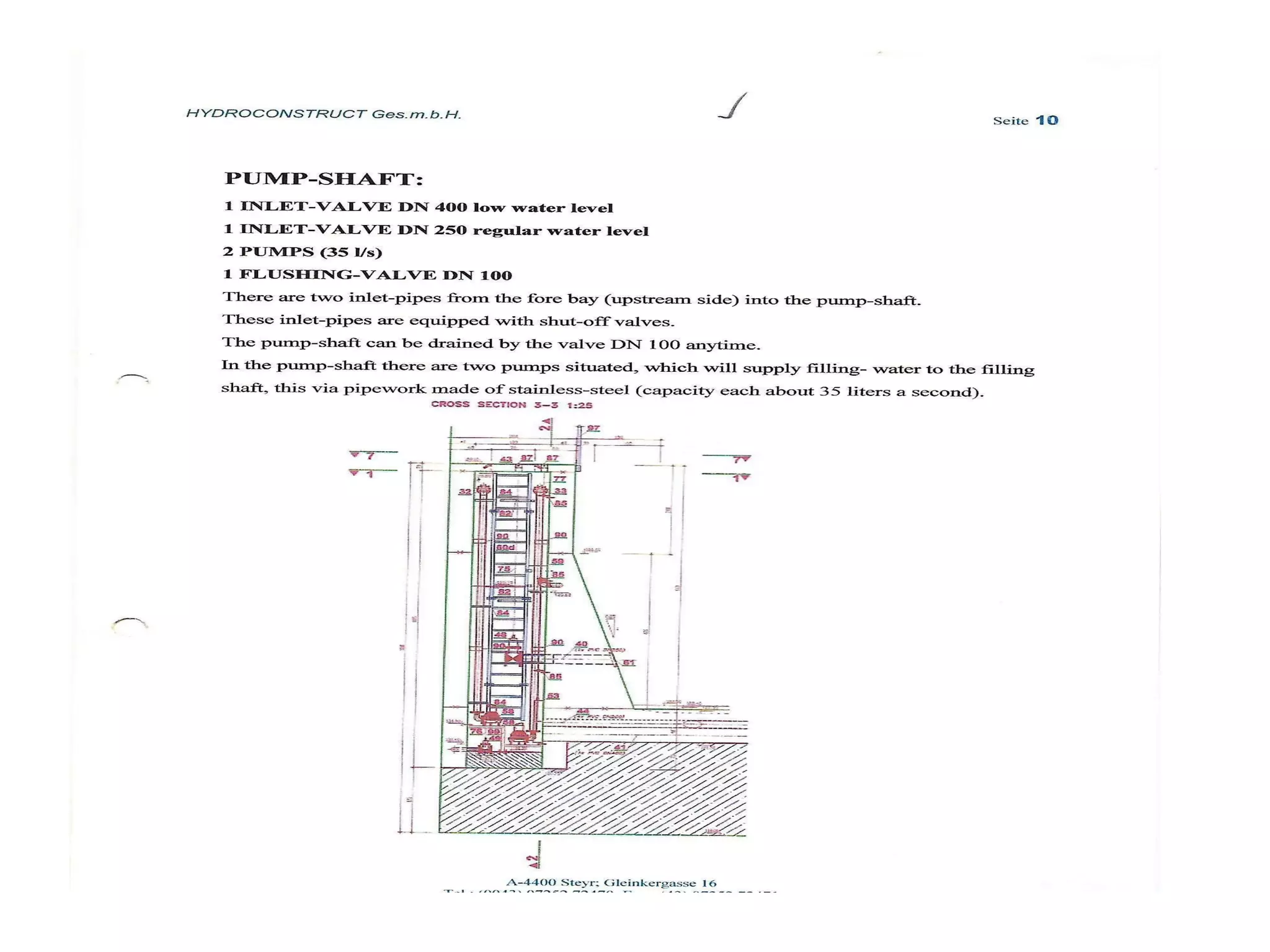
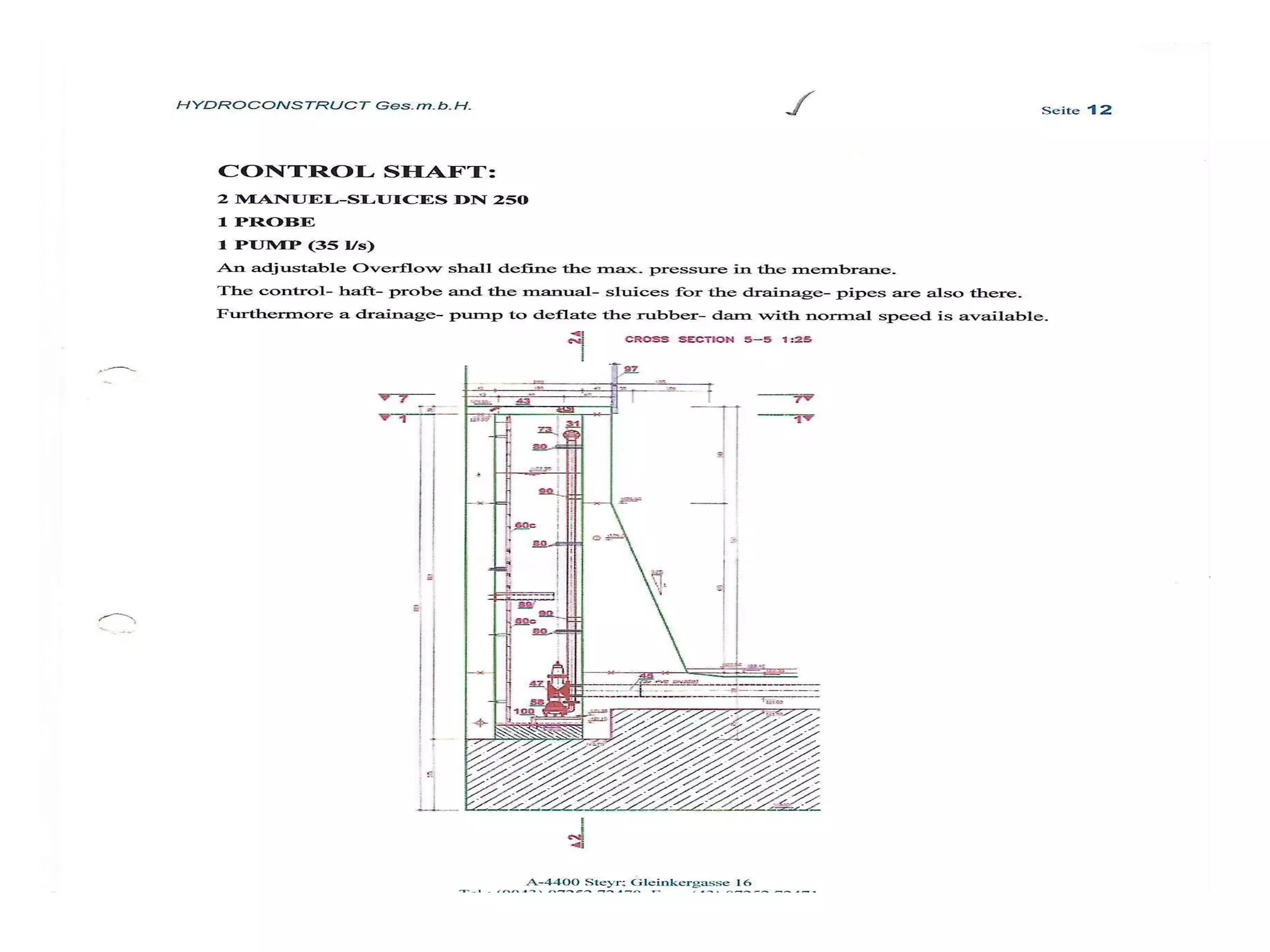
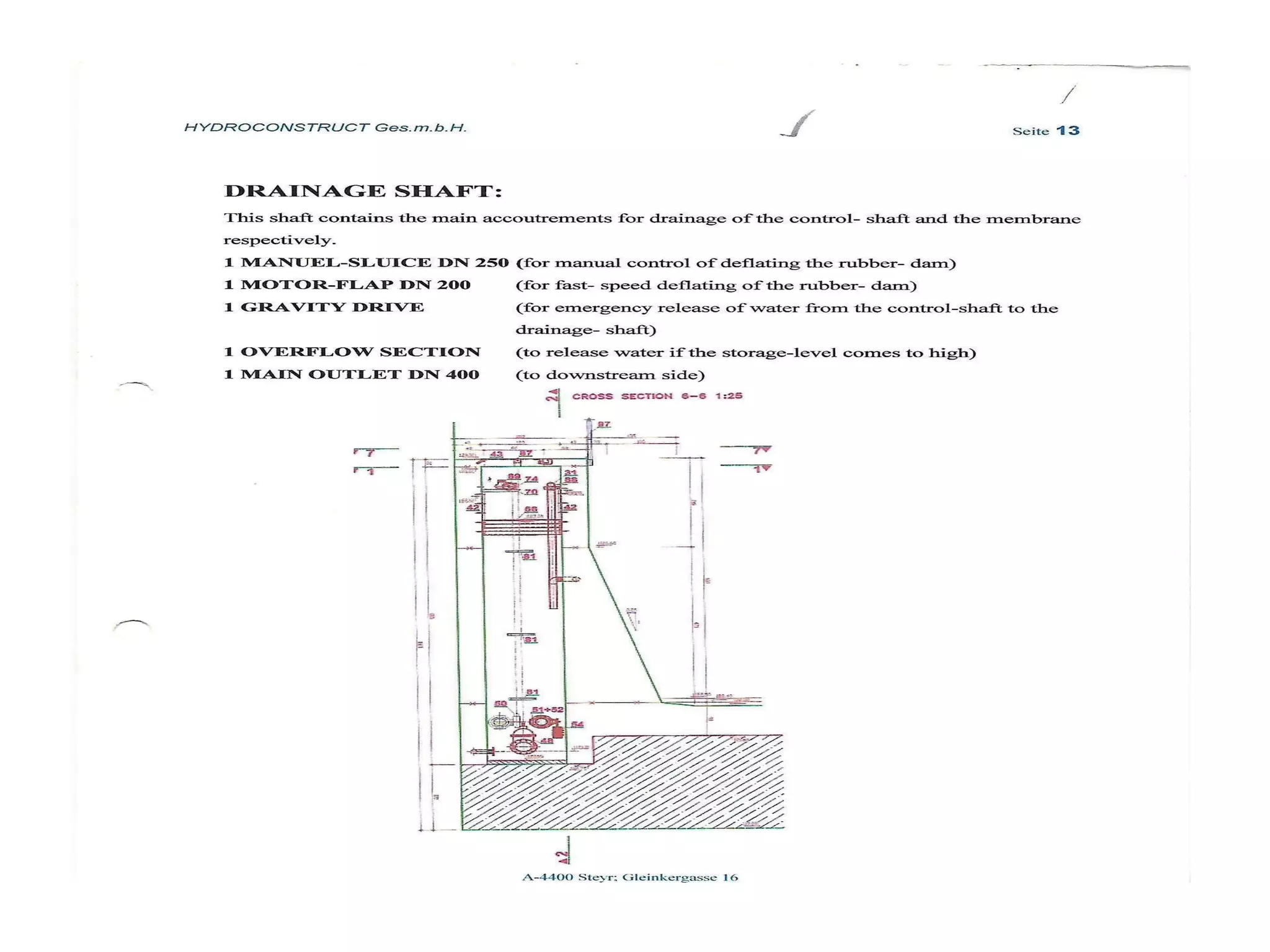
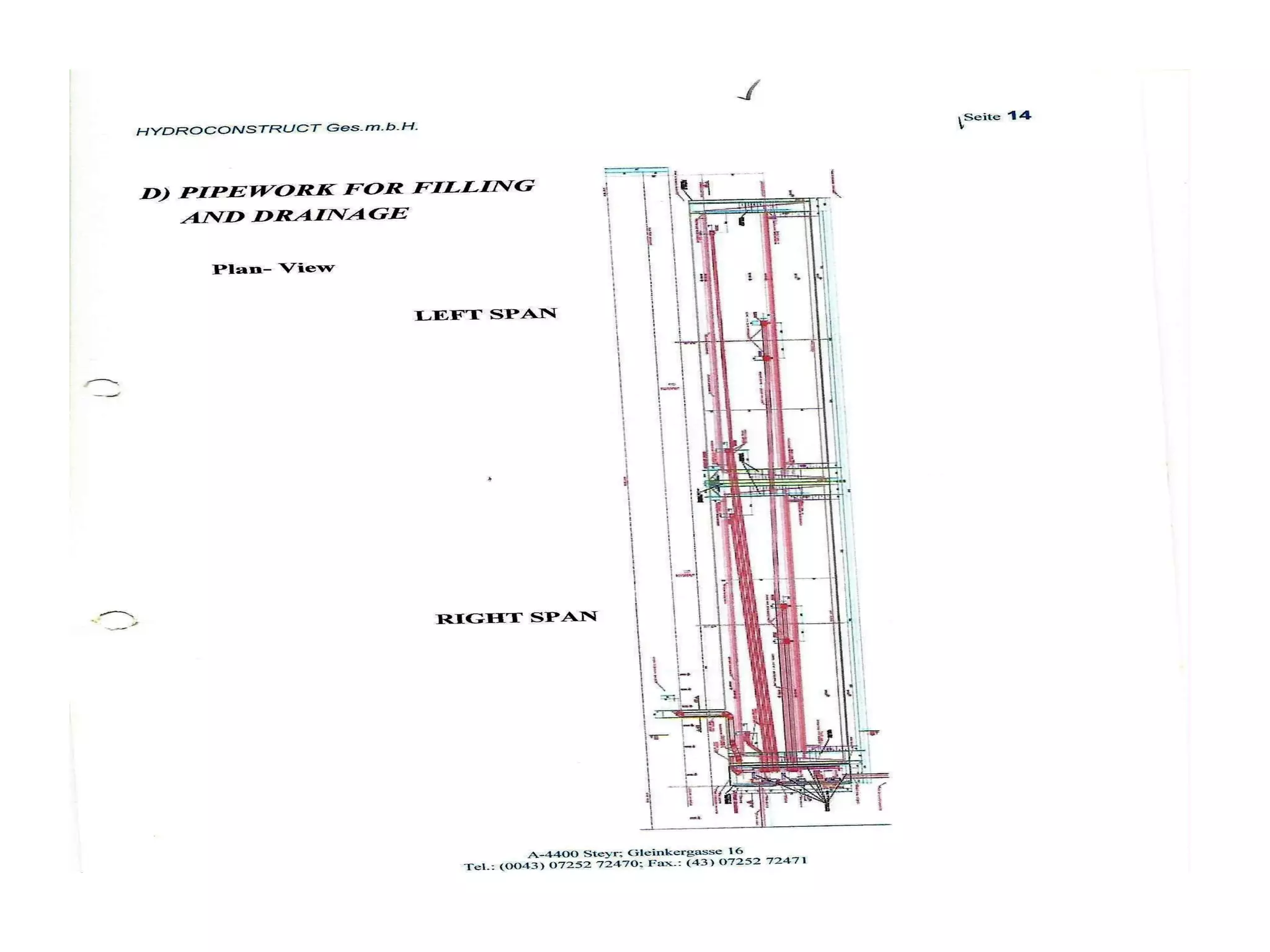
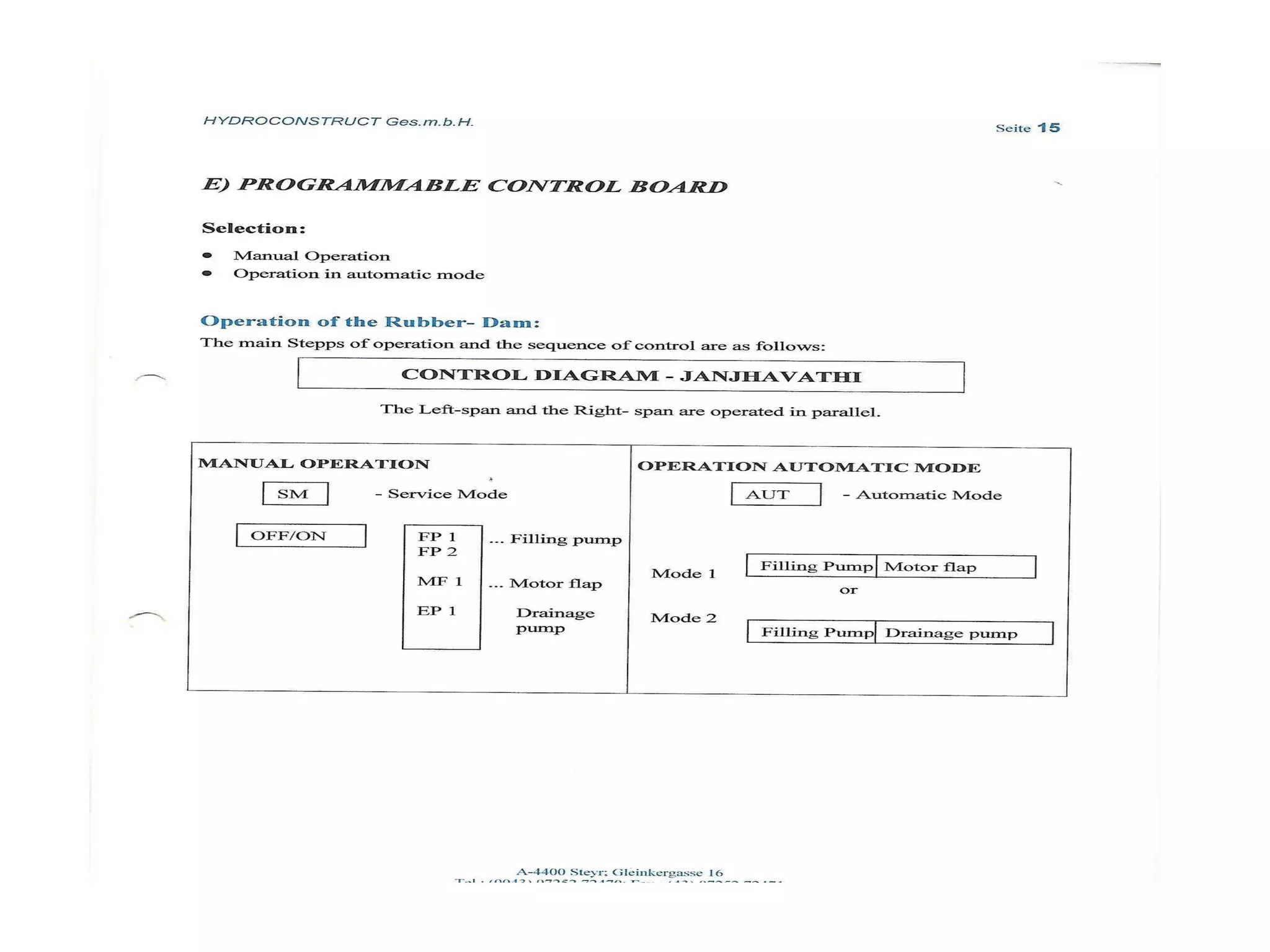
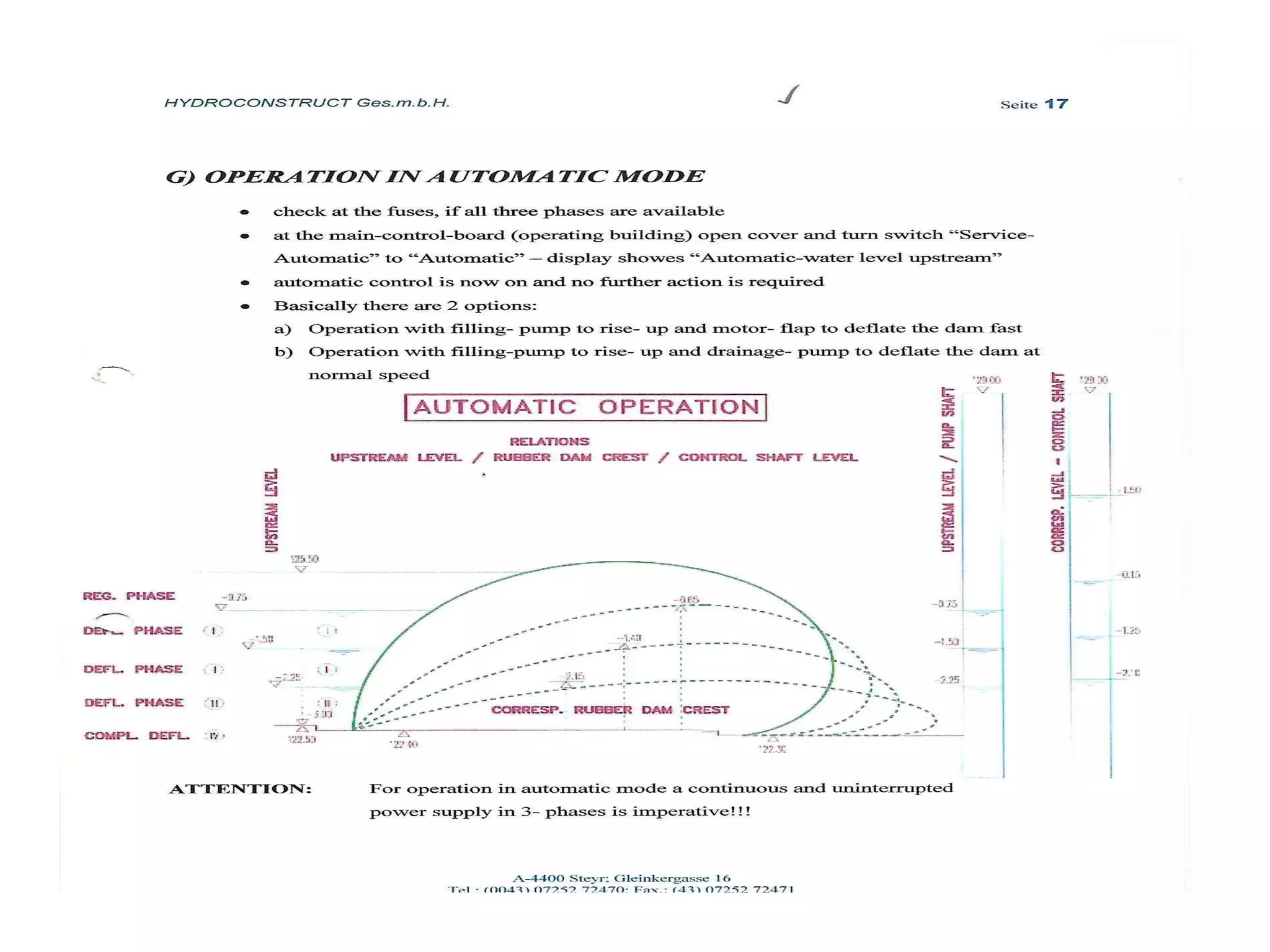
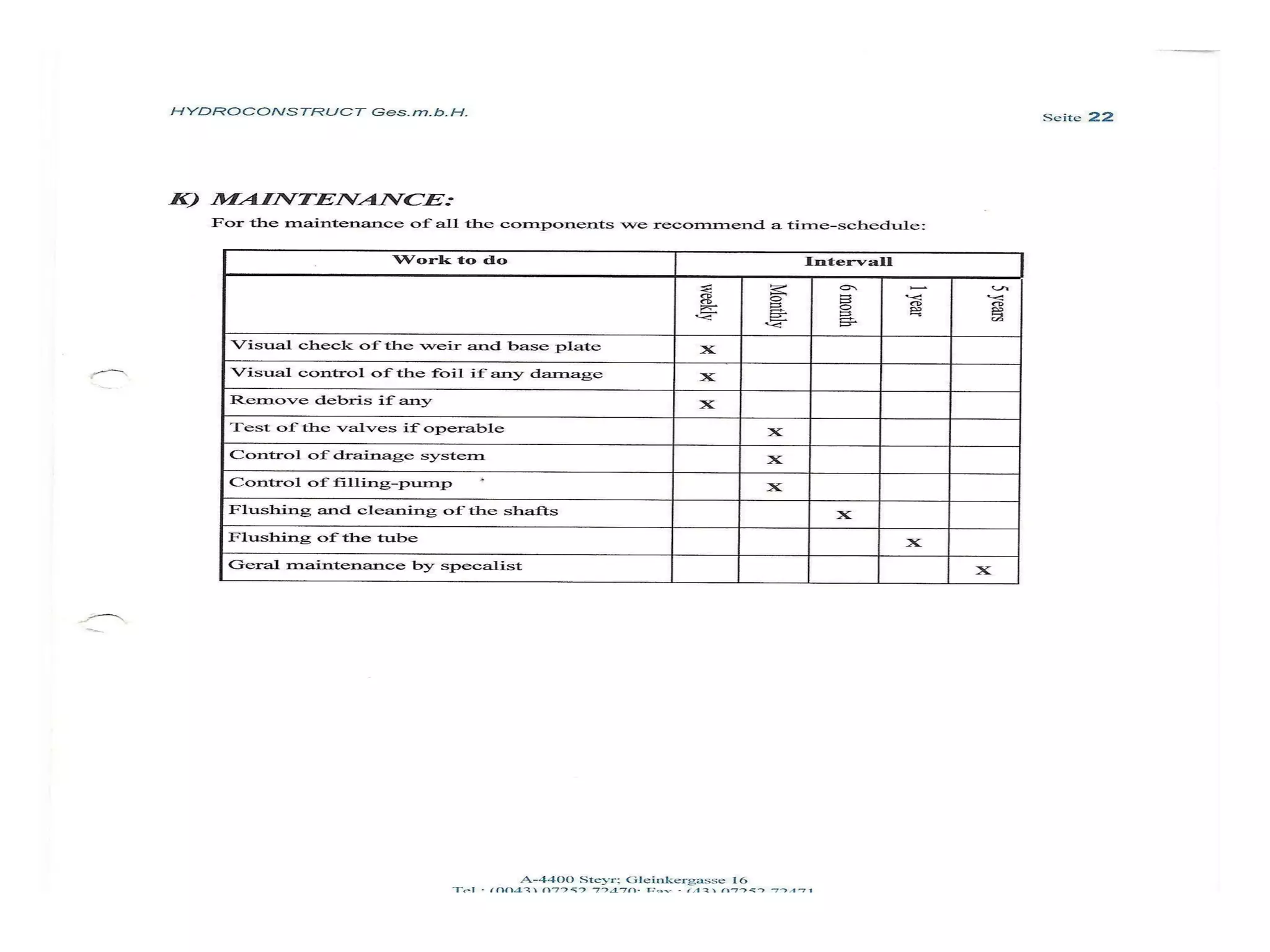
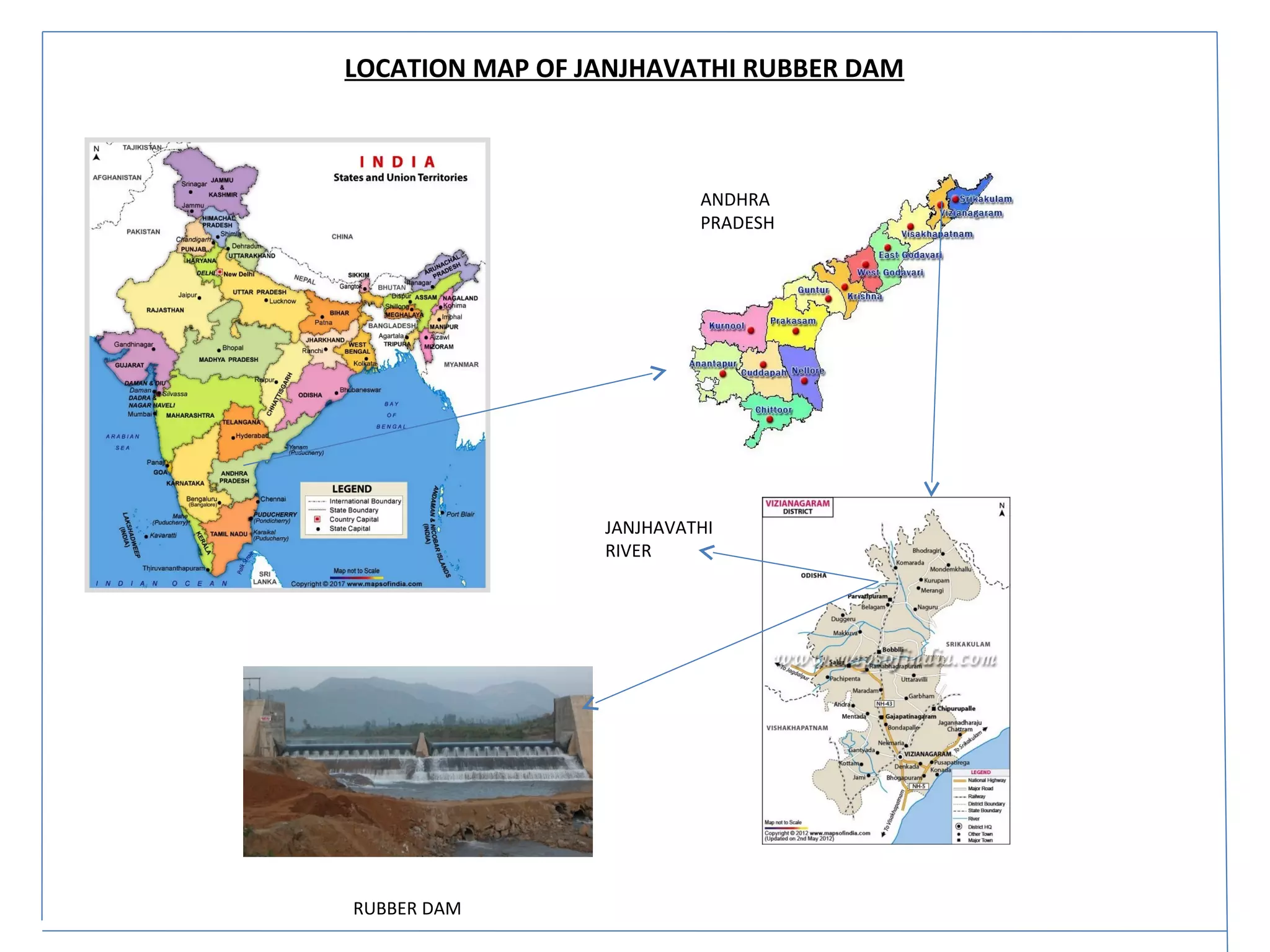
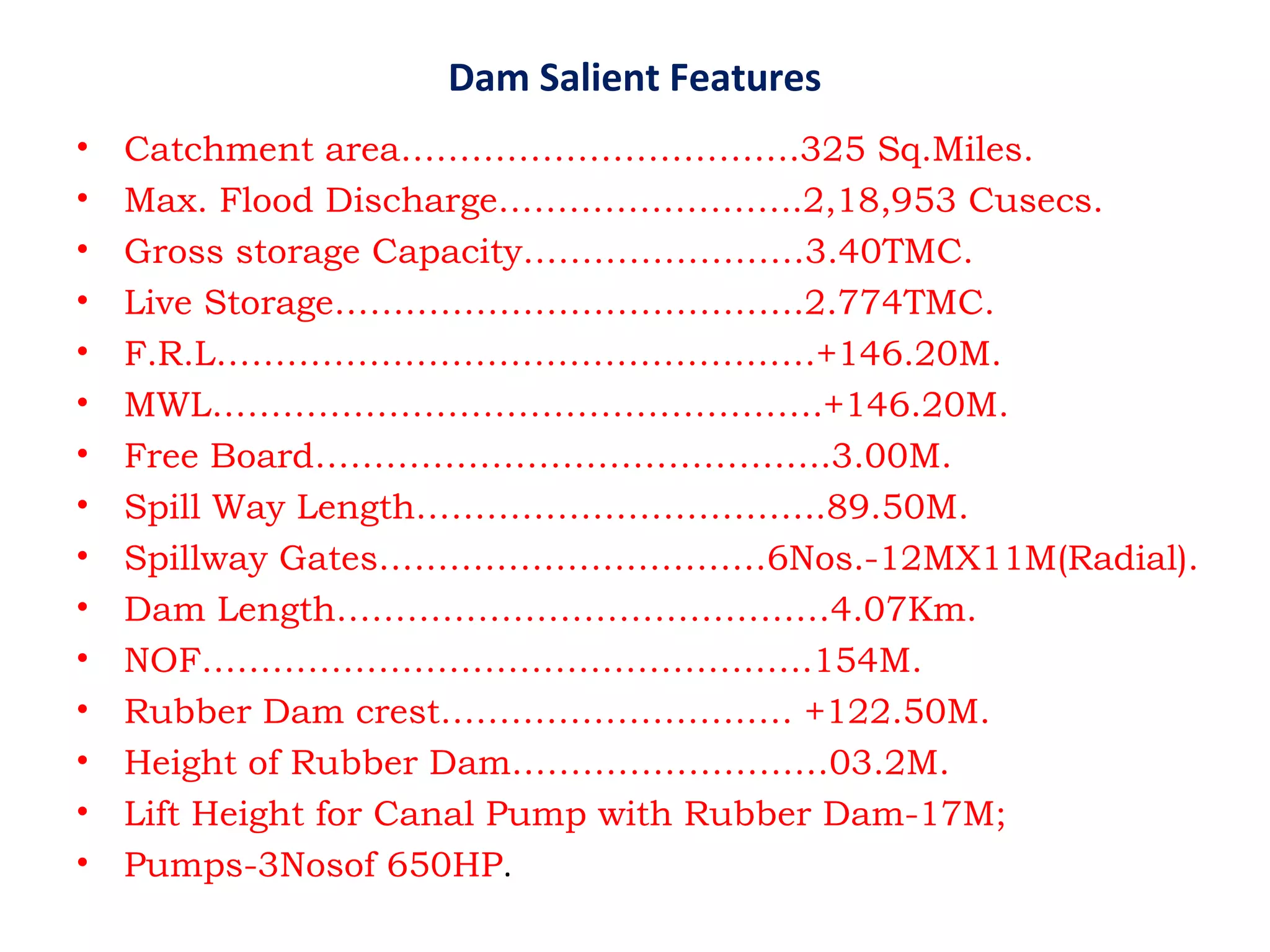
The document discusses advancements in hydraulic structures, particularly focusing on rubber dams as an innovative solution to water management in India, highlighting their advantages over traditional dams in terms of flexibility, cost, and environmental impact. It details the Janjavathi rubber dam project in Andhra Pradesh, which aims to address irrigation challenges while minimizing land acquisition and resettlement issues. The presentation emphasizes the importance of water conservation and irrigation efficiency in light of India's limited water resources and increasing population demands.