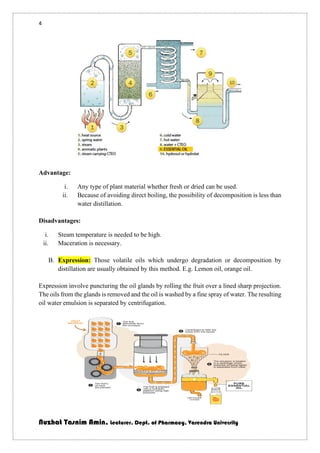
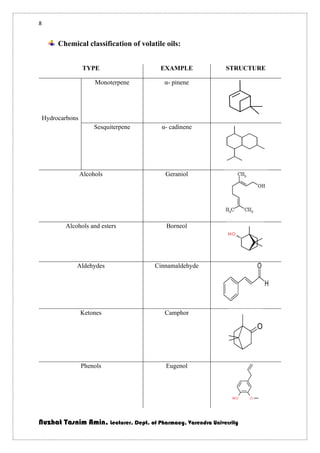
The document discusses volatile oils, their properties, uses, and methods of extraction from plants. It highlights their therapeutic actions, applications in perfumery, and various extraction techniques such as distillation, expression, and solvent extraction. Additionally, it differentiates between volatile oils and fixed oils, and provides specific examples of botanical sources and their chemical constituents.