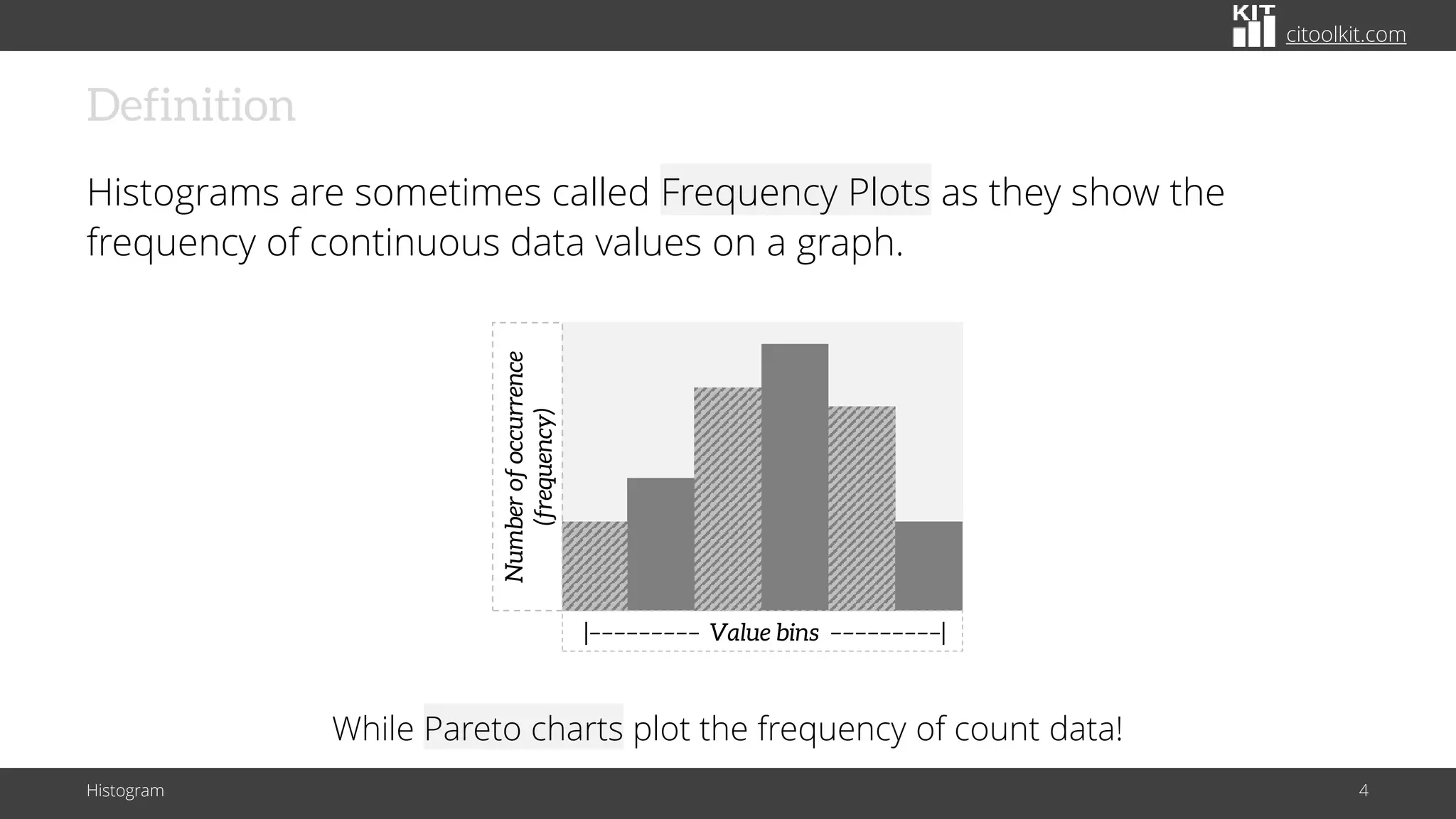
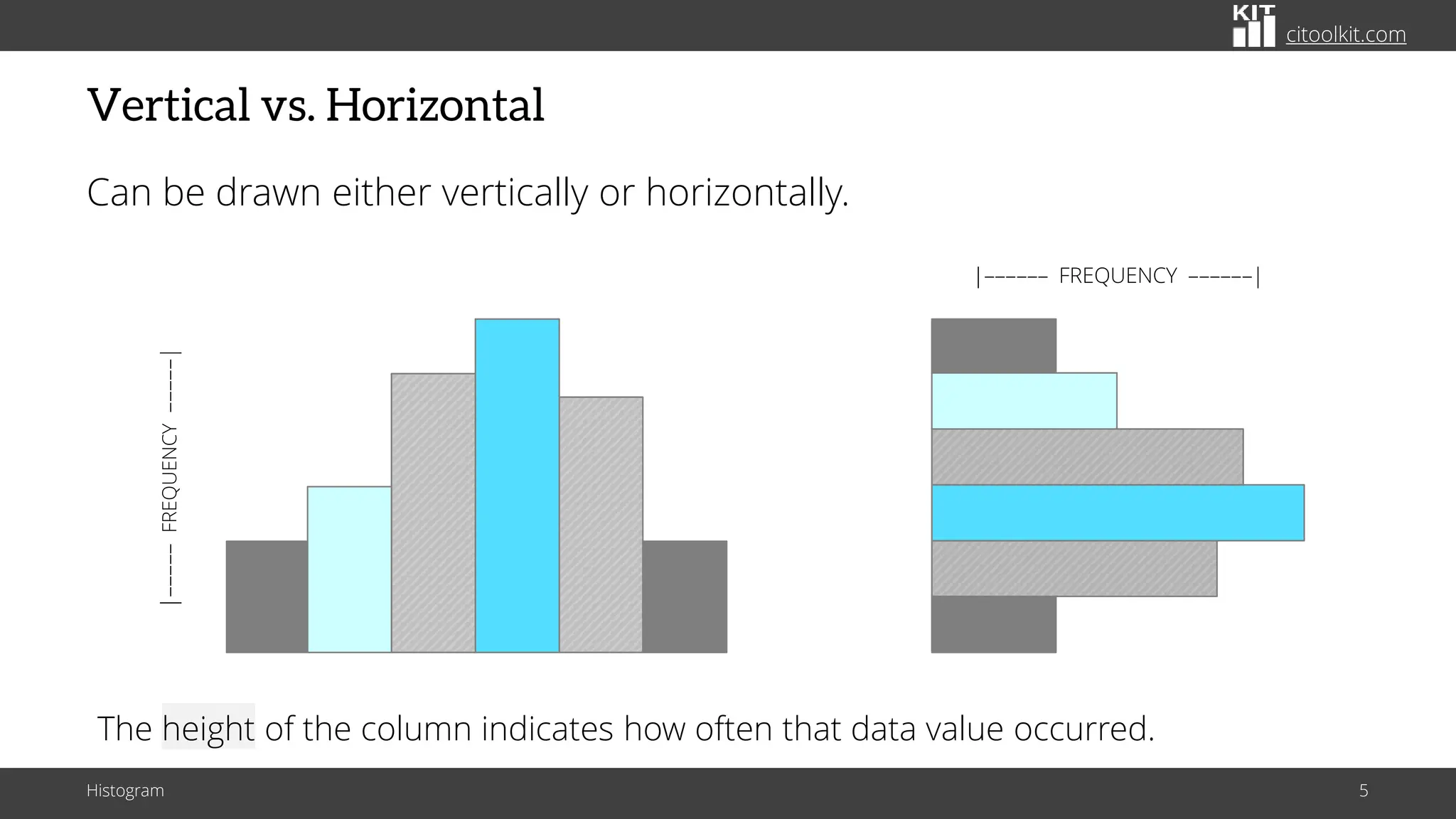
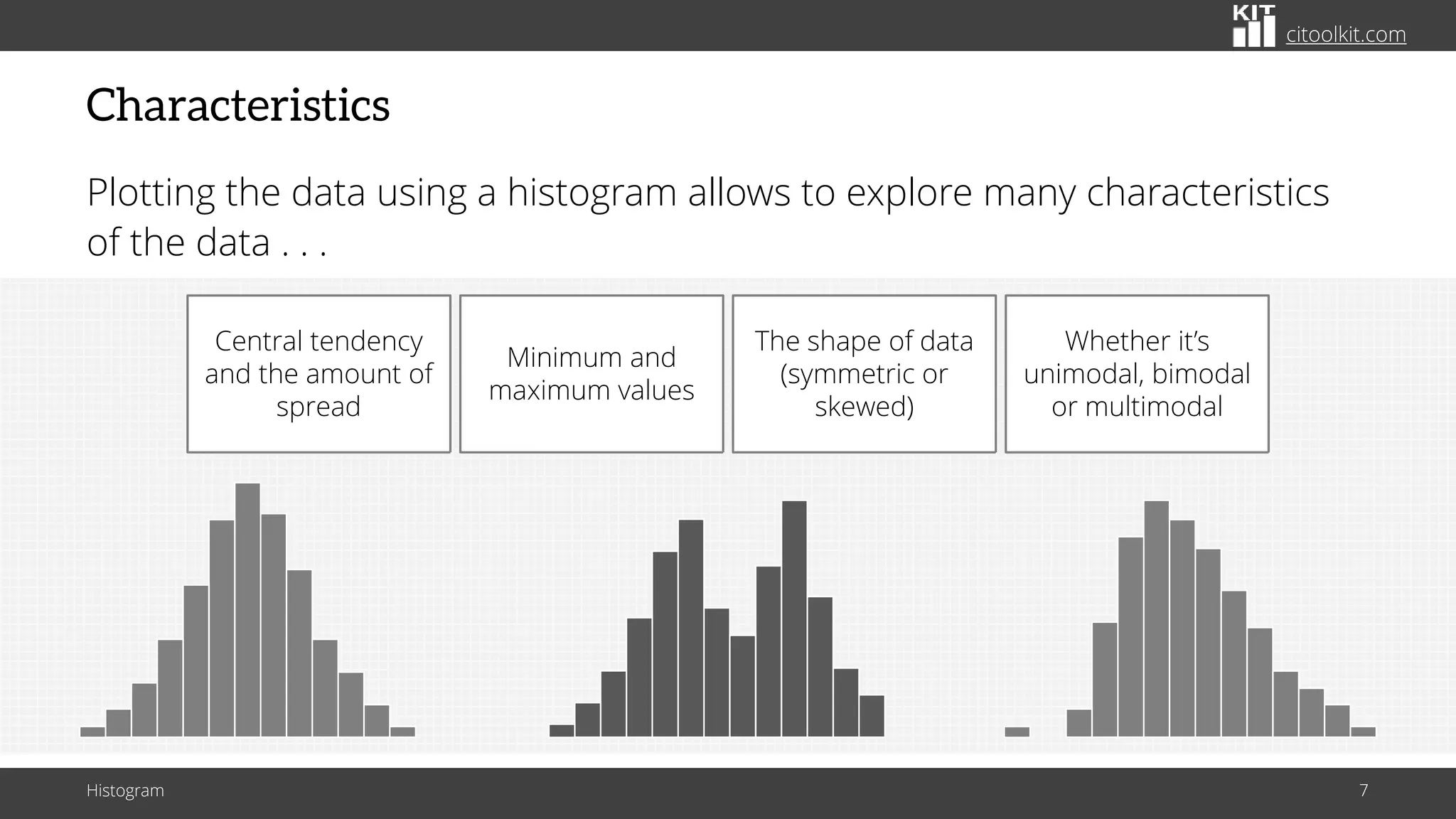
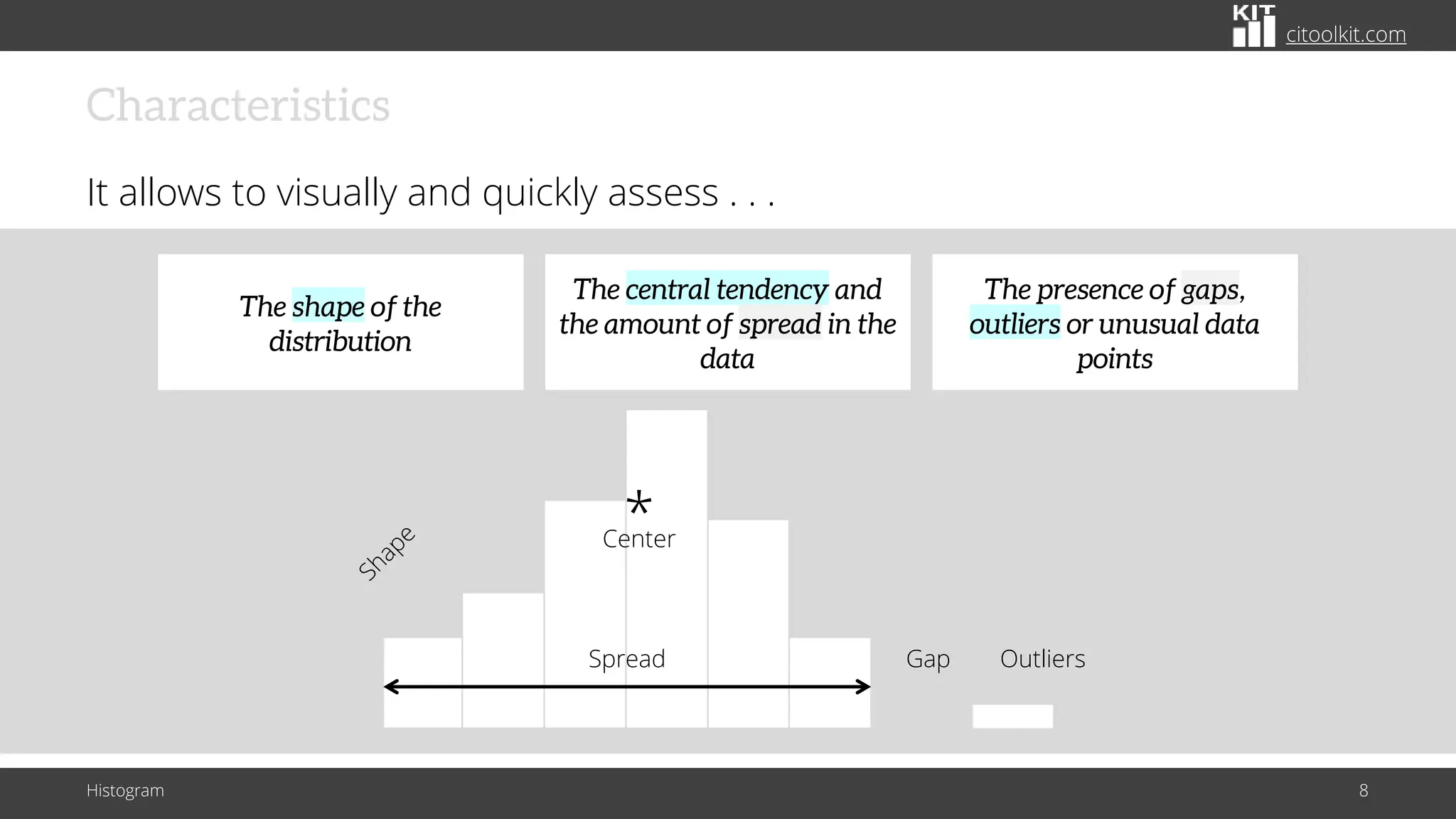
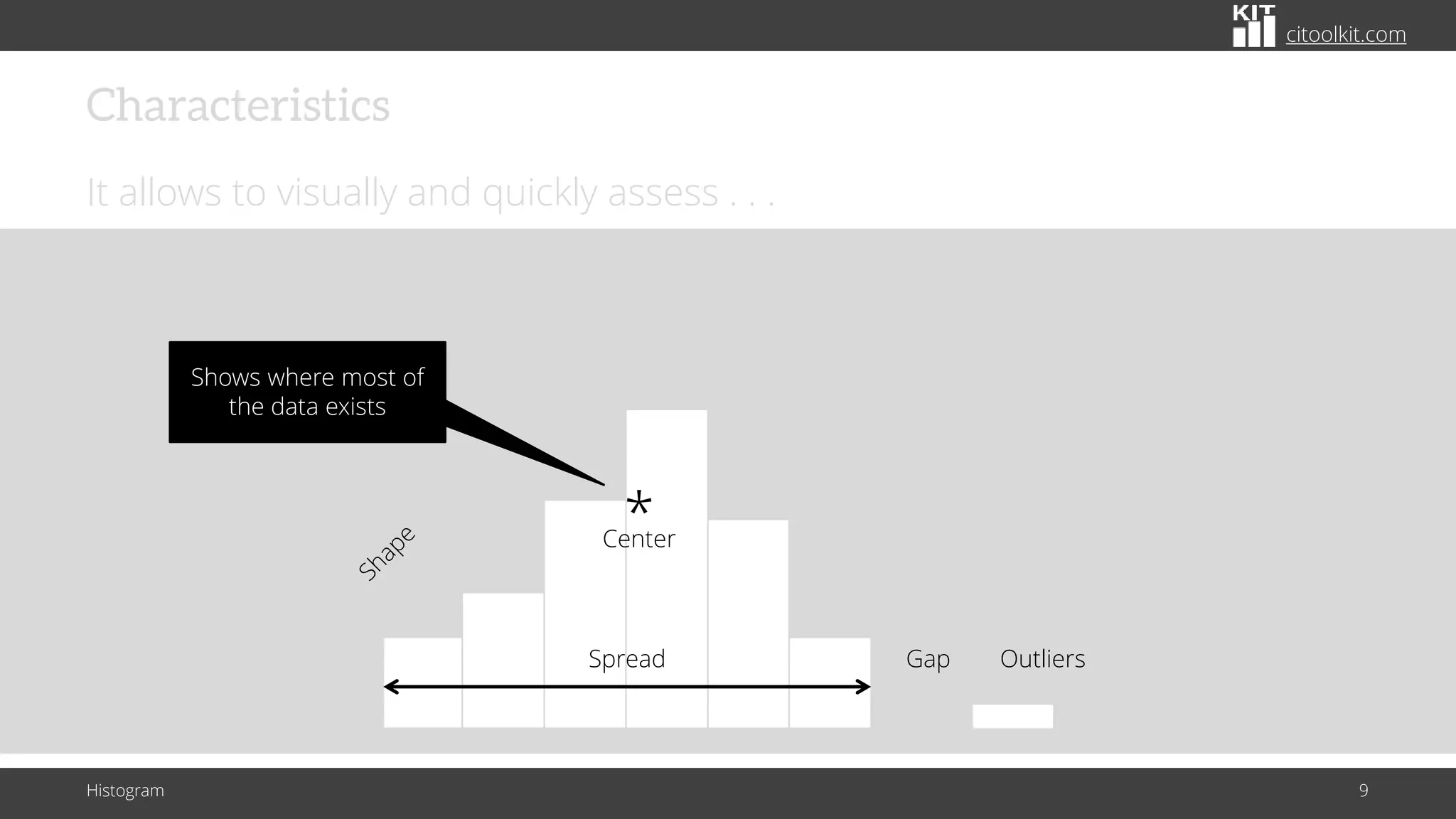
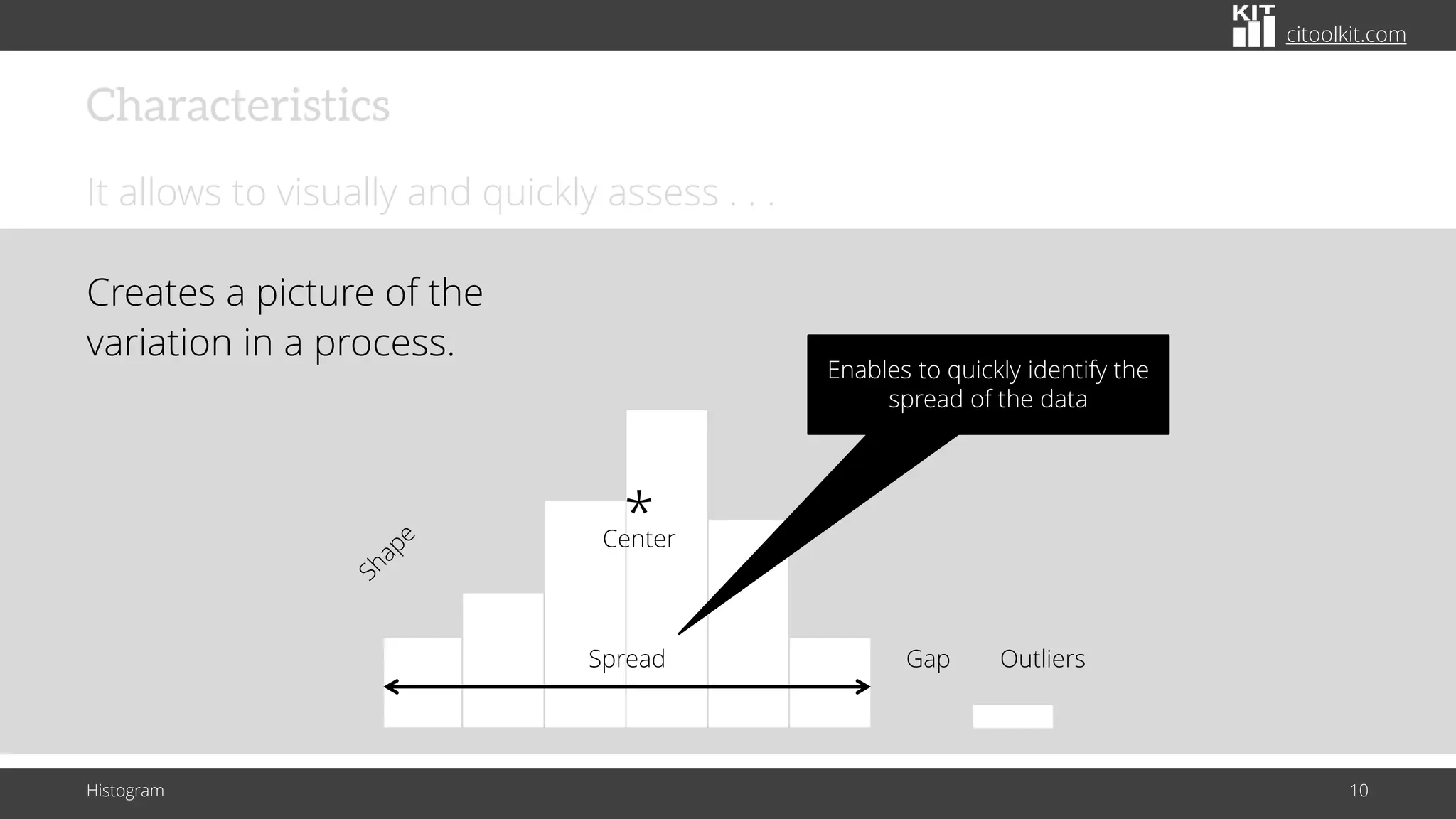
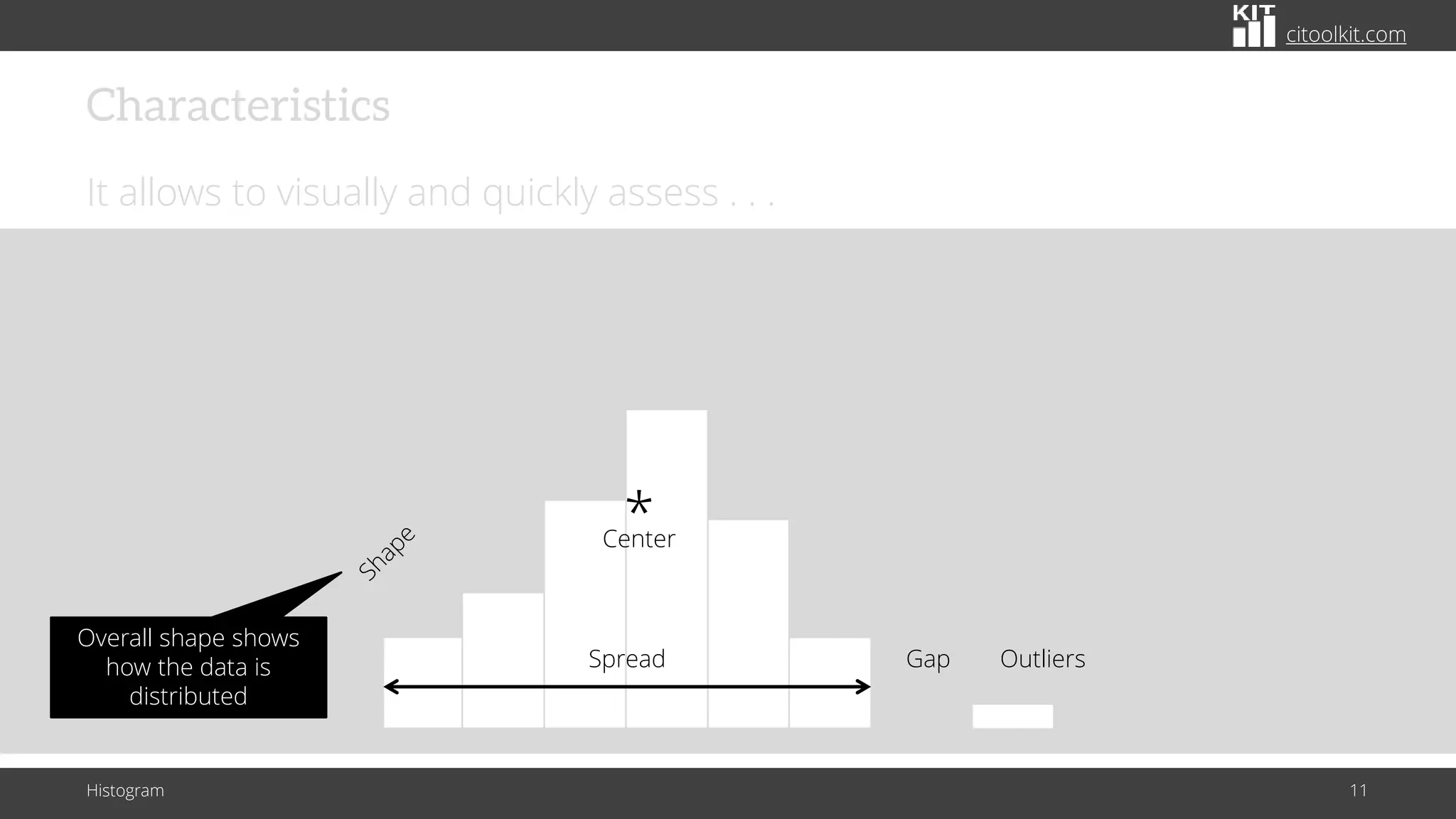
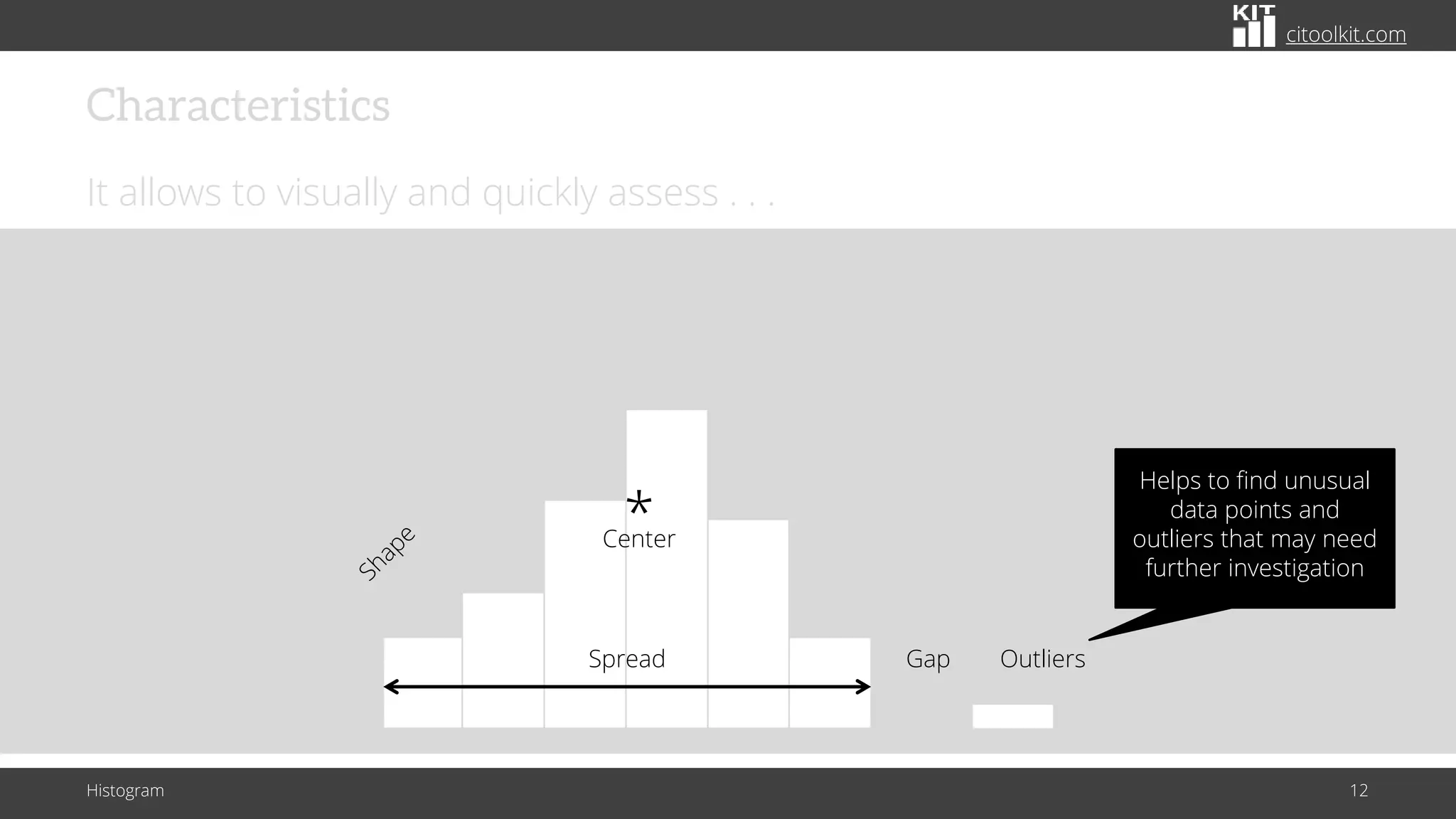
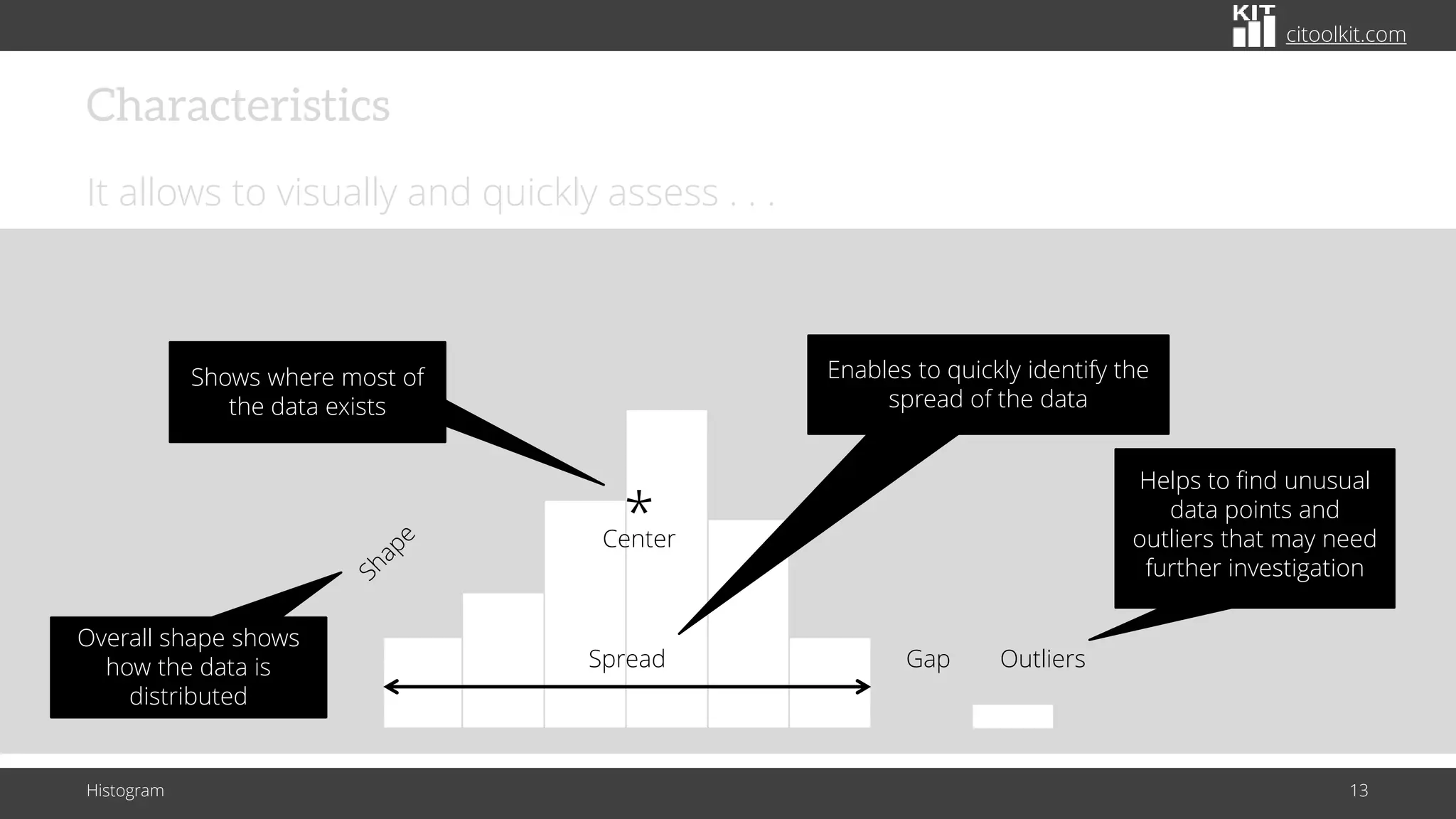
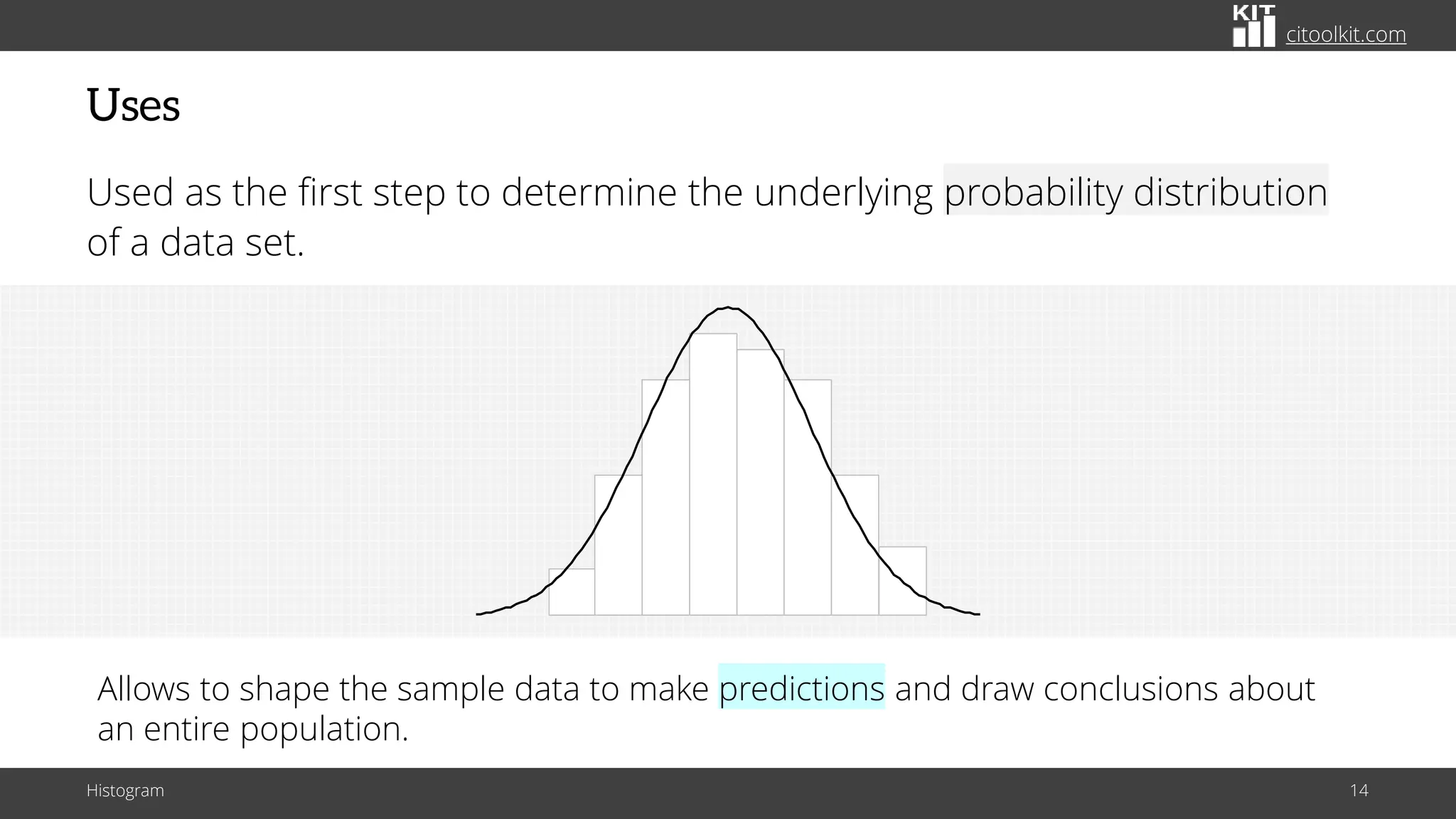
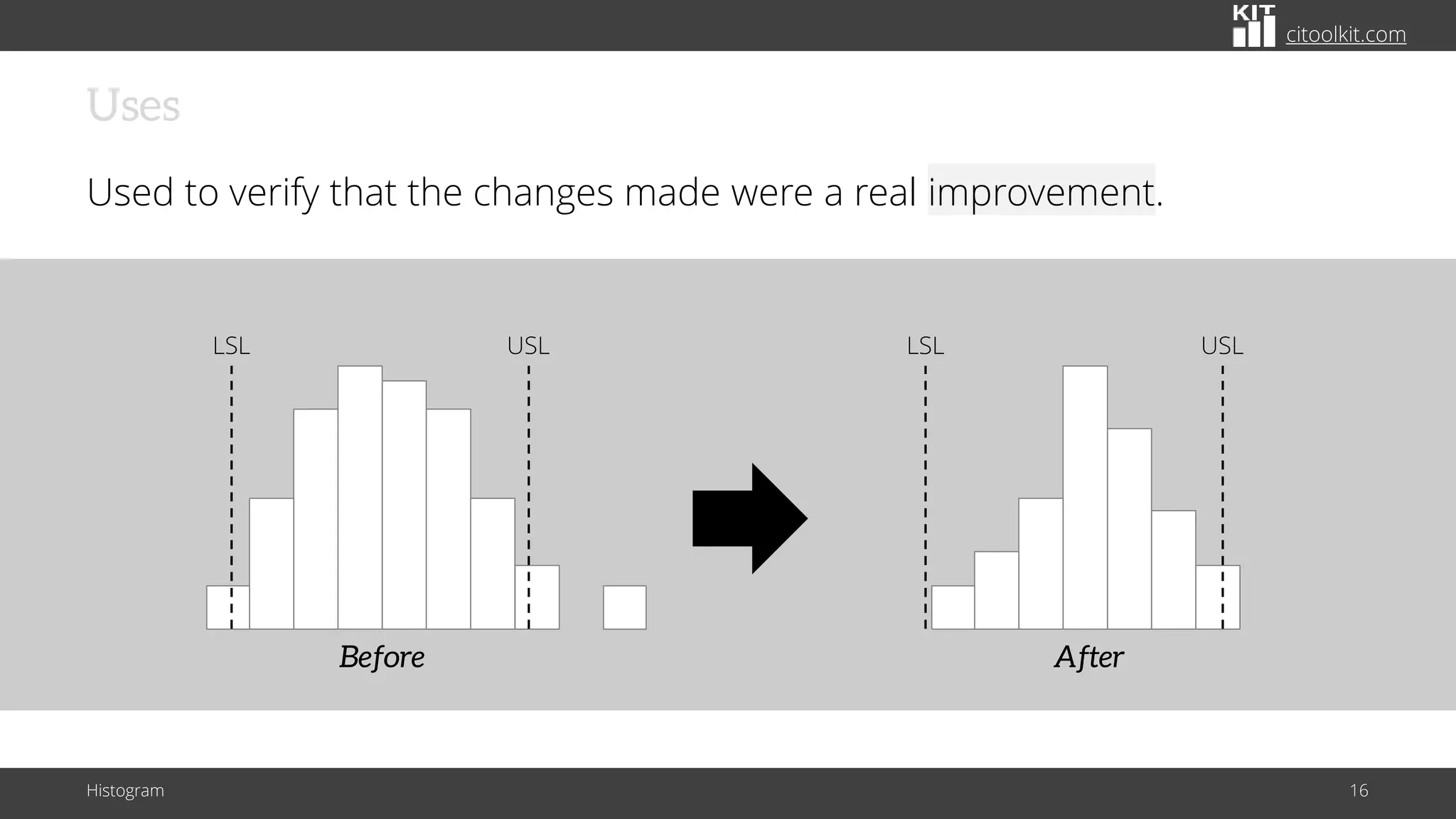
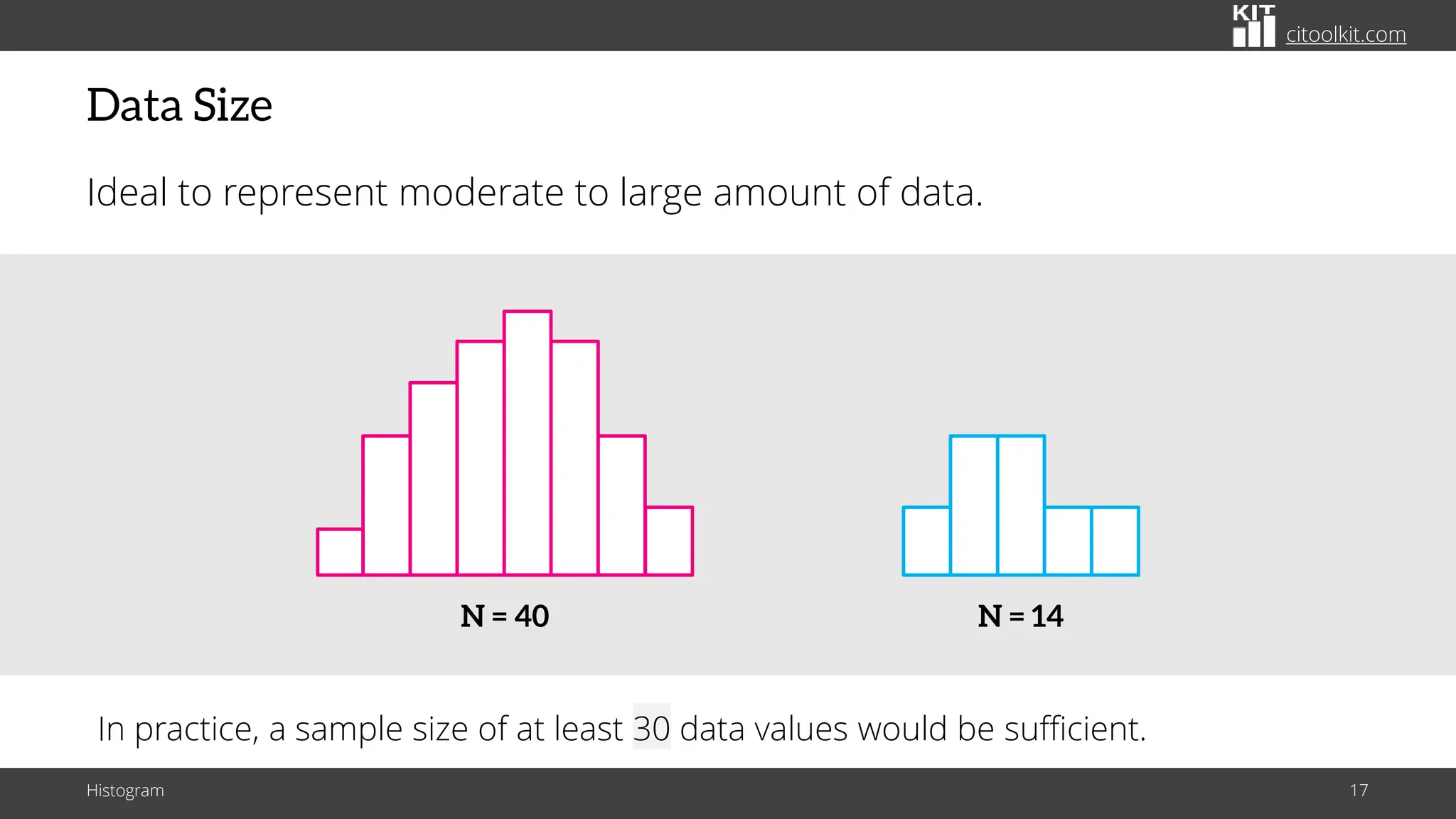
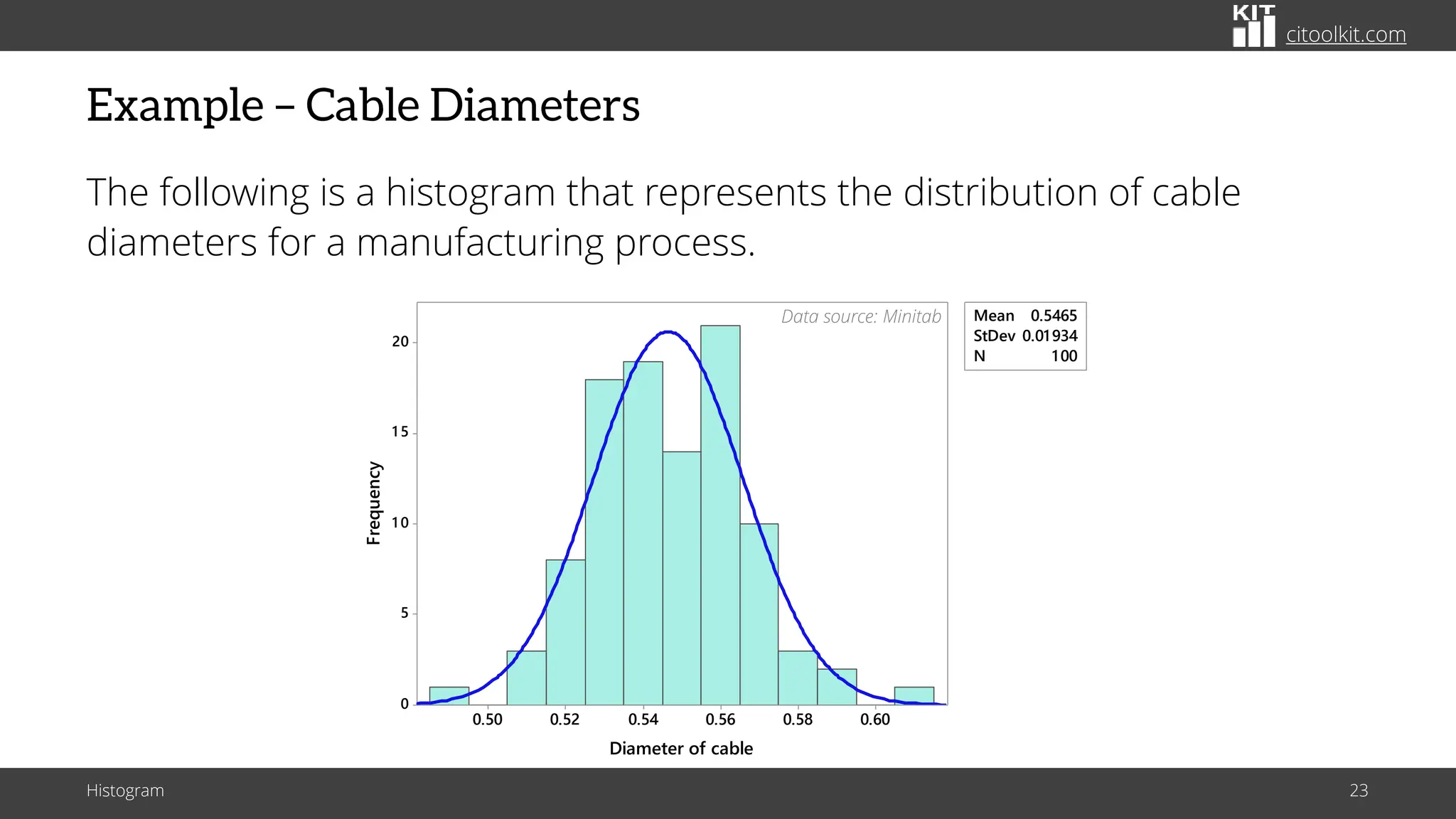
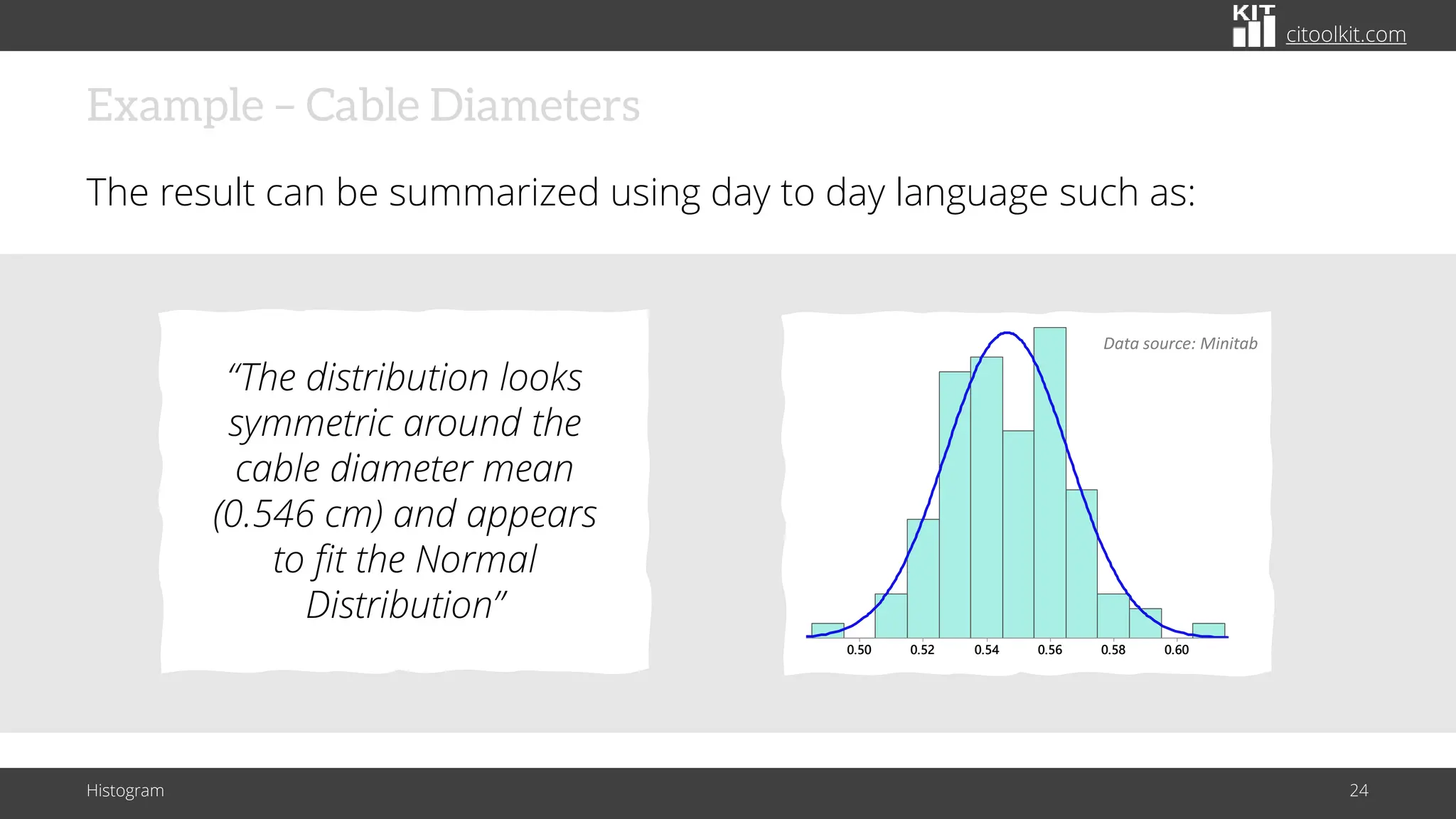
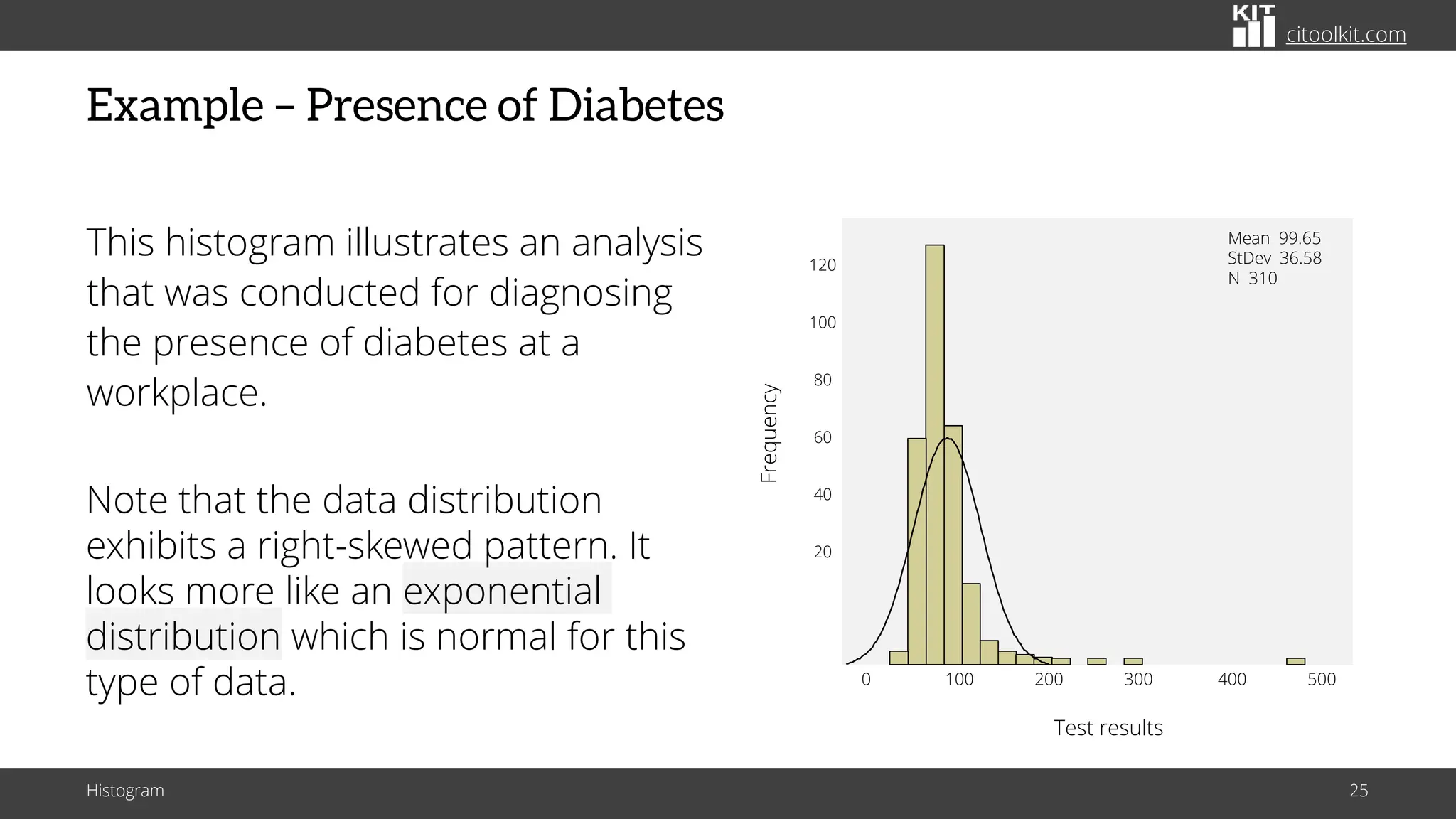
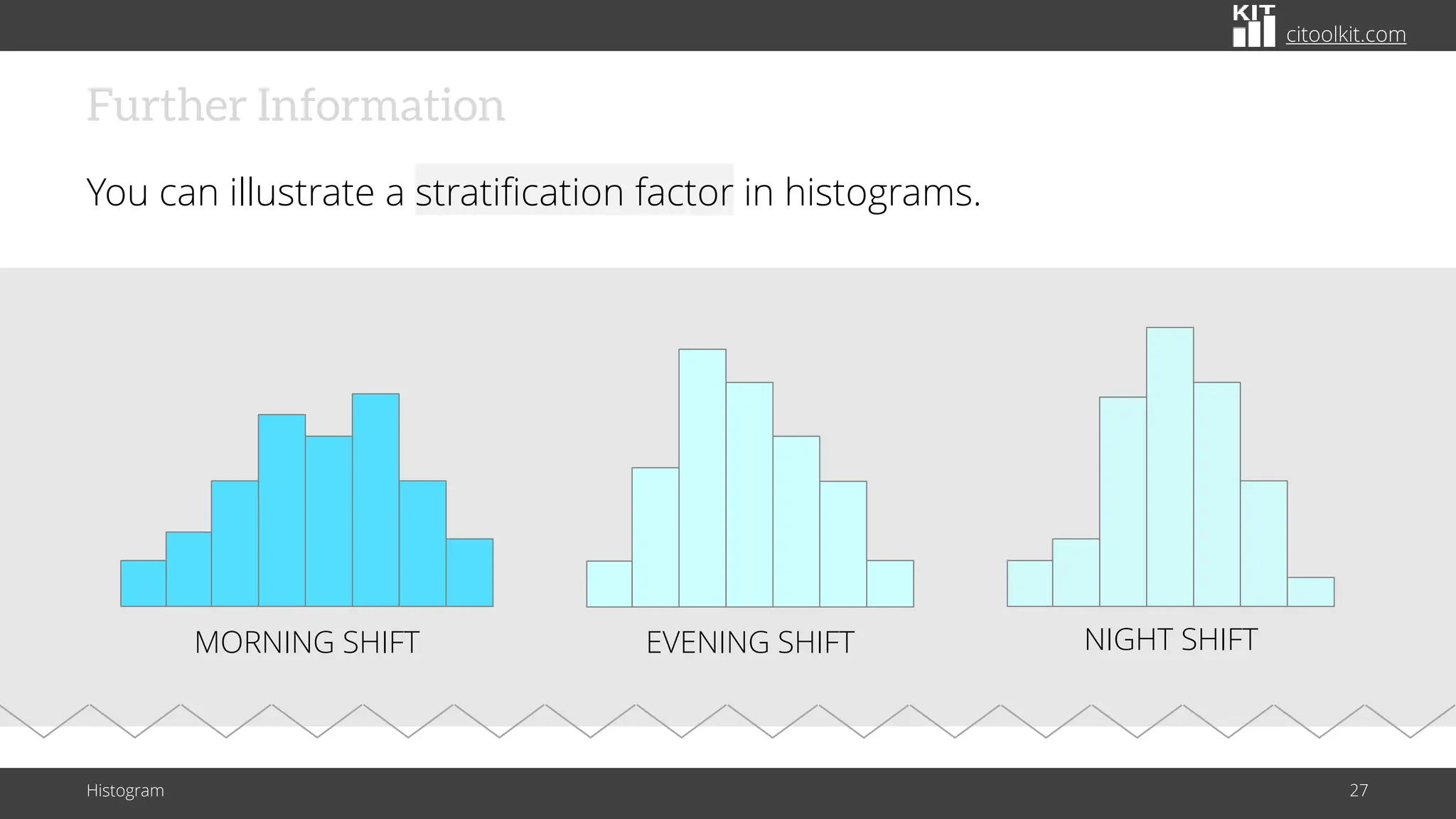
The document explains histograms as graphical representations that summarize the distribution of continuous data, highlighting their use in various fields such as statistics and scientific research. It details how to construct a histogram, its applications in identifying data characteristics like central tendency and outliers, and its limitations with small data sizes. Additionally, it provides examples of histograms used for analyzing cable diameters and diagnosing diabetes.