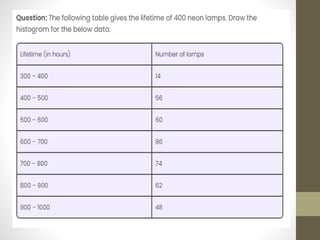
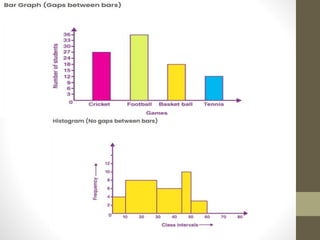
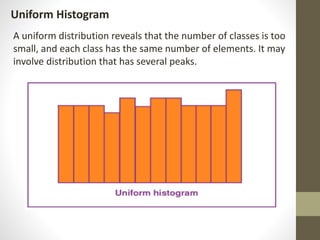
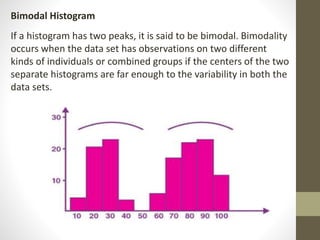
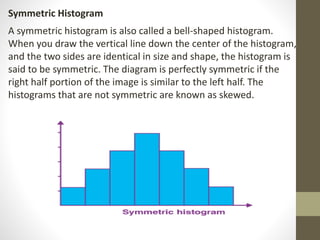
A histogram is a graphical representation of frequency distributions using rectangles, where the width represents class intervals and the height reflects frequency. It consists of five main components: title, x-axis, bars, y-axis, and legend, and is used to summarize large data sets and assist in decision making. Histograms can be categorized into types like uniform, bimodal, symmetric, and probability histograms based on the data distribution.