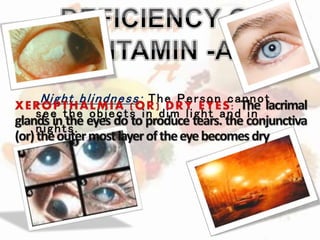
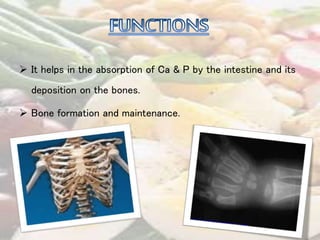
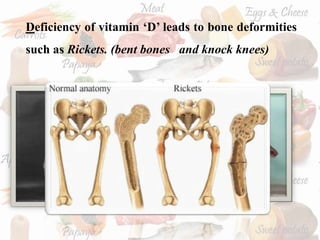
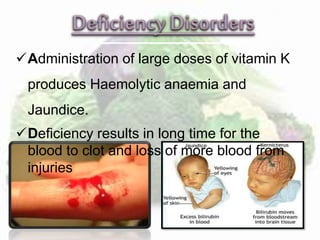
This document discusses the fat soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. It provides information on their chemical names, sources, functions, and deficiency disorders. Vitamin A is important for vision and is found in liver, eggs, and plants like carrots. Vitamin D aids in calcium absorption and is synthesized from sunlight exposure. Vitamin E functions in cell membrane integrity and vitamin K is required for blood clotting. The document also asks comprehension questions about the vitamins and requests a table summarizing their characteristics.