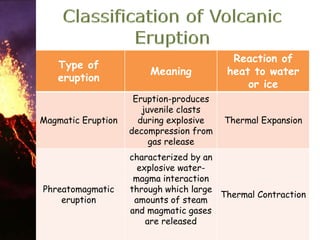
1. The document describes different types of volcanoes and volcanic eruptions including Hawaiian, Strombolian, Vulcanian, and Plinian eruptions.
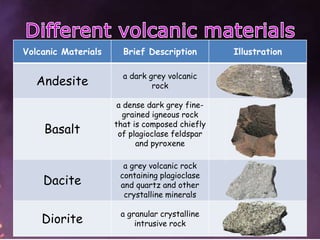
2. It also discusses volcanic materials like andesite, basalt, dacite, obsidian, peridotite, rhyolite, tuff, and volcanic gases.
3. Volcanic processes refer to eruptive and non-eruptive activities like decompression of rising magma and vapor pressure increases during magma crystallization.