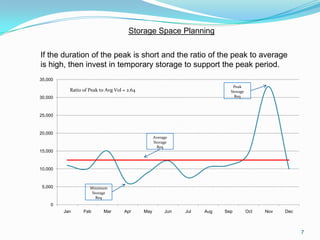
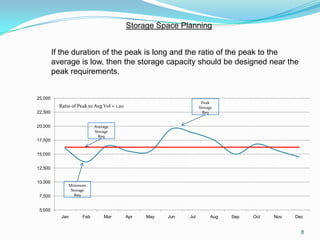
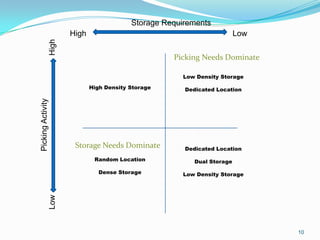
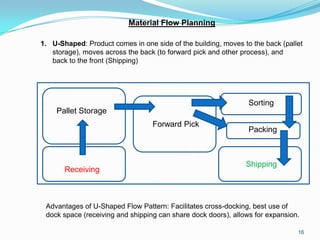
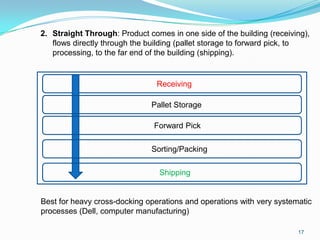
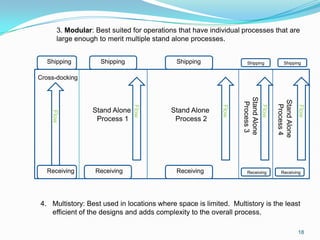
This document discusses warehouse layout and material flow planning. It provides details on key areas to consider when planning a warehouse layout, including product storage, inbound and outbound operations, value-added processes, and material flow patterns. The goal is to maximize efficiency and space utilization. Key factors discussed include storage requirements, peak vs. average volumes, receiving and shipping needs, picking methods, and value-added services. Common material flow patterns like U-shaped and straight through are also outlined. The overall aim is to design a layout that satisfies the primary warehouse functions in a way that reduces travel time and optimizes operations.