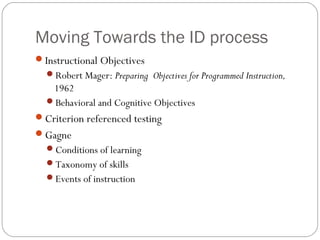
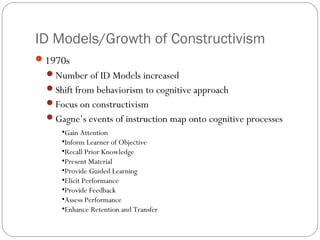
The document provides an overview of the definitions, history, and components of instructional design. It discusses how instructional design has been defined in various ways that focus on systematic application of strategies, needs analysis, and use of technology. The history outlines how instructional design has evolved from early uses of lantern projectors and films to incorporate computers, learning theories, and models. It notes key influences like Dewey, Skinner, Gagne and how the field has shifted from behaviorism to constructivism. The document concludes by noting current areas like performance technologies, digital literacies and how instructional designers now work across various domains.