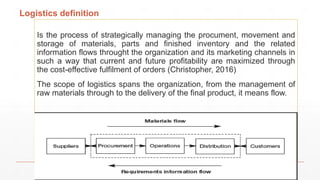
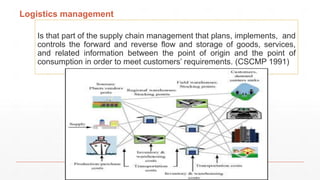
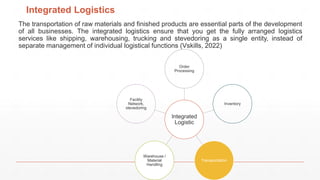
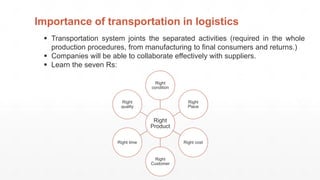
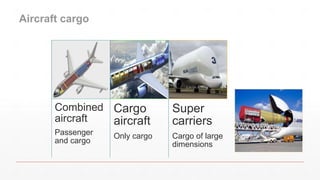
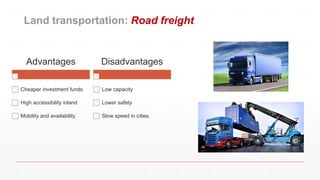
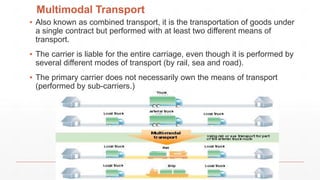
The document is an introduction to a logistics class that covers essential aspects of logistics, focusing primarily on transportation. It outlines the objectives of the lecture, definitions of logistics, various means and modes of transport, their advantages and disadvantages, and the importance of integrated logistics. The content emphasizes the relation between logistics and transportation within the context of global supply chains, especially considering current challenges such as port congestion and rising freight rates.