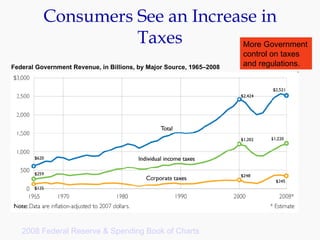
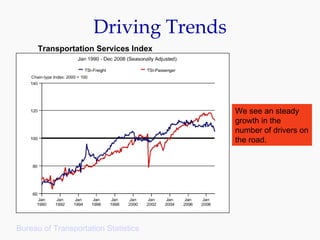
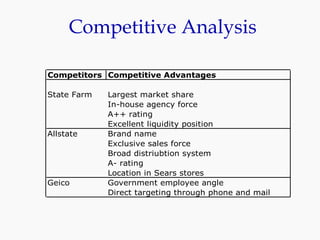
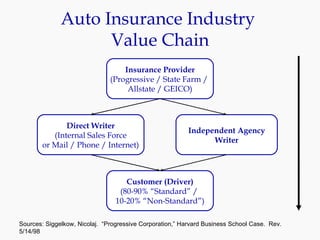
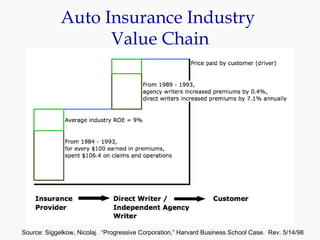
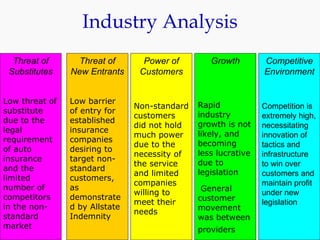
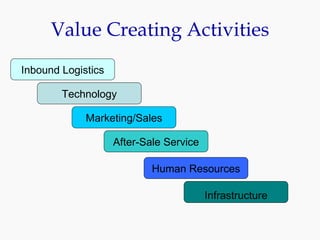
Progressive Corporation is an auto insurance provider that has grown by targeting non-standard customers through innovative strategies. It utilizes extensive customer data and technology to precisely price policies. Progressive also focuses on customer service through initiatives like its Immediate Response system and office on wheels. This emphasis on service has helped reduce costs from legal claims and improved customer retention. While competition is high in the auto insurance industry, Progressive has differentiated itself through its unique culture, focus on profitability over growth, and emphasis on customer experience.