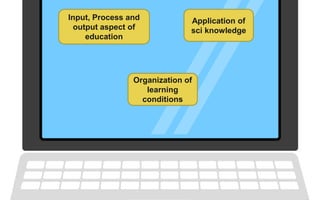
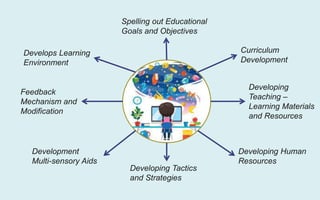
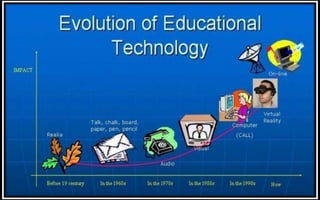
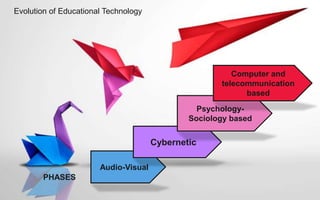
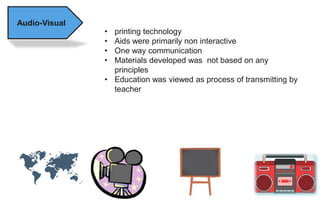
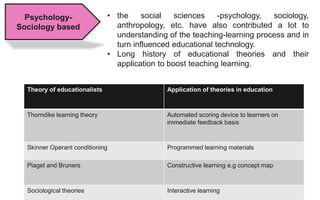
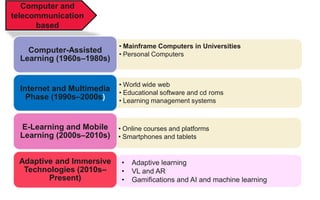
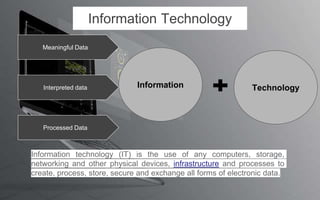
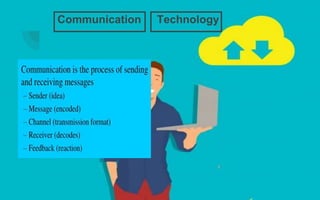
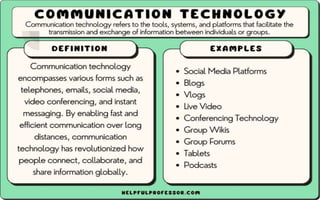
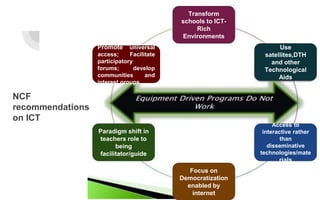
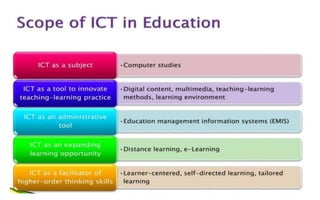
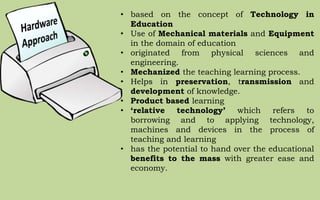
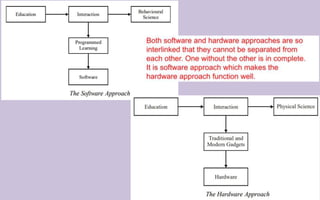
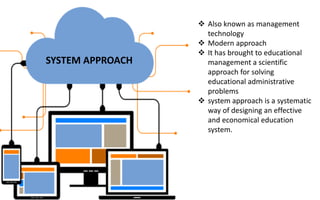
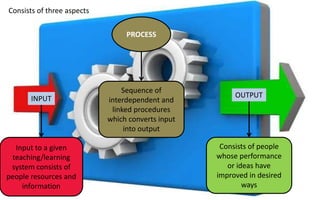
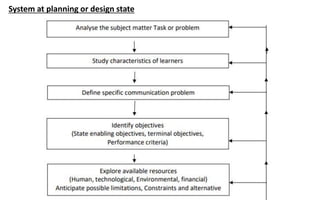
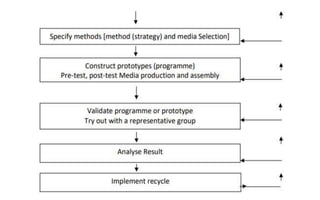
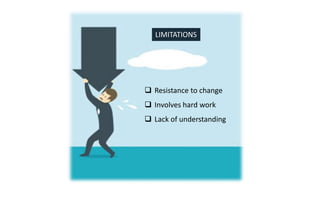
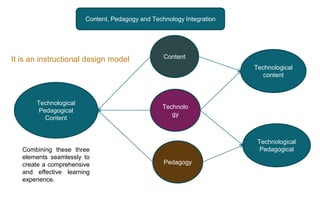
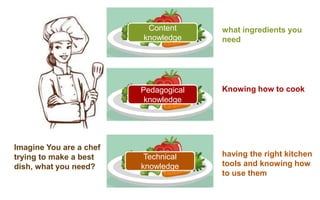
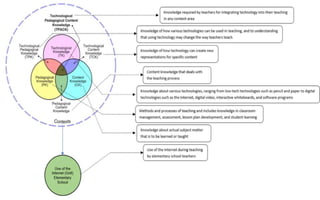
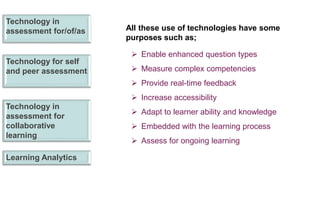
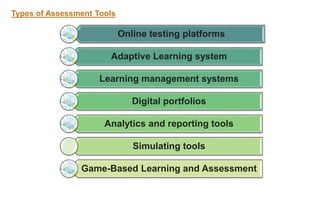
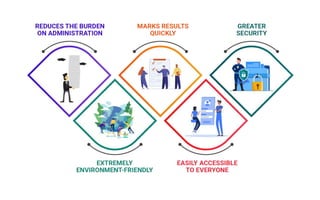
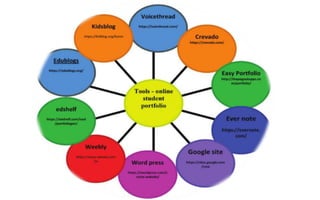
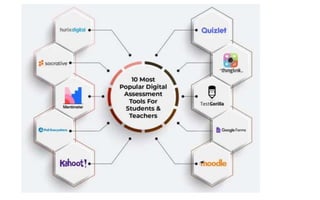
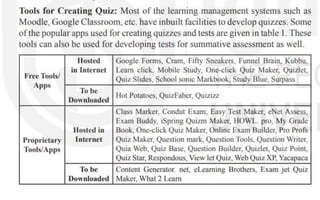
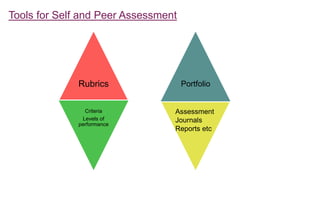
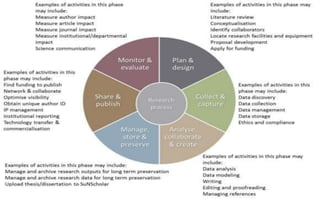
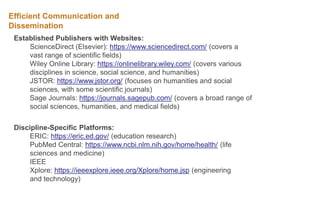
The document explores the evolution and application of educational technology, emphasizing its role in enhancing human learning through integrated processes, tools, and systems. It analyzes various phases and approaches, including hardware and software, while illustrating the impact of theories from psychology and sociology. Additionally, it discusses the importance of integrating technology in education to improve teaching methodologies, assessment techniques, and resource management.