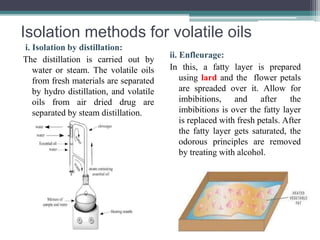
Volatile oils, also known as essential oils, are odorous, evaporative compounds derived from plants and animals, differing chemically and physically from fixed oils. They are soluble in organic solvents, possess specific densities, and are primarily found in special secretory tissues of various plants. Methods for isolation include distillation, enfleurage, ecuelle, and maceration, with applications in flavoring, perfuming, and medicinal uses.