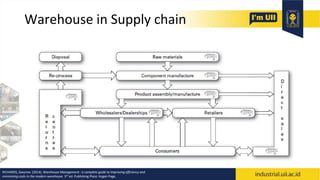
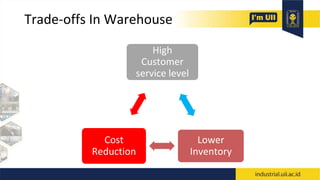
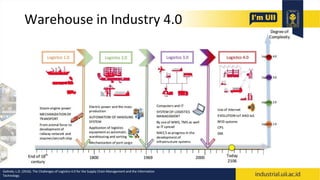
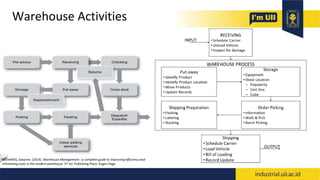
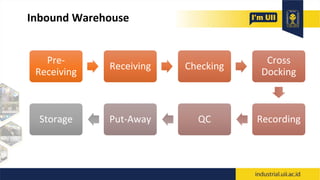
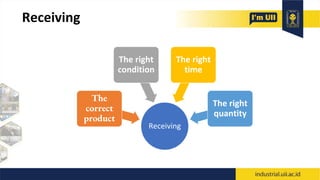
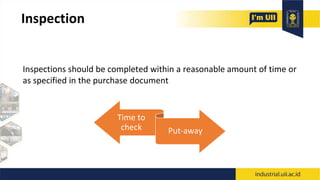
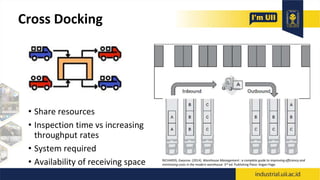
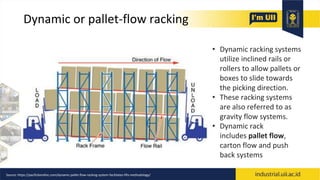
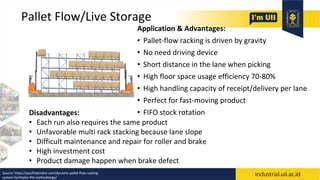
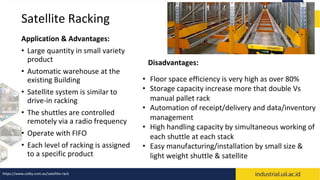
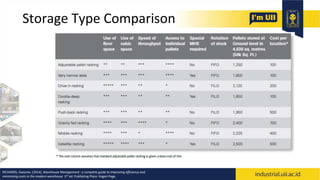
The document provides an overview of warehouses and storage. It defines a warehouse and explains their purpose in industry. Key points include: Warehouses provide storage and handling of goods, but many managers do not view them strategically. The document outlines various warehouse types and challenges. It also discusses warehouse management systems, storage types, and the functions of receiving, put-away, inspection, and cross-docking. The goal of warehouses is to efficiently store and move inventory through the supply chain.


![Warehouse
• According to Logistics Bureau [1], Warehouse can be defined as
planned space for the efficient storage and handling of goods and
materials
• A warehouse is a dynamic operation and can deliver a more
profitable return on investment than many people realise.
• Only 26% of company managers view warehouses and distribution
centers as an asset which can drive growth for their business [2]
• 34% of businesses ship late because products are sold which are not
actually in stock [3]
1. https://www.logisticsbureau.com/about-warehousing/
2. https://www.zebra.com/content/dam/zebra_new_ia/en-us/solutions-verticals/vertical-solutions/warehouse-management/vision-study/2024/warehouse-vision-study-
en-us.pdf
3. https://www.peoplevox.com/hubfs/Fulfilment%20Survey%202017/2017%20Peoplevox%20E-Commerce%20Fulfilment%20Report.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ptlf7warehouseandstorage-230905044248-3890c663/85/PTLF_7-Warehouse-and-Storage-pptx-4-320.jpg)