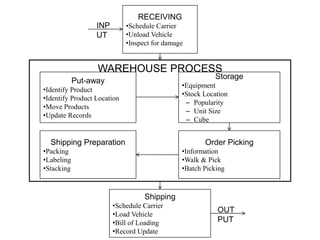
This document provides information about warehousing in the pharmaceutical industry. It defines warehousing and warehouses, and outlines the objectives, functions, purposes, types, and general guidelines of warehousing. It discusses finished product warehousing, warehouse layout, standard operating procedures, design and construction considerations, maintenance, sanitation, and good warehousing practices. The document emphasizes the importance of orderly storage, documentation, stock control, safety, and quality assurance in pharmaceutical warehousing.






























![warehousing[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mywarehousing1-161204060435/85/warehousing-1-37-320.jpg)