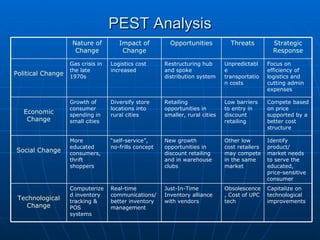
Walmart faces opportunities from technological improvements that can help optimize inventory management and distribution. They aim to serve price-sensitive consumers by focusing on efficiency and low costs. While competitors emerge, Walmart has strengths in logistics, bargaining power, and pioneering new rural markets. To sustain success, Walmart will leverage its supply chain expertise and scale to consistently offer low prices across a wide customer base.